Assignment
advertisement

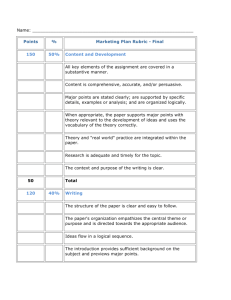
How an <emma> Partnership with the Library benefits First-year Composition University of Georgia Christy Desmet, Department of English (cdesmet@uga.edu) Ron Balthazor, Department of English ( rlbaltha@uga.edu ) Caroline Cason, University Library ( ccason@uga.edu ) Kristin Nielsen, University Library ( knielsen@uga.edu ) A Natural Alliance “In an informationrich world where human attention is the scarce commodity, the library’s business is orchestrating human attention structures.” Richard A. Lanham Working Together FYC offers all classes a computer orientation. Many instructors arrange for a librarian to conduct a personalized orientation for their classes. – Visit the FYC Computer Orientation Background: Citation Analysis Cornell Study – Undergraduate research Electronic Thesis and Dissertation study at UGA – Graduate research Cornell University Study Analyzed Cornell Economics 101 papers, 1996-2001 Between 1996-2000: – Citations to books 30% to 16% – Citations to newspapers 7% to 19% – Citations to Web sites 9% to 22% Cornell University Study The professor verbally stressed the importance of using scholarly resources All students attended a library instruction session taught by a librarian Result: “…little (if any) effect on improving the scholarly component of research papers” Cornell University Study In 2001, the professor added written guidelines to the assignment: – At least five sources had to be “published, scientific (peer-reviewed or university press) articles or pre-prints” – Students were warned that TAs would check all citations for accuracy and quality Result: The number of scholarly resources (books and journals) that students cited returned to 1996 levels “Bibliometrics…has been used extensively for studying the publication record of research faculty and their departments, and also to understand how scholars communicate through their publications. There has been very little application of bibliometric research to undergraduate research papers. The principal cause of this problem is that research papers are returned to the student after grading, leaving no repository of their work” (Davis & Cohen 2001). Graduate Students University of Georgia study of citations in electronic theses and dissertations – “… developed for evaluating the ‘fit’ of the UGA Libraries’ collections with the needs of their patrons.” Used electronic copies of dissertations in ETD database for citation analysis Acted as template for methodology used in <emma> study Where Research Meets Pedagogy Our study’s basic research questions: – What types of information are cited by students (e.g., websites, newspaper articles, journal articles, books)? – Does the University of Georgia Library own these items? – What was the method of access, print or electronic, for sources other than websites? Citation in Pedagogical Context Further research questions: – How did the teachers’ wording of her assignment affect students’ understanding of research? – What kinds of sources do teachers’ marginal and end comments suggest are valued most highly by the First-year Composition Program? – Is there a correlation between numbers of citations and grades? – Does formal intervention of a librarian improve the quality of students’ sources? Introducing <emma> Hardware/Software How it works How it is used in the classroom Demo Value Added <emma> concatenates assignment and essay with comments . . . Assignment-Comments-Evaluation . . .and with the departmental grading rubric. Pedagogical Implications <emma> allows teachers and students to see whether essays have addressed the topics in the terms set out by the written assignment. <emma> allows teachers and students to see whether teachers are grading according to the assignment’s criteria. Advantages for Teachers and Students Encourages selfconsciousness about teaching and writing; Helps both groups see writing assignments through the same lens; Allows both groups to see student essays with a unified pedagogical context. Assignment Essay Comments + Rubric <emma>’s Advantages for Citation Research Creates a large database of digital essays; Large Database and Storage Includes permanent storage for essays; Data Selection Uses XML tagging for fast, easy extraction of data; Growing Research Data Set Solicits Human Subjects permission for research on data set. Compiling the Data Questions and Issues –Accuracy of the citations –Defining the resource categories Citation Analysis: Case Studies Case Study 1: Fall 2003 English 1101, English Composition I Two sections, same instructor Final research project No library instruction session Case Study 1 Final project requirements: Analyze one aspect of an issue covered by essays in textbook Research the issue Write an argumentative paper Case Study 1 Possible topics: – Partial-birth abortion – Euthanasia/Right to Die – Affirmative action – Sex education – Immigration – Genetic engineering – Obesity in children – Homosexuality and Christianity Case Study 1 Assignment wording: “Identify a pool of good, credible research resources for your particular issue. The [course textbook] website…will help you. Also, use Lexis-Nexis and other library resources.” Breakdown of Citations 2% Books 1% Magazines 3% Newspapers 0% Journals 51% WWW 36% Textbook Books Magazines Journals Newspaper Textbook WWW Breakdown of Web Citations 25% Com/Net 36% News 5% Student Papers 8% Educational News Govt Org Educ Student Com/Net 6% Government 20% Organizations Fall 2003 Out of 153 works cited in the two sections, seven were owned by the library: – Two bibles – One magazine article accessed through Academic Search Premier – Four newspaper articles, three of which were accessed through Lexis/Nexis Case Study 2 – Fall 2004 Assignment: “For your first writing assignment, carefully craft an essay of 1000 to 1500 words on one of the topics below. You should include at least three secondary sources.” Received library instruction in handson lab prior to writing first draft Results Comparison of Draft versus Final version of paper Does a “library instruction intervention” have an effect? Influence of review process on revisions Resources Cited -- Draft vs Final 25 20 15 Draft Final 10 5 0 Bo ok e in az g a M al rn u Jo w Ne er ap sp W W W go v W W W g or W W W u ed W W W w ne s W W W m co et /n O er th Case Study 1 & 2 Compared Fall 2003 -- Types of Sources 2% 1% Fall 2004 (Final) -- Types of Sources 6% 9% 18% Books 39% 16% Magazines Magazines Journals Journals New s New s 54% 11% Textbook WWW 33% Books Textbook WWW 11% 0% Fall 2003 (no instruction) versus Fall 2004 (instruction) – types of sources cited Fall 2003 / 2004 Comparison – websites 2004 Websites Cited 2003 Websites Cited 25% 28% 36% Com 5% 8% 6% 20% News Govt Org Educ Student Com/Net 35% Com 0% 1% News Govt Org Educ Student Com/Net 16% 20% Similar amount of .com/.net and news websites No student paper sites in 2004 Will the library instruction “stick” over the course of the semester? Comparison of Assignment 1 & 2 2004 Assignment 1 (Final) -- Types of Sources Assignment 2 (Draft) -- Types of Sources 8% 13% 6% 18% 9% Books Magazines 6% Journals 54% New s 11% Textbook 49% 15% WWW 0% 11% Books Magazines Journals New s Textbook WWW Other 0% In draft stage, still using GALILEO resources but not as many Higher number of “books” – these were citing online edition of Encyclopedia Britannica New category – “Other” to include citations to media like DVDs Fewer citations overall and far fewer magazines and journals. Will this trend continue? FYC Competency Standard “Incorporates evidence from outside sources smoothly, appropriately, and responsibly” Partnership Possibilities? – Drafting practical guidelines for writing an effective assignment – Planning library instruction content to help meet course competency outcomes – Timing library sessions to work with the course assignments – Teaching correct citation style Additional areas of study Longitudinal studies – “Recidivism” rate over course of semester – Tracking trends over years Assignments – Influence of assignment specificity – Influence of library instruction – Influence of review process Library related questions – Ownership – are students using the collection – Method of access – print versus online Web research – What types of information are students using from the Web? – What sources do they cite? (.edu, .com, etc.) Other ideas? The End