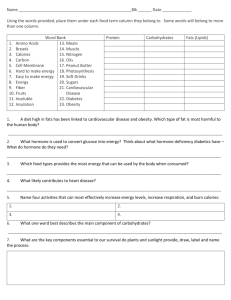
Healthy People 2020 Presentation

Nutrition and Weight Status
Janelle Reina Nunez, Benjamin Mason, Shelia Palmateer, Erin Nagel, Timothy Lee,
Noemline Omandan, and Charlotte Lamaster
•
•
•
Increase knowledge and ability to improve diet
Encourage/incentivize provision of healthier food choices vendors make available
Promote healthy body weight
In this country, more than one-third of adults and 17% of youth are obese
Obesity increases the risk for people to have heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and cancer
As of 2008, it was estimated that the medical cost of obesity in the U.S. was $147 billion
Moreover, the medical costs for people who are obese were $1, 429 higher that those of normal weight.
Obesity is defined as an excess amount of body fat when compared to lean body mass.
In men, the normal amount of body fat is between 15% and 20% body weight
In women, it is between 18% to 32%
For a person to be obese, they are at least
20% above the upper limit of normal range for ideal body weight
Obesity is higher among middle age adults ages 40-
59 years old (39.5%)
According to the CDC
National Center for Health
Statistics, amongst non-
Hispanic black and
Mexican-American men, those with higher incomes are likely to be obese
However women who earn a higher income are less likely to be obese than lower-income women
SAN ANTONIO’S
OBESITY RATE OF 31.9%
EXCEEDS THE US OBESITY
RATE OF 26.2 %
SAN ANTONIO HAS
THE SECOND HIGHEST
RATE OFOBESITY IN THE
UNITED STATES
.
Contributing Factors
Limited access to healthy food
Abundance of fast food
Unhealthy food culture
Decline Physical Activity
Lack of knowledge about nutrition
Cultural Traditions
Poverty
Percentages reflect Body
Mass Index (BMI) percentage of Adults in the United States
The chart above shows obesity rates for Texas from
1990 through 2007, a steady increase is shown.
Good News! With Texas and its’ communities coming together over the recent years to fight obesity, there is hope in combating this disease. According to the
SAMHD (San Antonio Metropolitan Health District), obesity rates declined in
San Antonio and Bexar County going from 35.1% in 2010 to 28.5% in 2012. This is potentially great news for this community and the state of Texas, as these statistics show that their hard work is paying off!
Community and
Worksite Wellness
Program
Growing Community
Video Series
Plan Healthy, Texas
Texas Interagency
Obesity Council
Nutrition Strategies
CWW nutrition strategies
Farm to work
Texas Nutrition
Environment Assessment
Physical Activity
Strategies
Get Fit Texas!
Your Health Matters:
Growing Active and
Healthy Communities
To specifically build awareness around the need for physical activity, Blue Cross piloted a decision prompt campaign in a few cities which grew into a statewide public awareness campaign called ‘do’.
The do campaign encourages Minnesotans to
“groove [their] body every day.” The campaign contains three components:
• do.in action to get people moving more and eating better.
• do.at work to encourage employees’ use of stairs, healthier eating, and more walking.
• do. Stories to inspire others through personal stories (4).
The State of New York has a number of community programs which focuses on making their residents healthier.
From healthy eating to physical fitness programs, New York is taking the health of its residents very seriously.
Tennessee, being one of the top obese states in the United States, have several programs to promote better nutrition and to increase physical activity to decrease the problem.
Programs are focused on both childhood and adult obesity but our focus will only be focusing on the adult population.
San Antonio is 59.3%
Hispanic (Texas
Department of State Health
Services, 2012)
12% of Bexar County’s low income population does not have easy access to grocery stores (Bexar County
Community Health
Assessment Data
Committee, 2013)
Por Vida Menu Criteria
Entire meal including entrée and 2 sides:
< 700 calories
< 23g total fat
< 8g saturated fat
< 0.5g trans-fat
< 750mg sodium
Single Entrée Item
< 300 calories
< 10g total fat
< 3.5g saturated fat
< 0.5g trans fat
<325mg sodium
Side Item
< 200 calories
< 7g total fat
< 2g saturated fat
< 0.5g trans fat
< 215mg sodium
Evidence for negative health effects of saturated fat is shaky.
