3/25 Daily Catalyst Pg. 98 Feedback Loops
advertisement

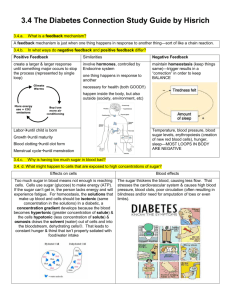
3/25 Daily Catalyst Pg. 98 Feedback Loops 1. Give an example of positive feedback in the human body. 2. What type of tissue functions to bind other tissues. 3. How is vasodilation and vasoconstriction part of thermoregulation? 3/25 Class Business Pg. 98 Feedback Loops Quiz #25 on Friday Report card extra credit Tutoring available after school 3/25 Agenda Pg. 98 Feedback Loops Daily Catalyst Class Business Thermoregulation essay Feedback Loops gone wrong! Homework: Gills in Fish and Lungs in humans Question Reptiles are ectotherms and cannot self regulate their internal body temperatures. Because of this, many reptiles must move around to find warm or cool areas. Dan the reptile has just woken up and is freezing, even though he's pretty fat. How could he become warm again? A: The hypothalamus sends impulses to his sweat glands. B: The hypothalamus sends impulses to his muscles to make him shiver C: He gets up and walks to a rock in sunlight D: He knits himself a sweater Essay Prompt Answer key Feedback Loops Negative feedback loops: communication loop between the body and the brain. Blood Clots In homeostasis: Why do not bleed to death every time we cut ourselves? Blood Clots! Blood Clots Key Point #1: Endothelium is damaged (Lines the cavities and organs) Key Point #2: Clotting factors convert fibrinogen into FIBRIN A protein Forms the clot How is blood clotting an example of positive feedback? Key Point #3 (on your own) Blood Clotting Does this cascade go as planned every time?? NOPE! Key Point #4: Hemophilia Caused by – Prevents the body from making clots Can bleed to death or have internal bleeding easily Blood Clotting What happens if there is TOO much positive feedback? Lack of homeostasis Key Point #5: Thrombus A blood clot that forms within a blood vessel and prevents the flow of blood. Can be spontaneous Diabetes In negative feedback, works to inhibit the original stimulus. At homeostasis, blood glucose is around 90 mg/100 mL To maintain homeostasis, insulin is released from the pancreas to lower blood sugar levels BY taking sugar into the cells for cellular respiration (remember glycolysis) Our body is not always at homeostasis. Diabetes Key Point #6: Diabetes is caused by lack of insulin or decrease in response to insulin in specific tissues. Key Point #7: When there is the stimulus of high glucose levels, the body, by negative feedback works to lower the blood sugar levels. Diabetes Key Point #8: Type I Key Point #9: Type II In summary The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is another good example of a negative feedback mechanism. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change . In turn, the control center (pancreas) secretes insulin into the blood effectively lowering blood sugar levels. Once blood sugar levels reach homeostasis, the pancreas stops releasing insulin. Key Point #9: How is diabetes an example of negative feedback loops? Work Time Complete the following problems on page#98 in your notebooks. Will be checked tomorrow! 1,4.7,8,9,10 and evolution connection.