2014
advertisement

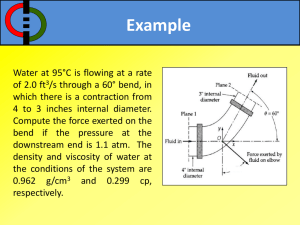
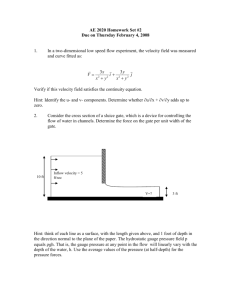
Code No: R21021 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2014 FLUID MECHANICS AND HYDRALICS MACHINES (Com. to EEE, ME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks 1. a) Differentiate i) Real fluids & Ideal fluids ii) Newtonian & non Newtonian fluids. b) An oil of viscosity 5 poise is used for lubrication between a shaft and sleeve. The diameter of shaft is 0.5m and it rotates at 200 rpm. Calculate the horse power lost in the oil for a sleeve length of 100mm. The thickness of the oil film is 1.00mm. 2. State the assumptions made in the derivation of Bernoulli’s equation. State the momentum equation and explain its significance. 3. Draw the datum line, hydraulic gradient line and total energy line for a fluid flow in a diverging pipe line and discuss. 4. A 75 mm diameter jet having a velocity of 30 m/sec strikes a fiat plate, the normal of which is inclined at 450 to the axis of the jet. Find the normal pressure on the plate i ) when the plate is stationary ii) When the plate is moving with a velocity of 5m/sec in the direction of the Jet away from the jet, also determine the power and efficiency of the jet when the plate is moving. 5. a) What are the different heads and efficiencies of the Hydro electric power stations? b) Explain about mass curve? 6. The following data is given for a Francis turbine: Net head = 70 m. speed = 600 rpm, shaft Power = 367.875 kW, ηo =85%, ηh=95%. Flow ratio 0.25. Breadth ratio = 0.1. Outer diameter of the runner = 2 X inner diameter of runner. The thicknesses of vanes occupy 10% of the circumferential area of the runner. Velocity of flow is constant at inlet and outlet and discharge is radial at outlet. Determine: i) Guide blade angle, ii) Runner vane angles at inlet and outlet. iii) Diameters of runner at inlet and outlet & iv) Width of wheel at inlet 7. Define the term ''governing of turbines”. Describe with a neat sketch the working of governor for Pelton wheel turbine. 8. A four-stage centrifugal pump has four identical impellers keyed to the same shaft. The shaft is running at 400rpm and the total manometric head developed by the multistage pump is 40m. The discharge through the pump is 0.2m3/s. The vanes of each impeller are having outlet angle as 450. If the width and diameter of each impeller at outlet is 5cm and 60cm respectively. Find the manometric efficiency. 1 of 1 |''|'||||''|''||'|'| R10 Code No: R21021 SET - 2 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2014 FLUID MECHANICS AND HYDRALICS MACHINES (Com. to EEE, ME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks 1. A U-tube containing mercury has its right limb open to atmosphere. The left limb is full of water and is connected to a pipe containing water under the pressure, the centre of which is in level with the free surface of mercury. Find the pressure of water in the pipe above atmosphere, if the difference of level of mercury in the limbs is 5.08cm. 2. Distinguish between a) Steady and unsteady flow. b) Uniform and Non-Uniform flow. c) Compressible and Incompressible flow. 3. a) Define Hydraulic Gradient Line and Total Energy Line. Represent HGL and TEL for real and ideal fluids in a pipe flow of varying cross section. b) A Pitot tube was used to measure the quantity of water flowing in a pipe of 0.30m diameter. The water was raised to a height of 0.25m above the centre line of pipe in the vertical limb of the tube. If the mean velocity is 0.78 times the velocity at the centre and coefficient of Pitot tube is 0.98, find the discharge in the pipe line. The static pressure head at the centre of the pipe is 0.2 m. 4. A jet of water having a velocity of l5m/s strikes a curved vane which is moving with a velocity of 5 m/s in the same direction as that of the jet at inlet. The vane is so shaped that the jet is deflected through 1350. The diameter of jet is l00mm. assuming the vane to be smooth find force exerted by the jet on the vane in the direction of motion, power exerted on the vane and efficiency of the vane 5. Discuss the relative merits and demerits of hydropower as compared to other power sources 6. A Pelton wheel turbine develops 9000kw under a head of 300m. The turbine speed is 550rpm and ratio of jet diameter to wheel diameter is 1/10. The hydraulic, volumetric and mechanical efficiencies are 0.98, 0.95 and 0.92 respectively. The speed ratio is 0.46 and coefficient of velocity is 0.98. Calculate the number of jets to be provided. 7. Define the terms unit power Unit speed and unit discharged with reference to hydraulic turbine. Also derive expressions for these terms. 