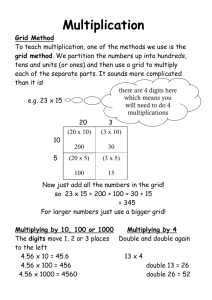
BGI Partner Institutions
advertisement

UNESCO http://www.unesco.org/new/en/education/themes/strengthening-education-systems/highereducation/reform-and-innovation/brain-gain-initiative/ Brain Gain Initiative The migration of highly-skilled people is having a significant impact on higher education and research, as universities and research centres have to adjust to increasingly mobile, competitive labour markets, and strive to retain highly-skilled professionals. Many skilled expatriates, wherever they may be located, have the potential and the willingness to contribute to the development of their home country, and information and distributed computing technologies provide a new way to enable distance cooperation. In an effort to change this trend, UNESCO and HP joined forces in 2003 to develop several projects, using innovative technology to create a “brain gain” for regions that are particularly impacted by the exodus of academics and scientists. In 2009 UNESCO and HP agreed to scale up the initiative to help create a sustainable university einfrastructure for science, bringing together higher education institutions and research centres in Africa and the Arab States region and allowing them to pursue innovative education projects. By the end of 2011, this infrastructure could span some 20 higher education institutions in 16 countries provided like-minded corporations and organizations join UNESCO and HP in this initiative. A digitally literate generation of young people will be able to take advantage of the opportunities provided by access to virtual classrooms and virtual laboratories. Remote access to rare or expensive resources can help small, low-budget universities enjoy access to infrastructure of the same quality as large, well-endowed ones. http://www.unesco.org/new/en/education/themes/strengthening-education-systems/highereducation/reform-and-innovation/brain-gain-initiative/africa-and-arab-states/ Africa and Arab States 2009-2011 In early 2009, UNESCO and HP agreed to extend the African pilot (link please) to over 20 higher education institutions in Africa and the Arab States region by 2011. The Brain Gain Initiative (BGI) should bring together over 20 institutions in some 16 countries. Through the use of distributed computing, UNESCO, HP and other partners plan to create the first African regional university network and help reduce the number of skilled workers, scientists, academics and researchers that leave the region. Innovative technology and funding support allows participating universities to re-establish links between researchers who have stayed in their countries and those living abroad, connect academics to international peers, research networks and funding opportunities. Faculties and students at beneficiary universities are able to work on innovative education projects with other institutions in their regions and around the world. Fifteen new institutions have joined the BGI in October 2009 and four of the African Pilot institutions. BGI Partner Institutions Burkina Faso: Ouagadougou University, Laboratoire d’analyse numérique, d’informatique et de biomathématique (LANIBIO) Burkina Faso: Ouagadougou University, Laboratoire de traitement de l’information et de la communication (LTIC) Cameroon: Douala University Cameroon: Yaoundé I University Côte d’Ivoire: Cocody University Ethiopia: Mekelle University Ghana: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology Kenya: Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology Kenya: University of Nairobi Kuwait: Kuwait University Lebanon: Saint-Joseph University Morocco: Centre National pour la Recherche Scientifique et Technique (CNRST) Nigeria : University of Nigeria, Nsukka Senegal: Cheikh Anta Diop University Senegal: Gaston Berger University Tunisia: Université de la Manouba, Ecole Nationale des Sciences de l’Informatique Uganda: Makerere University Uganda: Mbarara University Zimbabwe: Chinhoyi University of Technology Burkina Faso: Ouagadougou University, Laboratoire de traitement de l’information et de la communication (LTIC) Project: Implementation of a high performance computing grid at Ouagadougou University Project coordinator: Professor Oumarou Sie Training component: development of a curriculum for students in scientific Masters, so that they are trained in how to use the computing grid effectively, development of training modules for teaching and research staff. Teach modules to the target audience. Partnership component: gather a group of research and teaching staff and labs who will commit to awareness-raising as to the benefits of grid computing and will strive to kick start a local network of computing grids, particularly in West Africa, with UCAD (Senegal), UGB (Senegal), along with Côte d’Ivoire and Cameroon. Then work conjointly with other regional networks to build up on this initiative and help a more global network emerge. Institution/project website Project highlights: Research component: research and development of research on algorithms and distributed applications, take advantage of the grid for experiments. Supervision of Ph.D. and Masters students. http://www.univ-ouaga.bf/ Burkina Faso: Ouagadougou University, Laboratoire d’analyse numérique, d’informatique et de biomathématique (LANIBIO) Institution: Ouagadougou University, Laboratoire d’analyse numérique, d’informatique et de biomathématique (LANIBIO) Project: Mathematical modelling & computer simulation of pollutants transfer mechanism in the drainage basin of river Sourou Project coordinator: Professor Blaise Some Project highlights: Conduct “Mathematical modelling & computer simulation of pollutants transfer mechanism in the drainage basin of river Sourou” research project. In particular (1) in cooperation with experts and other institutions, collect and analyse data (measures, observation), identification of the shortages in existing models, proposal to address them; (2) mathematical analysis of data, establishment of new models and analysis of the latter; numerical equation solving and numerical modelling, comparison with observation data. Design mathematics forecasting