Week 12 - Faculty Website Directory
advertisement

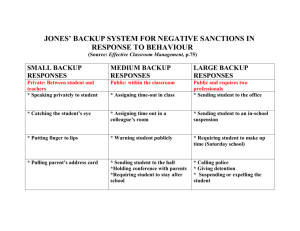
70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment Chapter 12: Managing and Implementing Backups and Disaster Recovery Objectives • Plan for disaster recovery of Windows Server 2003 systems • Back up and restore data • Implement shadow copy volumes • Understand the purpose of the Automated System Recovery feature 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 2 Objectives (continued) • Understand Windows Server 2003 advanced startup options • Install and use the Recovery Console 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 3 Planning for Disaster Recovery • Administrators need to be prepared for the possibility of server failure and/or file and folder loss at all times • Windows Server 2003 features: • • • • • The Backup utility Shadow Copies of Shared Volumes Automated System Recovery Advanced startup options The Recovery Console 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 4 Backing Up and Restoring Data • Backup utility designed to restore an operating system or data in case of failure • Improved version of utility originally introduced in Windows 2000 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 5 Backing Up and Restoring Data (continued) • Tasks that can be performed include: • • • • • Back up and restore files and folders Schedule a backup Back up Windows 2003 System State data Restore the Active Directory database Create an Automated System Recovery (ASR) backup 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 6 Backup and Restore Concepts • Types of backups and backup hardware and software is dictated largely by the size and type of organization • A key issue is backup authority: • Administrators, Backup Operators, and Server Operators have broad authority • Other users may have some limited authority to back up certain files and folders 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 7 Backup and Restore Concepts (continued) • Two main Group Policy rights are Back up files and directories and Restore files and directories 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 8 Backup Types • Backup types include: • • • • • Normal backup Incremental backup Differential backup Daily backup Copy backup 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 9 Normal Backup • Default type of backup performed by Backup utility • Backs up all selected files and folders and clears the archive attribute on each • This type of backup can be inefficient because it does not take into account whether files have changed 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 10 Incremental Backup • Backs up only files that have changed since last normal or incremental backup • Clears the archive attributes of the files • Reduces the size of backup jobs • Restore process is more complicated • Normal backup and incremental backups must be restored in order 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 11 Incremental Backup (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 12 Differential Backup • Backs up only files that have changed since last normal or incremental backup • Does not clear the archive attributes of those files • A second differential backup will back up the same files since the first backup is not recorded by the archive attributes • Reduces the size of backup jobs compared to normal backups but not incremental backups • Restore process requires only the normal backup and the latest differential backup 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 13 Differential Backup (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 14 Daily Backup and Copy Backup • Daily Backup • Backs up selected files or folders that were created or changed on the day of the backup • The archive attribute is not changed • Copy Backup • Exactly the same as a normal backup but doesn’t change the archive attribute • Intended as a backup that will not interrupt other backup procedures (perhaps an archival copy) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 15 Using the Backup Utility • Commonly used to back up critical data and operating system files • Can be used in two modes: Wizard mode and Advanced mode • Can be used to • Back up System State data • Restore Active Directory • Access Automated System Restore feature 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 16 Using the Backup Utility (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 17 Activity 12-1: Backing Up Files and Folders Using the Backup Utility • Objective: To explore the use of Windows Server 2003 Backup utility for backing up files and folders • Start All Programs Accessories System Tools Backup • Use Advanced Mode to back up the contents of a folder 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 18 Activity 12-1 (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 19 Activity 12-1 (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 20 Activity 12-2: Restoring Files and Folders Using the Backup Utility • Objective: To use Backup utility to restore previously backed up files • Start Run type ntbackup.exe Advanced Mode • Follow directions to restore the files backed up in Activity 12-1 to an alternate location • Verify that the files have been restored 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 21 Activity 12-2 (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 22 Scheduling Backups • Backups can be scheduled to occur without interaction from an administrator • Can schedule backups daily, weekly, monthly, predefined times, predefined days 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 23 Scheduling Backups (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 24 Activity 12-3: Scheduling Backup Operations Using the Backup Utility • Objective: Use the Windows Server 2003 Backup utility to schedule a backup • Open the Backup utility and use the Backup and Restore Wizard • Set the Schedule Job to Daily and select a time • Confirm that the backup has been scheduled • Confirm that the backup occurs as scheduled 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 25 Activity 12-3 (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 26 Backing Up and Restoring System State Data • System State data includes: • • • • • • • • • Registry (always) COM+ Class Registration database (always) Boot files (always) Certificate Services database (if installed) Active Directory (on domain controllers) SYSVOL directory (on domain controllers) Cluster service (if part of a cluster) IIS Metadirectory (if IIS is installed) System files (always) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 27 Backing Up and Restoring System State Data (continued) • These components should be backed up with standard backups and directed System State backups • Cannot back up individual components • To restore due to a corrupt Active Directory database, must restart and choose Directory Services Restore mode advanced startup • To restore Active Directory objects, must use authoritative restore so that replication doesn’t overwrite corrections 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 28 Activity 12-4: Backing Up System State Data • Objective: To use the Windows Server 2003 Backup utility to back up System State data on a domain controller • Open Backup in Advanced Mode • Back up System State as directed • Verify that System State is backed up and check the size of the file to better understand the amount of information needed for system state 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 29 Shadow Copies of Shared Folders • Purpose of this utility is to make recovery of user files in shared folders easy without requiring an administrator • Advantages for users: • Restoration of accidentally deleted files • Recovery of previous versions of files • Comparison of previous version to current version • Shadow Copies not enabled by default, must be explicitly enabled from Properties of a drive 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 30 Shadow Copies of Shared Folders (continued) • Shadow Copies is enabled for entire volume (cannot shadow specific files or folders) • Copies are made on a pre-defined schedule • By default, Shadow Copies uses 10% of available disk space (minimum 100 MB) • When limit is reached, older copies are deleted 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 31 Shadow Copies of Shared Folders (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 32 Activity 12-5: Enabling and Configuring Shadow Copies of Shared Folder Settings • Create a new shared folder with appropriate permissions • Create a text document in the folder • Enable Shadow Copying • Explore and configure settings and schedules 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 33 Previous Versions • Network users must install additional software on their systems to access previous versions of files via Shadow Copies • Client software provided in MSI format at %systemroot%\system32\clients\twclient\X86 (for Intel-based system) • Adds an additional tab (Previous Versions) to Properties of files stored in shared Folders 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 34 Activity 12-6: Installing and Using the Previous Versions Client • Objective: To install and use the Previous Versions Client and explore using it to restore a previous version of a file • Locate and launch the installation file and complete installation • Locate the Previous Versions tab in the Properties of the file created in Activity 12-5 • Review and restore the file using the Previous Versions dialog box 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 35 Activity 12-6 (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 36 Automated System Recovery • This utility was introduced in Windows Server 2003 • Main purpose is to restore a system to a functional state • Allows user to restore system configuration settings, not data files • Replaces ERD on earlier systems • Two different elements: • ASR backup (accessed from Backup Utility) • Floppy disk that contains information about backup, disk configuration, and how to perform a restore 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 37 Automated System Recovery (continued) • User data files should be backed up before ASR and restored after ASR • ASR backup should be done whenever system configuration is changed • ASR backup created using the Automated System Recovery Wizard • To recover, boot from Windows CD, select Repair option, use ASR floppy and backup to restore settings 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 38 Advanced Startup Options • Used to troubleshoot startup problems • Provides a safe mode • Only loads the default minimal required Windows Server 2003 settings and device drivers • Windows Advanced Startup Options is accessed during system startup • Press F8 from Boot Loader Operating System Selection menu 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 39 Advanced Startup Options (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 40 Advanced Startup Options (continued) 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 41 Activity 12-7: Viewing and Testing Advanced Startup Options • Objective: To explore and test Windows Server 2003 Advanced Startup Options • Restart your computer and access the Windows Advanced Options Menu as directed • Select Safe Mode and the appropriate operating system or profile and log on • Explore pinging • Reiterate these steps with Safe Mode with Command Prompt 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 42 Last Known Good Configuration • Allows you to recover from failed driver and registry changes • You should not log on to your server if problems are evident during boot process because any incorrect configuration changes will update last known good configuration • Cannot be used to resolve problems such as missing or corrupt files 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 43 Activity 12-8: Testing Last Known Good Configuration • Objective: To test the startup option for the last known good configuration • Start right-click My Computer Properties Hardware Device Manager • Open and disable network adapter and cd-rom or dvd drive • Test pinging (network adapter disabled) • Restart with Last Known Good Configuration • Verify that devices are enabled 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 44 The Recovery Console • The Recovery Console is an advanced tool for experienced administrators • It is used to: • • • • • Start and stop services Format drives Read and write data on a local hard drive Copy files from a floppy or CD to a local hard drive Perform administrative tasks 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 45 Installing the Recovery Console • Two ways to start Recovery Console: • Run it from CD after a serious error by booting from the CD • Install on computer permanently • Once it is installed, it will be an option in the list of available operating systems during the initial boot process • Recovery Console can only be run by an administrator 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 46 Installing the Recovery Console (continued) • Variety of commands available through Recovery Console • Use the Help command within the Console for a complete list of commands • Common commands include: copy, disable, enable, exit, fixboot, fixmbr, listsvc 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 47 Activity 12-9: Installing and Using the Recovery Console • Objective: to install and use the Recovery Console • Install the Recovery Console as directed • Restart the computer and start the Recovery Console • Explore the command options in the Console • Run the listsvc command • Configure the RemoteAccess service • Reboot as directed 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 48 Summary • Administrators prepare for disaster recovery through backups and startup recovery mechanisms • Backup utility • Normal, Incremental, Differential, Daily, and Copy • Can back up System State • Shadow Copies of Shared Folders gives users direct control over restoring deleted files or returning to previous versions of files 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 49 Summary (continued) • Automated System Recovery restores system configuration settings (not data files) • Windows Server 2003 provides several Advanced Startup Options to troubleshoot boot problems • Advanced Startup Options include • Safe mode • Last Known Good Configuration • The Recovery Console is used for system recovery 70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment 50