Cell Membrane
advertisement
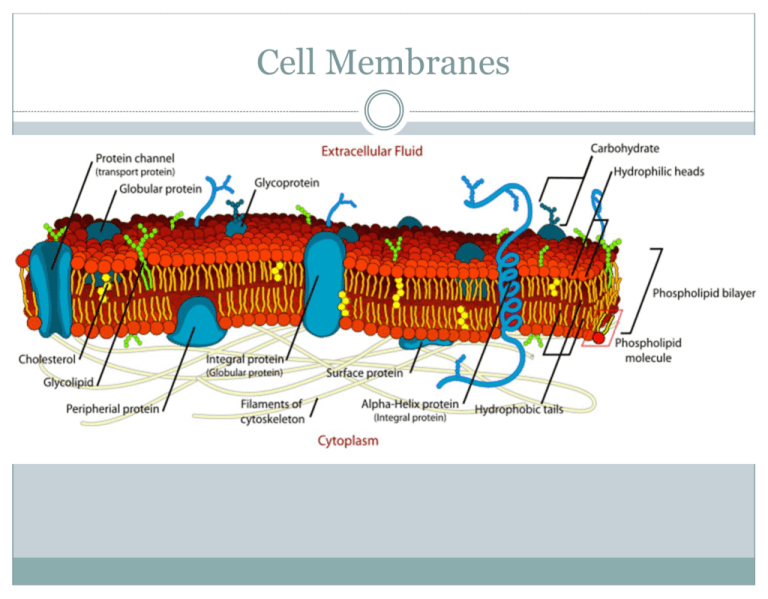
Cell Membranes PLO’s B9 - analyse the structure and function of the cell membrane Identify molecules in the membrane and how they contribute the characteristics of the membrane Describe hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions CELL MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Fluid Mosaic Model: • Plasma membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer with protein molecules embedded in it • Phospholipids give a “fluid” consistency • Proteins form the “mosaic” http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Cell_membrane_detailed_diagram_edit2.svg: http://www.bioteach.ubc.ca/Bio-industry/Inex/ Phospholipids Phosphate end is polar and hydrophilic (attracted to water) Fatty acid chains are non polar and hydrophobic http://bioinfo.bact.wisc.edu/themicrobialworld/Structure.html Since the membrane is surrounded by water inside and out, the phospholipids arrange themselves like this: Membrane Proteins Peripheral proteins - on the inner or outer surface Integral proteins - extend right through Many of the proteins are free to move around laterally within the membrane Membrane Protein Functions Channels to allow materials in and out of the cell Transport proteins that carry specific molecules in and out of the cell Receptors for hormones, growth factors and other chemicals that bind to the outside of the cell Enzymes to catalyze reactions in the cell Connecting cells to other cells at junctions Ex. Gap junctions (allow passage of materials from cell to cell), tight junctions (connect cells together) Carbohydrates Carbohydrate chains are attached to some lipid and protein molecules (glycolipids & glycoproteins) Usually attached to the outer surface These are different in each individual Cell recognition - “ID cards”, enable the body to recognize its own cells Cholesterol Embedded in the membrane Helps to maintain the fluidity and flexibility of the membrane Helps to hold the proteins in place Reduces permeability of the membrane Membrane Permeability Cell membranes are differentially (selectively) permeable Certain substances can move through freely (water, gases, small molecules, uncharged (non-polar) molecules Others cannot, and require special processes to get through (larger molecules, ions)







