PPT Version

OSPF Security Vulnerabilities Analysis draft-ietf-rpsec-ospf-vuln-02.txt
emanuele.jones@alcatel.com
olivier.le_moigne@alcatel.com
IETF 66 – RPSEC Working Group
July 2006
Montreal, Canada
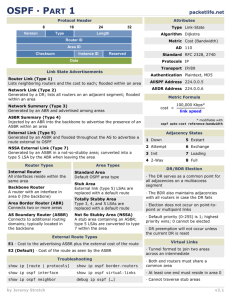
Draft’s overview
> Purpose
• Provide a complete vulnerability analysis coverage for OSPF
• Leverage OSPF vulnerabilities assessment:
–
–
Outline areas of intervention to harden the overall security of OSPF
Provide a reference to better mandate requirements for security of future routing protocols
> Approach
•
•
• systematic analysis of OSPF mechanisms and messages to identify potential security vulnerabilities
–
–
–
General Vulnerabilities not tied to any specific OSPF message
Per-Message Vulnerabilities
Resource Consumption (DoS) Vulnerabilities not implementation specific review of OSFP threats documents
Diff draft-ietf-rpsec-ospf-vuln-02.txt from 01
> Formatting: Nits have been fixed
• document converted to xml to use xml2rfc
• added missing sections (Security considerations)
Draft structure
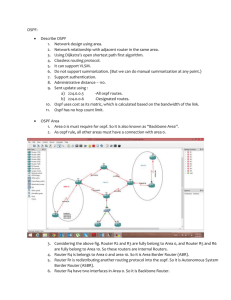
> Definition of attacker and location
•
• insider vs outsider remote vs local
> Vulnerabilities
•
•
• single intrusion, global impact
– one compromised router/link can impact all the stability of the network mechanism of “fight back”
–
– information sent on behalf of another routers will be corrected except in case of periodic inject where the attacker can induce a permanent network state analysis message per message
– malformed / malicious information
– resource consumption
Examples of anomalies
>
>
>
>
>
Neighborhood modification
• Cryptographic Sequence Number Gap
• Hello Replay
• DR modification
Rerouting by Modifying the Link State Database
• MaxAge
•
•
Max Sequence Number
LSA Modification
•
•
Introduction of False External LSAs
Non-Existing Stub Networks
Implementation Limits and Resources Consumption
•
•
•
Link State Database Overflow
Non-existing Links in Database Description
Multi Hellos Attack
• Big Router LSA
Other cases of IP Fragmentation
Malformed packets
Fight Back
>
>
•
What is fight back?
Every LSA that is circulating containing wrong information will be corrected by its owner
•
•
Papers on OSPF security suggest that
Fight Back corrects the damage of most attacks
Many theoretical attacks are not worth the effort just to cause a brief topology change
[ “An Experimental Study of Insider Attacks for the OSPF Routing Protocol” , Vetter et al.
“On the Vulnerabilities and Protection of OSPF Routing Protocol”
, Wang and Wu ]
Example: Modifying a network topology
> Get an injection point
• unprotected routing plane (no ACL, no authentication)
> Choose a LSA to modify
> Inject periodically (every second) the modify LSA with higher sequence numbers
• The legitimate router will try to correct this but will fail: “disabled fight back”
> Finalize the draft
Next steps
?
Back up slides
Three Examples from the Draft
> Three examples of vulnerabilities presented in the draft and how to exploit them :
Vulnerability
LSA Modification
“Phantom” LSAs
Outcome
Topology Changes
Database Overflow
External LSA Forwarding Data-Traffic Loop
ID’s Reference
3.2.4.3-4
3.3.5
3.2.4.6
Exploit #1 – Topology Changes
> Vulnerability: LSA Information Modification [3.2.4.3-4]
•
•
• Pre-condition:
– Being able to CONSTANTLY inject valid OSPF messages
–
–
Weak MD5 key choice/Compromised Router
No Cryptographic Authentication, etc…
Possible Impact: Topology Changes
–
–
Allow Eavesdropping
Starve/Overload a network
Expected Outcome:
– Highly unstable topology (loops, route-flapping) due to Fight Back of
LSAs between attacker and legitimate owner
• Observed Outcome (as supported by the RFC!)
– PERMANENT or SEMI-PERMANENT topology changes due to ineffective Fight Back
Fight Back
>
>
•
What is fight back?
Every LSA that is circulating containing wrong information will be corrected by its owner
•
•
Papers on OSPF security suggest that
Fight Back corrects the damage of most attacks
Many theoretical attacks are not worth the effort just to cause a brief topology change
[ “An Experimental Study of Insider Attacks for the OSPF Routing Protocol” , Vetter et al.
“On the Vulnerabilities and Protection of OSPF Routing Protocol”
, Wang and Wu ]
Disabling Fight Back
>
>
>
•
•
OSPF Fight Back can be
Disabled
Heavily Diluted
Attacks on LSA information are then SUCCESFUL
HOW?
1.
