Gothic Literature - AJSmith
advertisement

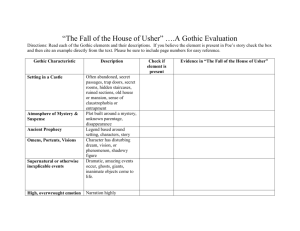
What’s Your Favorite Scary Movie Do you like reading scary books or watching scary movies? Think about a scary movie you enjoy Why/why not? What happens—plot? Why do people like to be scared? The Dark Romantics: Gothic Literature 1760-1820 (…and beyond) “Can we speak of ‘ghosts’ without transforming the whole world and ourselves, too, into phantoms?” Jean-Michale Rebaté The Origins of the term Gothic (“Gothick”) Gothic Originally referred to the northern Gothic tribes that invaded Europe in the 4th, 5th, and 6th centuries Later applied to Renaissance architecture (critics thought the style originated with the Gothic tribe) Was considered ugly, barbaric, archaic Gothic Architecture First Gothic Cathedral build in 1144 Gargoyles (originally for religious buildings) Vaulted ceilings Structural ribbing (skeletal) Stained glass Art Influences “The Nightmare” Johann Heinrick Fuseli The Beginning 1764- Horace Walpole publishes The Castle of Otranto: A Gothic Story anonymously Contains essentially all the elements associated with the genre Best-seller Had remodeled his home in “Gothick” style Said that the inspiration of his story was a dream that was so haunting, he had to write it down Elements of Gothic Literature 1. Setting Action takes place in or around an old castle Seems abandoned, or broken down Has secret passages, doors, rooms Usually very large, but seems claustrophobic Elements of Gothic Literature 2. An atmosphere of mystery or suspense Feeling of being threatened or fearful Plot is built around a mystery (such as unknown parentage, a disappearance, or some other inexplicable event) This is achieved by the next three elements… Elements of Gothic Literature 3. An ancient prophecy Usually connected with the castle or its inhabitants Obscure, partial, or confusing The characters struggle to understand Elements of Gothic Literature 4. Omens, visions Character may have a disturbing dream/vision Some phenomenon may be seen as an omen of coming events If the statue of the lord of the manor falls over, it may predict his death Elements of Gothic Literature 5. Supernatural or otherwise inexplicable events Dramatic or amazing events occur Such as ghosts or giants, or inanimate objects (such as a suit of armor or painting) coming to life In some works, the events are ultimately given a natural explanation, while in others the events are truly supernatural Elements of Gothic Literature 6. High, overwrought emotion Narration may be highly sentimental Characters are often overcome by anger, sorrow, surprise, and especially, terror. Suffer from raw nerves and a feelings of impending doom Crying and emotional speeches are frequent Breathlessness and panic are common Elements of Gothic Literature 7. Women in distress Female characters often face events that leave them fainting, terrified, screaming, and/or sobbing Lonely, pensive, and oppressed heroine is often the central figure of the novel Her sufferings are even more pronounced and the focus of attention than the other characters in the story Elements of Gothic Literature 8. Women threatened by a powerful, tyrannical male One or more male characters has the power (king, lord of the manor, father, or guardian) to demand that one or more of the female characters do something intolerable The woman may be commanded to marry someone she does not love (it may even be the powerful male himself), or commit a crime Elements of Gothic Literature 9. The metonymy of gloom and horror Metonymy is a subtype of metaphor, in which something (like rain) is used to stand for something else (like sorrow). For example, the film industry likes to use metonymy as a quick shorthand, so we often notice that it is raining in funeral scenes. Note: that the following metonymies for "doom and gloom" all suggest some element of mystery, danger, or the supernatural… Elements of Gothic Literature Wind, especially howling Doors grating on rusty hinges Footsteps approaching Gusts of wind blowing out lights Characters trapped in a room Baying of dogs (or wolves) Thunder and/or lightning Rain Sighs, moans, howls Clanking chains Lights in abandoned rooms Gusts of wind blowing out lights Doors suddenly slamming shut Crazed laughter Criticism Gothic tradition has not been very highly regarded Even though it attracted many “big” writers: Keats, Melville, Faulkner not these works that are highlighted Considered their “hobby writing” Women also wrote in this genre Jane Austin (Northanger Abbey) Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley (Frankenstein) Ann Radcliffe (The Mysteries of Udolpho (1764) were best-sellers Mass-market appeal vs. literary appeal Revivals 1818: Frankenstein 1897: Dracula 1960’s: Gothic was the best-selling mass-market fiction 1970: Stephen King 2005: biggest money making movie genre, averaging $75 million per movie in box office sales Works Used Bayer-Berenbaum, Linda. “Elements of a Gothic.” Horror. Ed. Michael Greenhaven Press, 2001. 72-83. Stuprich. San Diego: “Door: Metal: Squeaky Metal Restroom Door in Building: Close: Slow Creak.” Sound Ideas. 2007. Unitedstreaming. 17 April 2007. http://www.unitedstreaming.com/>. The Gothic Imagination. Ruthford: Associated University Press, Ltd., 1982. “Gothic Architecture.” Wikipedia Online. 2005. 6 March 2005 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gothic_architecture. Harris, Robert. “Elements of the Gothic Novel.” VirtualSalt. 2005. 6 March 2005. http://www.virtualsalt.com/gothic.htm. Williams, Anne. “The Gothic Novel.” Horror. Ed. Michael Stuprich. San Diego: Greenhaven Press, 2001. 62-71. Wolfreys, Julian. Victoria Haunting: Spectrality, Gothic, the Uncanny and Literature. Houndsmills: Palgrave, 2001.