31. Goc
advertisement

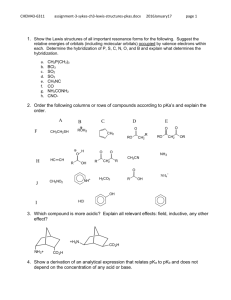
Chemistry Session GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - 4 Session Objectives Session Objectives 1. Resonance or Mesomeric effect 2. Inductive effect 3. Electromeric effect 4. Hydrogen bond 5. Hyper conjugation 6. Steric effect Resonance or Mesomerism 1. All the properties of a compound cannot be explained by single structure. 2. Canonical structures or resonance contributing structures–differ in position of electrons. 3. Delocalisation of electrons leads to decrease in potential energy of molecule. canonical structures of benezene Resonance hybrid structure of benezene Resonance or Mesomerism 4. Resonance hybrid is more stable than canonical structures. 5. Resonance structures are imaginary. 6. Resonance energy = Actual energy of hybrid–energy of most stable contributing structure. 7. Resonance is measure of stability. Rules for Drawing Resonance Structure 1. The molecule should be planar. 2. It contains an alternating system of single and double bonds (a conjugated system). 3. The relative positions of nuclei should remain unchanged (e.g. tautomerism). 4. The negative charge must preferably lie on the most electronegative atom. 5. The charge needs to be preserved in all the resonating structures. 6. The electrons always move away from a negative charge. 7. Arrows should be drawn to indicate the direction of the movement of electrons. Types of Resonance +R or +M effect C C – —C—C OH + OH (+M or +R effect of –OH group) –R or –M effect + C C CH O (–R effect of –CHO group) —C—C CH — O – Types of Resonance For substituted benzene + NH2 NH2 + NH2 – etc. +R effect of –NH2 group. – O + N O – O + N – O – O + N + – – O etc. + –R effect of –NO2 group. Inductive Effect 1. Permanent effect in saturated carbon chain compounds. 2. Group attached to carbon chain should have tendency to release or withdraw electrons. Types of inductive effect + I effect effect –electron donating groups e.g., CH3 , C2H5 – I effect effect –electron withdrawing groups e.g., - NO2 , –CN Features of Inductive Effect 1. Chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid because O Cl - CH2 C O Cl-CH2 - C OH + + -I H O Ka = 1.4 × 10-3 O CH3-C O + CH3-C OH Ka = 1.75 × 10-5 +I O + H Features of Inductive Effect 2. The larger is the electron-withdrawing effect of a group, the greater is the –I (inductive) effect. F CH2 COOH Ka 2.5×10-3 Br CH2 COOH 1.3×10-3 3. Inductive effect is additive Cl3CCOOH Ka 2.3×10-1 Cl2CHCOOH 5.4×10-2 Features of Inductive Effect 4. Since this effect is transmitted through a chain it becomes less effective with distance ClCH2CH2COOH Ka 8.32×10-4 ClCH2CH2CH2COOH 3.02×10-5 Electromeric Effect Temporary effect which is observed in presence of reagents involving transfer of electrons in an unsaturated system. in presence of reagent X Y in absence of reagent + X – Y Electromeric Effect Addition of HBr to an alkene R 1 C H R — CH — CH3 2 H C R HBr H Br – H R H Br H C—C + – + C — CH3 H H + Hyperconjugation or no bond resonance (a) Involves and bond orbitals (b) More the number of hyperconjugative structures, more will be the stability of ion or molecule H H H – C – C+ H H + H H H–C=C–H H H Structure of ethyl carbonium ion H H H–C=C + H H + H C=C H H H Hyperconjugation or no bond resonance (c) The number of hyperconjugative structures in an alkene is obtained by the number of C — H bonds attached to the carbon bonded directly to the double bonded carbon atoms. H+ H H C H CH CH2 H C H – CH H CH2 + C CH – CH2 H H H H C CH + H – CH2 Significance of Hyperconjugation H3C — CH — CH CH2 1–butene H3C — CH CH — CH3 H3C — CH + H CH — CH2 (2 hyperconjugative structures) – H3C — CH — CH CH2 H 2–butene + (6 hyperconjugative structures) More stable Relative strength of organic