Lab Equipment and Safety Procedures
advertisement

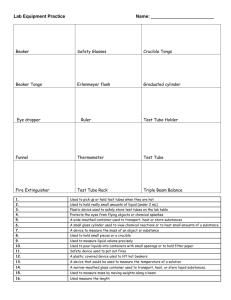
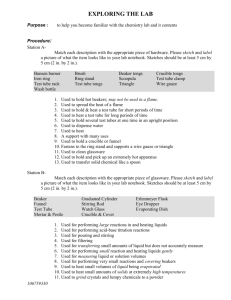
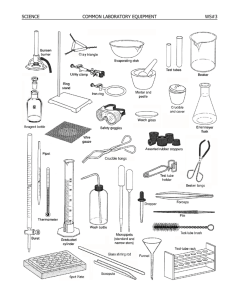
Lab Equipment and Safety Procedures Yes, you should take notes! Beaker Used to measure approximate liquid volumes Beakers are the most versatile glassware in the lab and can be used for just about anything. The volume graduations on beakers should be used only for "ballpark" estimates. A cylinder container used to hold liquids Clamp Used to close hoses by pinching them together Used during filtrations Clamps rubber tubing to stop the flow of liquid Wire Gauze Used as a support for beakers when placed across a support ring Allows for more even and gradual heating of glassware Test Tube Measures small amounts of liquids Come in different lengths and widths to serve various needs. They are typically used by chemists to hold different materials, usually liquids, during chemical experiments Test Tube Holder Used to hold test tubes for short periods of "gentle" heating Use a test tube holder to grasp hot test tubes Tongs These tongs are used for picking up crucibles and crucible covers Used to carry an evaporating dish May also be used to hold a piece of Mg when igniting it Bunsen Burner Before lighting, check to be sure barrel is turned so no oxygen is getting to flame Rubber tubing attaches to gas valve Adjust flame height after lit Gas valve perpendicular=OFF Gas valve parallel=ON Tie back hair and loose clothing TURN OFF WHEN NOT BEING USED Used for heating, sterilization, and combustion Striker/Sparker Used to light a bunsen burner Not a toy noisemaker or “sparkler” during lab Hot Plate Plug into electrical outlet TURN OFF AND UNPLUG WHEN NOT IN USE Increase hotplate temperature slowly so glass does not burst Used to heat liquids in glass beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks, and metal pans Ring Stand The base supporting the iron ring Test Tube Rack Device to hold test tubes in place while you can't hold them Divots for holding test tubes in upright position Pegs for drying of test tubes in upside down position Beaker Tongs Large, curved tongs Special tongs used for handling hot glassware Know the proper way to use beaker tongs Stirring Rod Glass – used for stirring in beakers and flasks Used to aide in dissolving a solute in a solvent, mixing Be sure to wash before using to mix different mixtures – you could cause contamination Wash Bottle Used for rinsing solids out of a container when filtering Filled with distilled water Plastic, with plastic straw Squeeze gently to rinse glassware Evaporating Dish This dish is used to recover dissolved solids by evaporation. While it can be heated, it should not be used for "strong" heating. Heat gently to avoid spattering Dropper Can be glass with rubber bulb on end or plastic (disposable) Squeeze air out of bulb Place end in liquid and release rubber bulb to fill dropper with liquid To dispense, squeeze bulb gently RINSE THOROUGHLY BETWEEN THE TRANSFER OF DIFFERING CHEMICALS TO ELIMINATE CONTAMINATION Funnel When lined with filter paper, used to filter suspended solids from a liquid. Used for filtration Filter paper- fold in half, fold in half again, open b/w 1 and 3, place in filter Slightly dampen filter with solvent to hold in place tube with a conical opening that is used to pour liquid through a smaller opening Filtration Setup Scoopula (Yes, this is a real scientific term!) Used to transfer solids from their original container to a scale for weighing A utensil used primarily in chemistry labs to transfer solids: to a weigh paper for weighing, to a cover slip to measure melting point, or to a watch glass from a flask or beaker through scraping Iron Ring When attached to the ring stand, this iron ring is used to support glassware above the lab table Supports beakers on the ring stand so that they may be heated Erlenmeyer Flask Is a widely used type of laboratory flask which has a conical base with a cylindrical neck It is used to contain reaction solutions. Used in filtrations and distillations Rubber Stopper Holds thermometer in place while measuring temperature Used to seal glassware to prevent contaminants from entering Graduated Cylinder Water is polar, glass is polar. The water “sticks” to the glass and causes the liquid being measured to look like a ‘u’ (meniscus) Read from bottom of MENISCUS A tall glass cylinder with a range of calibrated markings that is used for visually MEASURING THE VOLUMES OF LIQUIDS PLASTIC COLLAR USED TO READ MEASUREMENT OF LIQUID Used to make accurate measurements of liquid volumes. The bumper ring on larger cylinders is to prevent breakage if tipped over. Keep it near the top. Well Plate Plastic, several wells Used for microchemistry Use droppers to transfer liquids Timer Keep track of how long it takes a reaction to take place Measure in seconds Thermometer Measures temperature, glass tube with alcohol or mercury CBL, electrical temperature gauge. Place gauge in liquid and get a digital readout. CBL will not break as easily Hot Glove Move hot items Big, orange Safety Glasses Must be on at ALL times during a lab - not just when your teacher patiently reminds you Found in drawers at lab stations Triple Beam Balance Measures mass – amount of matter in an object Matter – takes up space Be sure all weights are pushed completely to the left Start with highest weight and work your way down You want the beam to balance in the middle of the arm Weighing paper – zero with paper on plate, measure from there (begin with too little, easier to add more) Watch Glass A circular, slightly concave piece of glass used in chemistry as a surface to evaporate a liquid, or as a cover for a beaker Cleaning Brushes Used to clean glassware Do NOT poke the wire brush into bottom of glassware – it will break Ceramic Triangle Place on iron ring to hold funnel Used for heating or cooling evaporating dish Used to hold a crucible while the crucible is heated Proper Setup for the Heating of a Crucible A Few extra reminders… Kill jar – labeled container for disposing of chemicals that cannot be rinsed down the sink If you have extra reagent, do NOT return to container. This will cause CONTAMINATION of the entire container. Dispose of it properly. If glassware is broken at your lab station, please CALL YOUR TEACHER. DO NOT ATTEMPT TO CLEAN IT UP YOURSELF! Safety Procedures Please COPY and KNOW these!! 1. Wear safety glasses at all times in the laboratory. 2. Wear sensible clothing. 3. Do not perform any unauthorized experiments. 4. Know exactly what you are supposed to be doing in a laboratory experiment. 5. Do not eat or drink in the laboratory. 6. Keep the laboratory clean at all times. 7. Dispose of waste and excess materials in the proper manner. 8. Light bunsen burners only when needed. 9. Avoid touching hot objects. 10. Report all accidents to your instructor promptly!