models and make them available to institutions, researchers, for (1) understanding and control of aquifer pollution mechanisms in the drainage basin of river Sourou and other similar drainage basins in Burkina Faso, and (2) the fight against aquifer contamination (prevention, cleanup systems) Make available to decision makers a tool for surveillance and control of drainage basin aquifers pollution. Use of numerical results obtained to conceive software that will be usable in Burkina Faso and elsewhere to act in real time and precisely against pollution cases in drainage basins. Institution/project website Cameroon Douala University Institution: Douala University Project: Strengthening local capacities for the study of climate change and consequences through distributed computing Project coordinator: Professor Georges Emmanuel Ekodeck Project highlights: Mobilize researchers in climate, atmospherics physics, hydrology, hydrogeology, biodiversity, to attain a better understanding of the effects of global climate change nationally. Ensure a better use of existing (global as well as regional) climate simulation models; establishment of new models to follow up on and foresee evolutions in malaria, water resources, water flows to hydroelectric dams, evolution in the surface of arable land, biodiversity. Collect climate and hydrological data, test existing models, write computer programmes and models that are specific to the project, run the models and analyse results. Teaching activities, development on courses on atmospheric pollution, renewable energies. Communication activities, tell the general public about causes and consequences of climate change. Institution/project website Cameroon Yaoundé I University Institution: Yaoundé I University Project: Information system for risk management through remote detection (SIMART) Project coordinator: Professor Emmanuel Tonye Project highlights: Elaborate a curriculum (for both distance and on-site training) on (1) remote detection and management of environmental risks (2) geographical information systems for students following courses in telecommunications, electronics, computing. Also, disseminate knowledge on distributed computing obtained through participation in the UNESCO-HP Brain Gain initiative. Elaborate simulation tools for urban pollution and modification of the coastline: train team members, collect data, create the GIS and run it as a computer simulation. Deploy the urban pollution and flood remote detection, alert and visualization system, make it available through the web and on resource constrained devices. Also, awareness-raising activities to the benefit of relevant departments/facilities, as well as the general public. Institution/project website Côte d’Ivoire Cocody University Institution: Cocody University Project: Climate modelling and distributed computing (MOCCAD) Project coordinator: Mr Abdourahamane Konare Project highlights: Training on distributed computing, with support from ICTP experts. Mobilize the resources brought through the initiative to support the development of a regional climate modelling tool and foster the emergence of a regional climate modelling centre. Mobilize the resources brought through the initiative to support the development of a Master’s Degree on climate modelling and scientific computation, open to students in the subregion. Hold training seminars and create distributed computing courses focused on themes that are relevant for the region. Institution/project website Ethiopia: Mekelle University Institution: Mekelle University Project: Distributed grid computing for climate change adaptation and biological modelling/simulation Project coordinator: Dr. Enquebaher Kassaye Project highlights: Establish a grid computing facility to facilitate the operation of grid-computing powered research projects in the areas of Biological and Climate Change Adaptation Modelling and Simulation, for the benefit of academics and students, researchers, at the regional and national levels. Offer the grid computing facilities free of charge to its users. Train technical staff (server and operations management) and instructors and researchers in using the grid computing environment for science. Conduct research project in Modelling and Analysis Environment for climate change analysis and forecasting. Conduct research project in Modelling and Simulation Environment for biology, medicine and other natural sciences and engineering. Institution/project website Ghana: Nkrumah University of Science and TechnologyNkrumah University of Science and Technology Institution: Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology Project: Mobilizing the Ghanaian Diaspora for Renewable Energy Research and Development Project coordinator: Professor Abeeku Brew-Hammond Project highlights: The project will identify specific areas and applications of Grid Computing for energy research in order facilitate to promotion of Grid Computing within and without KNUST. The specific objectives are: To provide a forum for discussion between energy professionals within and outside the university to identify specific areas of Grid exploitation in Petroleum, GIS, and Renewable Energy; To identify available grid applications for energy research in the context of Ghana’s developmental needs; To promote Grid Computing concepts within and outside KNUST; Institution/project website Kenya Institution: Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology Project: Computer supported collaborative e-waste management research towards developing a national e-waste management strategy Project coordinator: Mr Simon Maina Karume Project highlights: Develop a collaborative web-based e-waste information system, i.e., an e-waste management information clearing house for information exchange and collaborative learning: develop a web-based bulletin board for educating the general public about effects of e-waste and the need to adhere to strict procedures of e-waste management. Use the collaborative web-based platform and organize an online curriculum symposium to refine the e-waste management curriculum developed by MMUST and Computers for