Using Social Media to Rank Online Search - HSLS
advertisement

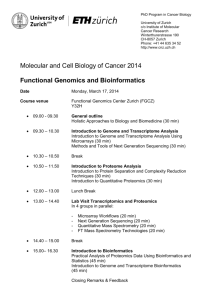
Flying to the Top, One Tweet at a Time: Using Social Media to Rank Online Search Results Robyn B. Reed, MA, MLIS Co-authors: Carrie L. Iwema, PhD, MLS Ansuman Chattopadhyay, PhD Health Sciences Library System University of Pittsburgh Molecular Biology Information Service Workshops Consultations Website Software Licensing Online Bioinformatics Resources Collection (OBRC) http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/obrc/ Resources displayed by keyword ranking http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/obrc/ Challenges: Many tools exist and increasing in number User may retrieve several resources Common question – How do I know which one(s) to use? Goal: Provide up-to-date ratings of most highly regarded resources in bioinformatics Objectives: Using social media, design ranking system of OBRC resources Determine if social media results reflect opinions of bioinformatics experts Why use the social media?? • No official rankings of bioinformatics tools • Opinions of several people • Social media data has many applications http://beta.socialguide.com/ Methodology Wrote 5 research questions Common bioinformatics queries Each question listed 3 possible resources to accomplish that task Methodology Research questions Experts (2) independently ranked resources Resources were ranked using social media data Methodology – Social Media Ranking Sources used for data collection Google Blogs Google Discussions Google Discussions includes • Forums • Groups • Comments www.google.com Methodology – Data Sources Twitter considered and removed • 50% of the resources had zero Tweets • 20% captured non-specific Tweets Facebook not included • Concern over private settings Methodology – Social Media Ranking Searched “all time” Optimized for most accurate retrieval • Resource in quotes • Increased specificity, decreased noise • Fewer hits Methodology – Search Filter • Put all OBRC resources in bioinformatics context • Automate the searches [(“ucsc genome browser”) AND ( bioinformatics | genome | genetics | genomics | computer | algorithm | software | server | database | computer model | protein | proteomics | proteome | gene | DNA | RNA | sequence | alignment | interactions | structure | modeling | prediction | biochemistry | molecular biology | systems biology | computational biology)] Example of search of UCSC genome browser Results Bioinformatics Tools CPHmodels Blogs + Discussion Raw Numbers Social Media Expert 1 Expert 2 Rank Rank Rank 49 2 2 2 17 3 3 3 228 1 1 1 4 2 2 2 728 1 1 1 Primer Design Assistant 0 3 3 3 DIANA-microT 12 1 1 2 9 2 2 3 3 3 3 1 1494 1 1 3 8 3 3 1 63 2 2 2 3070 1 3 2 56 3 2 3 928 2 1 1 3-D protein prediction ESypred3D SWISS-MODEL IDT SciTools PCR primer design Primer3 microRNA target design miRGator siRNA target finder Ambion ClustalW multiple sequence alignment ECR Browser Tcoffee Ensembl genome browsers NCBI Map Viewer UCSC Genome Browser Results Bioinformatics Tools CPHmodels Blogs + Discussion Raw Numbers Social Media Expert 1 Expert 2 Rank Rank Rank 49 2 2 2 17 3 3 3 228 1 1 1 4 2 2 2 728 1 1 1 Primer Design Assistant 0 3 3 3 DIANA-microT 12 1 1 2 9 2 2 3 3 3 3 1 1494 1 1 3 8 3 3 1 63 2 2 2 3070 1 3 2 56 3 2 3 928 2 1 1 3-D protein prediction ESypred3D SWISS-MODEL IDT SciTools PCR primer design Primer3 microRNA target design miRGator siRNA target finder Ambion ClustalW multiple sequence alignment ECR Browser Tcoffee Ensembl genome browsers NCBI Map Viewer UCSC Genome Browser Results Bioinformatics Tools CPHmodels Blogs + Discussion Raw Numbers Social Media Expert 1 Expert 2 Rank Rank Rank 49 2 2 2 17 3 3 3 228 1 1 1 4 2 2 2 728 1 1 1 Primer Design Assistant 0 3 3 3 DIANA-microT 12 1 1 2 9 2 2 3 3 3 3 1 1494 1 1 3 8 3 3 1 63 2 2 2 3070 1 3 2 56 3 2 3 928 2 1 1 3-D protein prediction ESypred3D SWISS-MODEL IDT SciTools PCR primer design Primer3 microRNA target design miRGator siRNA target finder Ambion ClustalW multiple sequence alignment ECR Browser Tcoffee Ensembl genome browsers NCBI Map Viewer UCSC Genome Browser Conclusions: This system can be used to determine highly regarded tools Explain that rankings are subjective; try the top 3-5 resources Provides patron with a starting point when using the OBRC Limitations • Quotation marks can be limiting if resource >1 word • Very small part of the total social media • “Negative” discussion about a resource Future Directions • Test > 3 bioinformatics tools/category • Increase number of expert ratings • Test applicability of system in areas other than bioinformatics Special thanks to: Project collaborators and experts: Ansuman Chattopadhyay, PhD Carrie Iwema, PhD, MLS Research and academic advisors: Nancy Tannery, MLS Rebecca Crowley, MD, MS Funding from the Pittsburgh Biomedical Informatics Training Program NLM Grant 3 T15 LM007059-23S1 Thank you! Any questions? Robyn Reed rreed@pitt.edu