acids O R-C O R-C OH + + H O R-C O O Resonance structures Class Exercise Class exercise 1 The hybridization of carbon atoms C — C single bond in vinylacetylene is (a) sp3 - sp3 (b) sp - sp2 (c) sp2 - sp (d) sp3 - sp Solution : 1 H2 C 2 3 CH — C Vinylacetylene 4 CH Hence answer is (c). Class exercise 2 Allyl isocyanide has (a) 9 bonds and 4 bonds (b) 8 bonds and 5 bonds (c) 8 bonds, 5 bonds and 4 non-bonding electrons (d) 9 bonds, 2 bonds and 2 non-bonding electrons Solution: + H2C CH — CH2 — N – C Allyl isocyanide The compound has 3 bonds and one lone pair, i.e. two non-bonding electrons. It also contains 9 bonds. Hence answer is (d). Class exercise 3 Among the following which has the most acidic -hydrogen? O O O (a) CH3CCH2CHO (b) CH3CCH2CCH3 O (c) CH CCH COOCH 3 2 3 (d) CH3CHO Solution O O H3 C — C — CH2 — CH O O H3 C — C — CH2 C — CH3 O one keto and one aldehydic carbonyl group. two e-withdrawing keto groups. O H3 C — C — CH2 C — OCH3 keto and ester group. O H3 C CH one aldehyde group. Solution Since e-withdrawing nature of C O gas varies as aldehyde > keto > ester Then most acidic a-H atom is present in O O H3C C — CH2 — CH Hence answer is (a). Class exercise 4 The decreasing order of acidity among phenol, p-methylphenol, m-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol is (a) m-nitrophenol, p-nitrophenol, phenol, p-methylphenol (b) p-nitrophenol, m-nitrophenol, phenol, p-methylphenol (c) p-methylphenol, phenol, m-nitrophenol, p-nitrophenol (d) phenol, p-methyl phenol, p-nitrophenol, m-nitrophenol Solution OH OH OH OH NO2 CH3 –I, –R –I +I NO2 Electron withdrawing groups increase acidic strength while electron donating group decreases the same. So the proper decreasing order of acidic strength is OH > NO2 OH OH OH > NO2 > Hence answer is (b). CH3 Class exercise 5 In the following compounds, the order of basicity is O N N H H (I) N (II) (III) N H (IV) (a) I > IV > II > I (b) II > I > IV > III (c) III > I > IV > II (d) IV > I > III > II Solution O N H I N sp3 N sp2 II H IV N sp3 H III sp2 Between I and IV, IV is less basic because of the –I effect of oxygen atom. II is more basic than III as the lone pair on N-atom in III is not available for protonation as it is involved in resonance. Therefore, the correct order is I > IV > II > III Hence answer is (a). Class exercise 6 Account for the order acidity in the following compounds. O (i) CH3CCH2COOH (ii) HC CCH2COOH CH3CH2COOH H2C = CHCH2COOH Solution O (i) H3C C CH2 COOH > CH3 CH2 COOH (a) (b) In compound (a), electron-withdrawing keto group increases the acidic strength by decreasing the O — H bond strength, while no such effect is there in compound (b). (ii) HC C CH2 COOH > CH2 CH CH2 COOH Carbon atoms attached to triple bond is sp hybridised and more electron-withdrawing than sp2 hybridised carbon atom. Hence, such order in acidic strength is observed. Class exercise 7 Which of the following two amines is more basic and why? CCl3CH2CH2CH2NH2 or CCl3CH2CH2NH2 Solution Electron-withdrawing groups decrease the charge density on N-atom of organic amines and hence decrease the basic strength. In Cl3C CH2 CH2 CH2 NH2, the electron withdrawing — CCl3 is far apart from — NH2 group as compared to Cl3C CH2 CH2 NH2. Hence, the former is more basic in nature. Class exercise 8 Do you think CH3CH CH2 OH can show tautomerism? Solution: Yes. The tautomeric form is CH3COCH3. Class exercise 9 Which one will be more acidic ? OH CH3 NO2 OH CH3 CH3 CH3 C N I II Solution Because of steric inhibition of resonance conjugate base of I will not be stabilised by resonance. But for II there is no such steric inhibition of resonance. Class exercise 10 Which hydrogen is maximum acidic in the following compound? H—C C NO2 O—H COOH Solution: Carboxylic hydrogen is maximum acidic. Thank you