Schools, Kenya (CFSK). Conduct investigation of existing e-waste management systems and post findings in the clearing house for other researchers to access. Develop web-based content for the modules in the e-waste management curriculum and post it in the clearing house for students and lecturers/researchers of concerned departments to access. Collaboratively craft an environment-friendly e-waste management strategy for Kenya. Establish an e-waste recycling centre at MMUST to cater for e-waste generated in Western Kenya. Disseminate research findings by posting them on the clearing house and the bulletin board, publishing them in e-journal. Disseminate knowledge about distributed computing through seminars and workshops to science, engineering and environment science lecturers/researchers. Said lecturers/researchers to identify a project within their department that can benefit from distributed computing technology. Implement the distributed computing project that has been identified. Institution/project website Kenya - University of Nairobi Institution: University of Nairobi Project: Diasporas and distributed computing for development, towards creating a regional centre of excellence for distributed systems and modelling Project coordinator: Professor William Okelo-Odongo Project highlights: Train support and technical and research staff in grid, cloud and volunteer computing hardware, sensitize the user community on the existence of the node. Investigate the application services needs of user disciplines, train computing professionals on how to use and submit their work to the node. Develop, in collaboration with user disciplines, useful applications services on the grid, develop the web services software and packages. Involve local and regional participation in joint research and resource sharing and collaborations, conduct joint conferences/meetings in which research results are shared and disseminated. Support subproject 1: Nucleic Acid Structural Biology Platform for 3D structure predictions of RNA and DNA motifs. Support subproject 2: Medical Image Processing using Volunteer Computing. Support subproject 3: Monte Carlo simulation techniques to track and image radiation transport through materials. Institution/project website Morocco - Centre National pour la Recherche Scientifique et Technique (CNRST) Project: Development & strengthening of the Moroccan computing grid “MaGrid” Project coordinator: Mr Redouane Merrouch Project highlights: Extend the computing and storage capacity of the existing main MaGrid cluster hosted at CNRST Provide training on installing, managing and using the node and computing grid, administration of services and the infrastructure. Hold an application gridification school (i.e. how to port to the grid existing applications, in various scientific fields). Strengthen links with expatriate experts. Mobilize the resources brought through the initiative in support of MaGrid’s contribution to LHC/ATLAS. Install analysis and simulation tools within MaGrid, raise awareness and promote the use of MaGrid within the Moroccan scientific community. Support the establishment, from 2010, of a grid computing/distributed computing training module within the existing “Computational Physics” Master’s Degree, Faculty of Sciences, Rabat, Morocco. Institution/project website Nigeria Institution: University of Nigeria, Nsukka Project: Sustaining the Research and Grid Computing Components of the University of Nigeria Project coordinator: Dr. Benjamin A. Ogwo Project highlights: The project aims at strengthening the research and grid computing components of the Project through expanding existing facilities in the grid computing laboratory, further research on different aspects of animal and plant tissue culture, as well as updating the Project’s website. Specifically, this collaboration focuses on the Centre’s ongoing tissue culture research on mushrooms, cassava and indigenous plants for local staple foods. Concrete objectives include: 1. Establish more experiments on animal and plant tissue culture techniques in mushrooms, cassava and other local staples relative to the gains on the first phase of the Project. 2. Develop training modules on tissue culture for researchers and students of the University of Nigeria and affiliate institutions, drawing from resources gained for the first phase of the Project. 3. Expand and upgrade existing facilities at the University of Nigeria grid computing laboratory. 4. Updating and revising the UNESCO-HP website in order to make it more user friendly for the collaborating local and Nigerian scientists in the Diaspora. 5. Disseminate the findings of the three major experiments on plant and animal tissue culture. Institution/project website http://www.unn.edu.ng/ Senegal Back to top Institution: Cheikh Anta Diop University Project: Gestion optimale de ressources distribuées hétérogènes sur des Grilles de calcul pour la recherche scientifique Project coordinator: Mr Ibrahima Niang Project highlights: The project will promote the use of grids and grid computing in scientific research in Senegal. Specific project objectives include: Train faculty and PhD students on the utilization of grids/grid computing Train engineers in grid administration and configuration Optimize distributed and heterogeneous grid resources Build Senegalese expertise in the field of grid computing Enhance collaboration with the Senegalese Diaspora Strengthen North-South and South-South partnerships Institution/project website http://www.cci.ucad.sn/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=67&Itemid=76 Senegal - Gaston Berger University Institution: Gaston Berger University Project: Setting up a distributed socio-economic infrastructure for a knowledge-based development approach Project coordinator: Mr Moussa Lo Project highlights: Study and disseminate within the institution grid computing know-how. Include training modules on grid computing within existing Master’s degree. Foster the use of grid computing within existing labs and projects (e.g. project MOMIES – Modèles Mathématiques et Informatiques de l'Eau et du Sable – Mathematical and