San Antonio Metropolitan Health District, 2015
Program Improvement:
Removal of Sodium Restriction from Por Vida
Entire meal including entrée and 2 sides:
< 700 calories
< 23g total fat
< 8g saturated fat
< 0.5g trans-fat
< 750mg sodium
Single Entrée Item
< 300 calories
< 10g total fat
< 3.5g saturated fat
< 0.5g trans fat
<325mg sodium
Side Item
< 200 calories
< 7g total fat
< 2g saturated fat
< 0.5g trans fat
< 215mg sodium
Evidence for the health benefits of reducing sodium intake in the general population is also shaky.
San Antonio Metropolitan Health District, 2015
Alderman, M., Baslund, B., Jurgens, G., & Graudal, N. (2014). Compared with usual sodium intake, low- and excessive-sodium diets are associated with increased mortality: A meta-analysis. American Journal of Hypertension, 27(9), 1129-1137.
Bexar County Community Health Assessment Data Committee. (2013). Bexar County community health assessment report. Retrieved from http://iims.uthscsa.edu/sites/iims/files/Newsletters/bexar%20CHA%202013%20final.pdf
Center for Disease Control. (2010). Sodium fact sheet. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/salt/pdfs/Sodium_Fact_Sheet.pdf
Center For Disease Control. (2015). Data, trends and maps: Obesity prevalence maps. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/prevalence-maps.html
Chowdhury, R. (2014). Association of dietary, circulating, and supplement fatty acids with coronary risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Annals of Internal Medicine, 160(6), 398-406. doi:10.7326/M13-1788
Ignatavicius, D. D. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care (7th ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier Saunders.
Gallup. (2014). Boulder, Colo., residents still least likely to be obese. Retrieved from http://www.gallup.com/poll/168230/boulder-colo-residentsleast-likely-obese.aspx
Gallup. (2015). U.S. obesity rate inches up to 27.7% in 2014. Retrieved from http://www.gallup.com/poll/181271/obesity-rate-inches-2014.aspx
HealthyPeople.gov. 2015. Nutrition and weight status. http://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topics-objectives/topic/nutrition-and-weight-status.
Ogden, C., Carroll, M., Kit, B., & Flegal, K. (2014). Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011-2012. JAMA, 311(8), 806. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.732
Ogden, C., Lamb, M., Carroll, M., & Flegel, K. (2015). Obesity and socioeconomic status in adults: United States, 2005-2008. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db50.pdf
San Antonio Metropolitan Health District . (2013) Obesity in Bexar County. Retrieved from https://www.sanantonio.gov/Portals/0/Files/health/HealthyLiving/FactSheet-Obesity.pdf
San Antonio Metropolitan Health District. (2015a). Por Vida. Retrieved from http://www.porvidasa.com
San Antonio Metropolitan Health District (2015b). Texas Department of State Health Services. Retrieved from https://www.dshs.state.tx.us/obesity/san-antonio-metropolitan-health-district.doc
Siri-Tarino, P., Sun, Q., Hu, F., & Krauss, R. (2010). Meta-analysis of prospective cohort sutides evaluating the association of saturated fat with cardiovascular disease. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 91(3), 535-546.
Sosa, E., Biediger-Friedman, L., & Yin, Z. (2013). Lessons learned from training of promotores de salud for obesity and diabetes prevention. Journal
of Health Disparities Research and Practice, 6(1), 1-13.
Texas Department of State Health Services. (2012). healthdata.dshs.texas.gov. Retrieved from http://healthdata.dshs.texas.gov/HealthFactsProfiles
Ward, Z., Long, M., Resch, S., Gortmaker, S., Cradock, A., & Hsiao, A. (2014). Redrawing the US obesity landscape: Bias-corrected estimates of state-specific adult obesity prevalence. Retrieved from http://www.researchgate.net/publication/266779334_Redrawing_the_US_Obesity_Landscape_Bias_corrected_estimates_of_statespecific_adult_obesity_prevalence