Network Content & Applications in Mobile Devices
advertisement
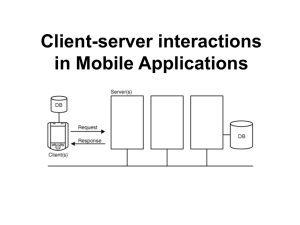
Network Content & Applications in Mobile Devices http://mobilepit.com/ Mohammad Hafiz bin Ismail (info@mypapit.net) Do you have Bluetooth Capable Phone ? Please turn Bluetooth on now for demonstration section Mobile Devices Handheld electronic device with limited processing power and connectivity commonly use by enduser consumers Examples of Mobile Devices Mobile Phones / Smart Phones PDA (Pocket PC / Palm) Internet Tablet (Blackberry / Nokia 880) Navigation Device What is not Mobile Device Laptop Personal Computer Game Console Why Mobile Device ? Mobile devices has become increasingly popular during the last 10 years. Estimate mobile subscribers around the world 2.7 billions. Currently Malaysia alone have has about 11 millions of mobile phone users a figure which expected to increase over the years. (Agar, 2004) Devices Popularity (Mobref,2007) Why Mobile Device Advancement of cellular technology has allowed Greater data transfer Faster processing power Greater interactivity Wider connectivity Early “Mobile Application” Limited processing power Relies heavily on a server-side language Depends on external browser Characteristic by the use of WML, XHTML, cHTML technology Does not actually 'run' on the mobile device. Early “Mobile Application” Relies on the server-side to provide both processing power and User Interface Little or no client-side processing No client side record/database storage – everything on the server Solely depends on internet connection Emerging Trends of Mobile Application Runs natively on the mobile device itself Does not rely on external browser Depends more on Web Service API (SOAP/XML-RPC/REST) rather than the website itself. Concentrates more on usability and content delivery Why do we need Native Network Mobile Application Easy to deploy in commercial sense Tightly integrated into user interface Does not rely on external browser The application can store data on mobile phone Faster retrieval and response time The application can access mobile phone functionalities (camera/sms/caller-id/files) Examples “Jeffrey wants to create an application which enables him to share photos taken from his phone camera to some of his friends” Can it be done with WML/XHTML based mobile application? Types of Mobile Application Email Applications Video Streaming Multiplayer game News reader Instant Messenger Application Weather Forecast application Currency converter Location Base application Home/Security Monitoring Application Ways Mobile Internet Application Communicate Low Level TCP/IP Socket Connection UDP Datagram Bluetooth RFComm ‘Virtual’ Serial COM port (on PDA) Ways Mobile Internet Application Communicate High Level (The BEST Way!) Achieve through the use of Web Services XML-RPC SOAP ATOM api Representational-State Transfer (REST) Why Web Services is the best way? Uses distributed computing concept Widely accepted as a ways to publish API Portable, Web Services only relies on HTTP/HTTPS availability Becomes an Emerging standards of publishing services (W3C, RFC 4287) Organization that uses Web Service Google.com (ATOM -GData, SOAP) Yahoo.com (SOAP) Amazon.com (SOAP) Wordpress.com (XML-RPC) Haze.net.my (REST) Foxrate.org (XML-RPC) Organization that uses Web Service Amazon.com Publish Web API to enable developers to create application that can list latest Amazon product, price comparison and heavily discounted and popular items Organization that uses Web Service Flickr.com Uses web service API to enable its users to post/update photos using any application. Mobile application that uses Flickr API : MobUp (http://mobup.blogspot.com) j2meMap (http://j2memap.sf.net) Mickr (http://www.mickr.de/) Flickr.com Client Screenshots MobUp Mickr How Web Services Architecture Works ? DB DB Procedure stored on the server XML-RPC API Server (http://foxrate.org) currencyConvert(USD,MYR,100) Less of 1KB data DB Result() = 353.71 Less than 1KB data User Interface is inside the phone But the same application can be written in WML! Why bother? Any opinion ? Web Service is better because It separates the developers work and the service providers work Developers only concentrates on their best expertise, developing mobile clients. Developers does not need to maintain the information itself Web Service is better because In mobile application, size DOES matter! Data transfer need to be optimized for faster response time (latency) and cost) Locally run Mobile Internet Application that uses Web Service do just that! Bandwidth & Data transfer efficiency Typical WML Application Request website Website (interface) displayed index.wml – 4KB foxrate.org foxrate.org foxrate.org User request currency exchange (process.php) – less than 1KB Bandwidth & Data transfer efficiency DB DB Procedure stored on the server XML-RPC API Server (http://foxrate.org) currencyConvert(USD,MYR,100) Less of 1KB data Total Data transfer = 1KB + 1KB = 2KB DB Result() = RM 353.71 Less than 1KB data User Interface is inside the phone Bandwidth & Data transfer efficiency Typical WML Application foxrate.org Result displayed result.wml (3KB) Total Data transfer = 4KB + 3KB + 1KB = 8KB Web Services is 4 times smaller than a typical WML application ! Why? The main reason is the user interface of WML application is stored on the server not client By using web service we are free to create our own user interface independent of the service provider. WML Drawbacks from Commercial Aspect WML application are hard to sell Hard to distribute Require constant maintenance (server) Hard to customize on the mobile phone part (different vendor wants to put their own logo, endorsement) WML application can’t use phone features (camera,bluetooth, GPS, InfraRed) Further Reading on Web Services XML-RPC http://xmlrpc.com http://www.xml-rpc.net/ SOAP http://www.w3.org/TR/soap/ http://www.soaprpc.com/ws_implementatio ns.html What Next ? Location Base Application (GPS) Car Navigation Fishing Spot Finder Speed Warning (GPS Auto) GPSolat More mobile phones are equipped with GPS receiver, it’s the latest trend! Location Base Application GPSolat – Prayer time base on GPS Prayer time is different according to location, season and direction. GPSolat uses location data to determine the Kiblah direction and users’ current location Base on that it can calculates prayers time. No need to worry about prayers time when travelling anymore!! Internet Mobile Application SDK You can create Internet Mobile Application using any of these platforms JavaME (http://sun.java.com/javame) Symbian (http://forums.nokia.com) (Nokia) .NET Compact Framework (http://msdn.microsoft.com/mobility/netcf/) (PDA) JavaME The best SDK for learning Supported by almost all modern phones Has great documentation Uses Java Has a lot of libraries Implementations guaranteed to support HTTP/HTTPS protocol for communication. Portable .NET Compact Framework Great for people who are familiar with .NET Supported by Windows Mobile PDA devices only More powerful than JavaME Tighter integration with device (Microsoft+Microsoft) Symbian Uses C++ Harder to code compared with others Very close to hardware implementation Limited device, only supported on some Nokia and Sony Ericsson Smartphone Screenshots Why Develop Mobile Application? The Desktop application market has been saturated and controlled by bigger companies. (i.e nobody uses other application than MS-Word, Powerpoint) Mobile devices is the new playground. Opportunities to develop localized content Huge marketplace, can compete with each other fairly. Niche Market, you can sell through telcos Places to publish Mobile Application Handago.com GetJar.com Payloadz.com PocketGear.com MypdaCafe.com And many others! Network Content Applications in Mobile Devices Q&A