Computing Models for Water and Sand) Study semantic web and social web in the framework of the development of a living socio-cultural encyclopedia of Senegalese communities. Train researchers. Conduct field work to gather the initial corpus and geographical data. Install and develop software and hardware infrastructures (GIS + semantic layer) on which the encyclopedia will operate. Make the encyclopedia available to communities; present it and raise awareness, encourage its use. Incorporate UGB’s grid note within the national efforts to develop and network these tools, ideally in cooperation with managers of the node that is already operating at UCAD. Institution/project website Tunisia Institution: Université de la Manouba, Ecole Nationale des Sciences de l’Informatique (ENSI) Project: e-infrastructure for academic cooperation and resource sharing in Africa and the Arab States region (ECUMA) Project coordinator: Ms Leila Azzouz Saïdane Project highlights: Develop capacities in the establishment of grid infrastructures and the development of application on grids. Conduct the Neuroweb project as a pilot grid activity, so as to develop capacities in distributed computing. Analyze and communicate on skills acquired to encourage other institutions to develop their own applications and join the e-infrastructure. Establish an e-learning tool so as to learn how to develop grid applications. Train support (technical) and research staff in grid technologies. Establish a network with national and international well-skilled partners. Develop joint supervision of Master’s degrees and PhD theses together with HEPIA (Switzerland), promote the exchange of expertise between both institutions, especially thanks to expatriate experts. Deploy a national grid, develop its services and guarantee that it delivers satisfying performance, relying on latest advances in grid computing technologies. Establish and strengthen cooperation with other institutions in Africa and the Arab region, strengthen cooperation with international partners and expatriate experts so as to promote scientific and economic development. Institution/project website Uganda Makerere University Project: Towards Fostering Localized Innovative ICT Solutions Project coordinator: Professor Idris Ahmada Rai Project highlights: Identify four projects proposing ICT-based solutions to address local challenges and use the funds defined in the budget to facilitate implementations of these projects. Visit other institutions participating in the Brain Gain Initiative from different parts of Africa/the Arab States region in order to forge collaborations and try to establish long term collaborations, mainly with ICT units. Sign MoU with some of these institutions. Organize seminars to train staff and students from both Makerere University and other Ugandan institutions on distributed computing, thus enhancing the existing relationship with other public Ugandan universities. Further the existing collaboration with researchers in the Diaspora via visits both ways. Establish a grid node at Makerere University. Present the project in university activities – seminars, conferences and workshops. Institution/project website http://mak.ac.ug/ Back to top Uganda Mbarara University of Science and Technology Project: Training and implementation of e-learning Project coordinator: Ms Theodora M. Twongyirwe Project highlights: (1) Increase use of ICT in teaching and research Develop an e-learning management policy. Establish an e-learning resource unit that will coordinate e-learning activities, vet proposals on e-learning, monitor and evaluate e-learning activities at the institution, promote e-learning. Train trainers of trainers in e-learning, and then all teaching staff in e-learning. Establish the appropriate distance learning education infrastructure and software. (2) Provide greater access to university education by developing capacity in distance education Develop e-learning degree programmes. Notably, use e-learning at the Faculty of Medicine to train health workers in a rural set-up; at the Faculty of Education to train primary and secondary school teachers in ICT. Widen the participation in education from e.g. students with disabilities or with care responsibilities, who can only take courses from home. Ensure visibility of these activities by engaging in community outreach. Make secondary schools aware of distance learning opportunities; train primary and secondary schools teachers; train leaders, especially women, to advance the involvement of girls in research and technology; involve radios and other media. Develop e-learning networks based on academic interests groups and research collaborations. (3) Assess the potential of distributed/grid computing at the institution Install the initiative's specific hardware and software, which will support the implementation/strengthening of a grid node at the institution. Disseminate the grid/distributed computing know-how obtained through the initiative. Have the Institute of Computer Science host a research project to investigate uses of grid/distributed computing in supporting health, education and enterprise development in rural areas. Institution/project website http://www.must.ac.ug/must.php Back to top Zimbabwe - Chinjoyi University of Technology Project: Use of grid and cloud computing applications as technical interventions to manage brain drain dynamics Project coordinator: Dr. Raphael Jingura Project summary: The project proposes to use grid and cloud computing technologies as technical interventions to turn brain drain into brain gain by linking local academics and researchers with their international counterparts; and build their capacity to participate in mainstream research activities. The specific objectives of the project are: Advocate and popularize grid and cloud computing as research tools in the University Develop a t-infrastructure in grid and cloud computing for University faculty Set up an institutional platform for grid and cloud computing Establish a Diaspora digital connection model for the University Institution/project website http://www.cut.ac.zw/ABOUTCUT/aboutcut.html