Periodic Injection
>
Exploiting an architectural “flaw” in the OSPF flooding algorithm
> [ RFC 2328, 13.5 (a) (b) and (f) ]
> MinLSInterval (5 seconds)
2.
3.
Prevent information from reaching the router legitimate owner
> Subverted router that partitions the network
Inject information on behalf of non-existing routers
Exploit #2 - Resource Consumption
>
“Phantom LSAs” are Router/Network LSAs sent on behalf of non-existing OSPF peers
> These entries are ignored by the Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm (do not produce topology changes)
>
“Phantom LSAs” are entered in the Link State Database
•
• Each entry is kept for MaxAge (1hour)
No fight back is triggered since there is no legitimate owner
> Exhausting Link-State Database resources will put OSPF in a very delicate state and stress implementation’s robustness
Exploit #3 - Creating a Data-Traffic Loop
> Vulnerability: Modifying External LSA Forwarding Field [3.2.4.6]
•
• Pre-Condition:
–
–
–
Being able to inject valid OSPF messages
–
–
Weak MD5 key choice/Compromised Router
No Cryptographic Authentication, etc…
E-
Bit Enabled on advertising peer’s Router LSA
Change Forwarding Address 0.0.0.0 to a router (host) in any Stub Area
Possible Impact:
–
–
Data never gets to its destination because it is stuck in a loop.
Outgoing External Traffic forwarded to a Stub Area router (host) will LOOP between the ABR and its next hop towards the forwarding point. [RFC 2328, 3.6]
Periodic Injection
> When a legitimate owner receives a malicious copy of its own LSAs:
• SINCE
–
– the malicious LSA has higher sequence number a copy of the LSA is already present in the LinkStateDB and this copy was not received by flooding but installed by the router itself
•
• THEN Flood the malicious LSA and AFTER check ownership
THEN TRY to update the malicious LSA [RFC 2328, 13, p.143-6]
•
• Why try?
– Because a router cannot inject two same LSAs faster than
MinLSInterval (5 seconds) BUT it will immediately flood any
LSA received. [RFC 2328, 12.4, p.125]
If the attacker is injecting malicious LSAs with a rate higher than
MinLSInterval, the legitimate owner will collaborate in the flooding
123.1.2.0
Data-Traffic Loop
Attacker is advertising
External Route to 123.1.2.0 with Forward to F
B
Ext. LSA 123.1.2.0 Forward F is present in LinkStateDB
A
Compromised Router
D direct
F direct
0.0.0.0 D
BACKBONE
C
1 DATA Traffic
TO: 123.1.2.0
D
2
E
3
STUB AREA
F E
...
123.1.2.0 E
G
NO Ext. LSAs: 123.1.2.0 is pointed to DEFAULT ROUTE
F
D E
F direct
0.0.0.0 E
Attacker’s Location
>
An OSPF router could be attacked from ANYWHERE in the internet if the router’s IP address is known.
ATTACKER
ATTACKER
ATTACKER
Telnet or SSH
INTERNET
Session
OSPF
Router
INTERNET
OSPF
Router
OSPF
Domain
OSPF
Router
OSPF
Router
OSPF
Domain
OSPF
Router
Physical access to the link
Attacker “On the Path”
OSPF
Router
•
•
Access to a router
Access to the link’s password
Extremely easy to mount DDoS attacks for outsider attackers.
Extremely difficult to trace back the attacker
Remote Attacker Backup
“The IP destination address for the packet is selected as follows.
On physical point-to-point networks, the IP destination is always set to the address AllSPFRouters. On all other network types (including virtual links), the majority of OSPF packets are sent as unicasts, i.e., sent directly to the other end of the adjacency. In this case, the IP destination is just the Neighbor
IP address associated with the other end of the adjacency (see
Section 10).” RFC 2328, 8.1
Hop-byhop OSPF’s Security
> All OSPF peers (on the same network) share the same secret key.
> If the attacker compromises ONE single link it can now attack the entire domain.
• From the compromised link attacker can inject LSAs on behalf of every other OSPF router (even if other links use a different secret!)
> Security Consequences:
•
• Local Intrusion Global Impact
– Attacker that compromises one link/peer can possibly then attack anywhere in the entire domain
Never know which is the compromised/malicious router
– Even if an attack/suspicious behaviour is detected, it may not be immediate to identify the malicious router
Stub-Area Default Route
“One or more of the stub area's area border routers must advertise a default route into the stub area via summary-LSAs. These summary defaults are flooded throughout the stub area, but no further.”
“These summary default routes will be used for any destination that is not explicitly reachable by an intra-area or inter-area path (i.e., AS external destinations).”
“An area can be configured as a stub when there is a single exit point from the area, or when the choice of exit point need not be made on a per-externaldestination basis”
RFC 2328, 3.6, pag. 37
“Forwarding address Data traffic for the advertised destination will be forwarded to this address. If the Forwarding address is set to 0.0.0.0, data traffic will be forwarded instead to the LSA's originator (i.e., the responsible AS boundary router).”
RFC 2328, A.4.5, pag. 215