8. A centrifugal pump discharges 1200 lit/minute against a head of 16.5m when the speed is 1500 rpm. The diameter of the impeller is 35cm and the power required is 6hp a geometrically similar pump of 45cm to run at l750rpm. Assuming equal efficiencies, find: i) The head developed ii) The discharge and iii) Power developed by the 45cm pump. 1 of 1 |''|'||||''|''||'|'| Code No: R21021 R10 SET - 3 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2014 FLUID MECHANICS AND HYDRALICS MACHINES (Com. to EEE, ME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks 1. a) Explain the fluid property vapour pressure. Give its significance in Engineering. A body weighing 450N with a flat surface area of 0.033m2 slides down lubricated inclined plane making a 300 angle with the horizontal. For viscosity of 0.2 N-s/m2 and body speed of 3m/s, determine the lubricant film thickness. b) What is the difference between U - tube differential monometer and inverted U - tube differential manometer? 2. What are the surface and body forces associated with fluid flow? How are they incorporated in Euler’s equation? 3. a) Derive the Darcy-Weisbach equation for friction head loss in a pipe b) An oil of relative density 0.90 flows through a vertical pipe of diameter 20 cm. The flow is measured by a 20 cm x 10 cm venturimeter. The throat is 30 cm above the inlet section. A differential U-tube manometer containing mercury is coefficient of discharge is 0.99. What is the manometer reading for a flow of 50lit/sec? 4. A jet of water having a velocity of 30m/s strikes a series of- radial curved vanes mounted on a wheel which is rotating at 200 rpm, The jet makes an angle of 200 with the tangent to the wheel at inlet and leaves the wheel with a velocity of 5m/s at an angle of 130 0 to the tangent to the wheel at outlet. Water is flowing from outward in a radial direction. The outer and inner radii of the wheel are 0.5m and 0.25m respectively. Determine vane angles at inlet and outlet. Work done per unit weight of water and efficiency of the wheel. 5. Write short notes on : a) Load factor b) Utilization factor c) Capacity factor 6. Differentiate between : i) Impulse and Reaction turbines ii) Radial and Axial flow Turbines iii) Inward and Outward Radial flow turbines iv) Kaplan and Propeller turbines 7. Define specific speed of a turbine and derive an expression for the specific speed 8. A single acting reciprocating pump running at 60 rpm delivers 0.53m3 of water per minute. The diameter of the piston is 200mm and stroke length 300mm. the suction and delivery heads are 4m and 12m respectively. Determine i) Theoretical discharge ii) Coefficient of discharge iii) Percentage slip of the pump iv) Power required to run the pump 1 of 1 |''|'||||''|''||'|'| Code No: R21021 R10 SET - 4 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2014 FLUID MECHANICS AND HYDRALICS MACHINES (Com. to EEE, ME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks 1. a) What is Kinetic Viscosity? Why is it so called? Give its dimensions and units. If a certain liquid has Viscosity 0.1548 N-s/m2 and Kinetic Viscosity 1.76×10 -4 m2/s. What is its specific gravity? b) Define gauge pressure, vacuum pressure and absolute pressure. Indicate their relative position on a chart. Convert a pressure head of 18m of water into i) Meters of oil of specific gravity 0.750 ii) Meters of mercury of specific gravity 13.6. 2. a) Classify and explain the types of fluid flow. b) What are the applications of continuity equation? Derive the continuity equation from fundamentals 3. a) Define ‘Hydraulic gradient line’ and ‘Total energy line’. The cross section of a pipe carrying a given discharge is suddenly enlarged. What would be the ratio of the two diameters of the pipe if the magnitude of the loss of head at this change of section is same irrespective of the direction of flow? Assume CC = 0.64. b) Determine the throat diameter of a venturimeter for installation in a100mm diameter pipeline carrying oil of sp. Gravity 0.87. The maximum range of available oil - mercury differential gauges is 0.5 m of mercury deflection. Find the maximum throat diameter which would show full gauge deflection when the rate of flow is 20 litres per second. Assume Cd= 0.984 4. A jet of diameter 150mm strikes a flat plate normally with a velocity of 20 m/sec. the plate is moving with a velocity of 5 m/sec in the direction of the jet and away from the jet. Find i) The force exerted by the jet on the plate ii) Work done by the jet on the plate per second. 5. Briefly explain the classification of hydro electric power plants 6. What are the purposes served by a draft tube? What is efficiency of the draft tube? Derive the expression for the efficiency of the draft tube. 7. What is a surge tank? What ate the purposes served by it? Briefly explain the types of surge tanks. 8. Find the number of pumps required to take water from a deep well under a total head of 89m. All the pumps are identical and are running at 800 rpm. The specific speed of each pump is given as 25 while the rated capacity of each pump is 0.l6 m3/s. 1 of 1 |''|'||||''|''||'|'|