Rectus Femoris
advertisement

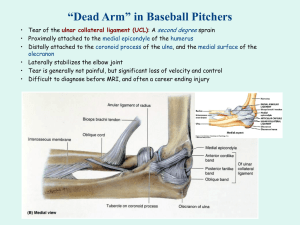
OTA 106 Knee and Foot Joint By Kaylee, Jessica and Travis Bones Femur: o Lateral condyle o Medial condyle o medial epicondyle o Lateral epicondyle o Intercondylar fossa Patella o Left or right Bones cont.. Tibia: o Lateral condyle o Medial condyle o Tibial tuberosity o Intercondylar eminence o Medial malleolus o Fibular notch Fibula: o Head o Lateral malleolus Foot Tarsal (or tarsus) bones: The Circus Needs More Interesting Little Clowns o Talus o Calcaneus o Navicular o Cuneiforms: Medial (first) o Cuneiforms: Intermediate (second) o Cuneiforms: Lateral (third) o Cuboid Foot cont… Metatarsal bones: o Numbered 1-5 (big toe side is #1) Phalangeal bones: o Toes numbered 1-5 (big toe is #1) o Proximal o Middle (Intermediate) o Distal * Big toe only has proximal and distal phalanx Surface Anatomy • Knee: -Popliteal fossa Surface Anatomy • Knee -Patella Surface Anatomy • Knee -Medial head of Gastronemius -Lateral head of Gastronemius Surface Anatomy • Knee -Soleus Surface Anatomy • Knee -Semimembranosus tendon -Semitendinosus tendon Surface Anatomy • Knee -Biceps femoris tendon Surface Anatomy • Knee -Vastus laterailis -Vastus medialis Surface Anatomy • Foot -Calcaneal tendon (Achilles tendon) Surface Anatomy • Foot -Fibularis longus tendon -Fibularis brevis tendon Surface Anatomy • Foot -Lateral malleolus -Medial malleolus Surface Anatomy • Foot -Extensor digitorum longus tendon: -Extensor halluces longus tendon: -Extensor halluces brevis tendon: Surface Anatomy • Foot -Tibialis anterior tendon Surface Anatomy • Foot -Site of dorsalis pedis Pulse site on foot Surface Anatomy • Great Saphenous vein Surface Anatomy • Arches -Longitudinal Arch -Lateral longitudinal arch -Medial Longitudinal arch -Transverse arch Rectus Femoris (11a) Origin: Anterior inferior iliac spine Insertion: Patella via the quadriceps tendon Action: Extension at the knee and flexion at the hip Vastus Medialis (11b) O: Linea Aspera of femur I: Patella via quadriceps tendon and then tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament A: Extension at knee Vastus Laterals (11c) O: Intertrochanteric line and linea aspera of the femur I: : Patella via quadriceps tendon and then tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament A: Extension Vastus Intermedius (11d) O: Anterior 2/3 and lateral shaft of femur I: Patella via quadriceps tendon and then tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament A: Extension Biceps Femoris (18a and 18b) O: Long head-Ischial tuberosity, Short head- linea aspera of femur I: Head of fibula and lateral condyle of tibia A:Long head- Extends hip and flexes knee. Short head: Flexes knee and laterally rotates hip and laterally rotates flexed knee Semimembranosus (17) O: Ischial tuberosity I: Posterior medial condyle of tibia A: Flexes knee, medially rotated flexed knee and extends hip Semitendinosus (16) O: Ischial tuberosity I: Proximal medial shaft of tibia at Pes Anserinus tendon A: Flexes knee. Medially rotates flexed knee and extends hip Tibialis Anterior (19) O: lateral condyle, superior lateral 2/3 surface of tibia, interosseous membrane I: Medial inferior surface of the 1st cuneiform and base of 1st metatarsal A:Dorsiflexes ankle, inverts foot, supports longitudinal arch Fibularis Longus (22) O: Head, superior 2/3 of lateral fibula I: Plantar surface of base of 1st metatarsal and 1st cuneiform A Everts foot, weakly plantar flexes ankle, supports transverse Fibularis Brevis (23) O: Lateral inferior 2/3 of fibula I: Dorsal surface of tuberosity of 5th metatarsal metatarsal A: Everts foot, weakly plantar flexes ankle, supports transverse arch Gastrocnemuis (24a and 24b) O: Lateral head: Lateral condyle of femur. Medial Head: Superior to medial condyle of femur. I: Calcaneus via calcaneal tendon A:Plantarflexes ankle, flexes leg at knee Soleus O: Posterior head of fibula, posterior medial tibia I: Calcaneus via calcaneal tendon A: Plantarflexes ankle Ligaments: Knee o Anterior cruciate ligament o Transverse ligament Ligament: Knee cont.. o Tibial collateral ligament o Fibular collateral ligament o Posterior cruciate ligament Ligament: Knee cont… o Quadriceps femoris tendon o Patellar ligament Ligaments: Ankle/Foot o Long plantar ligament o Short plantar ligament o Plantar aponeurosis o Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring) Ligaments cont.… o Anterior tibiofibular ligament o Posterior tibiofibular ligament o Extensor retinacula o Interosseous membrane o Interosseous tibiofibular ligament Cartilage o Lateral Meniscus o Medial Meniscus Bursae o Prepatellar bursa (Subcutaneous) o Deep Infrapatellar bursa o Suprapatellar bursa o Subcutaneous infrapatellar bursa Nerves o Femoral nerve o Sciatic nerve o Tibial nerve o Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve o Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve Branches of the Femoral nerve Nerve cont… Femoral nerve: Roots: Rectus femoris L2-L4 Vastus medialis L2-L4 Vastus lateralis L2-L4 Vastus intermedius L2-L4 Biceps femoris L5, S1 &S2 Nerve cont… Tibial Nerve: Roots: Biceps femoris L5, S1 & S2 Semitendinosus L5, S1 & S2 Semimembranosus L5, S1 &2 Gastrocnemuis S1-2 Soleus S1-2 Nerve cont… Deep Fibular nerve: Roots: Tibialis Anteior L4 &5 Nerve cont… Superficial Fibular nerve: Roots: Fibularis Longus L5 & S1-2 Fibularis Longus L5 &S1-2 • Femoral Artery • Popliteal Artery • Anterior Tibial Artery • Posterior Tibial Artery • Tibial Artery • Dorsalis Pedis Artery Arteries Arteries • Fibular (Peroneal) Artery Arteries • Inferior Gluteal Artery Arteries • Lateral circumflex femoral artery • Medial circumflex femoral artery Veins • Femoral Vein • Great Saphenous Vein • Small Saphenous Vein • Anterior Tibial Vein • Posterior Tibial Vein • Dorsal Venous Arch Veins • Popliteal Vein • Fibular (Peroneal) Vein • Plantar Arch Vein Torn ACL Also called: Anterior cruciate ligament injury Athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball are more likely to get injured. The knee joint is located where the end of the thigh bone (femur) meets the top of the shin bone (tibia). This tear is more common in women responds differently to certain maneuvers such as jumps, sudden stops, pivoting and cutting. Recovering time may take six to nine months to return to full activity ACL reconstruction surgery right away after tear Physical therapy and/or occupational therapy following surgery is needed. Torn ACL In Conclusion o Remember the mnemonic The Circus Needs More Interesting Little Clowns for the foot bones o Torn ACL happen most often in women, however they can happen in men as well o For the patella, whichever way it leans when put down on a flat surface with the point pointed upwards is the side it belongs to o o Calcaneal tendon and Achilles tendon are the same thing Great saphenous vein is the longest vein in the body, running all the length of leg