International Trade Policy Trade Restrictions: Tariffs
advertisement

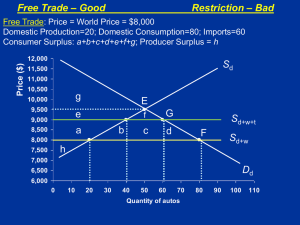
International Trade Policy Trade Restrictions: Tariffs Focuses on barriers to free trade Tariffs • Tariff – tax imposed on an imported/ exported of a good or service that crosses a national boundary. • Import tariff- Imposed on imports • Export tariff-Imposed on exports • Types of tariffs Ad valorem – % of value of import Specific – fixed amt per physical unit. Composite – combination of 1 and 2 Concept review • Consumer surplus – is the difference between what consumers pay and the value they receive. This is because, given a downward-sloping demand curve that shows what consumers will demand at different prices, what consumers end up paying (market price) is sometimes lower that what they were willing to pay. This is the consumer surplus. It is given as the area beneath the demand curve but above the market price. • Producer surplus – is the difference between the prices at which producers are willing to supply different quantities and the prices they actually receive. The surplus arises because producers are sometimes willing to supply at prices lower than the market price. It is given by the area between the market price and the supply curve. Partial equilibrium analysis of a tariff Effects of a tariff: • Consumption • Production • Trade • Revenue • Producer and Consumer surplus Effects on producer and consumer surplus • An Decrease in CC and Increase in PC Partial Equilibrium cost and benefits • Consumer and producer surplus used to measure costs and benefits • Deadweight losses - Net loss to society • Additional outlays for producers and loss to consumers from moving to lower indifference curves Rate of effective protection • Nations often impose lower tariffs on raw materials/inputs than on final commodities to encourage domestic processing and employment. • Appropriate measure of degree of protection is the effective rate of protection (g) • Formula for the effective rate of protection • g = t - ai t i 1- ai Where g = the rate of effective protection to producers of the final commodity t = nominal tariff rate on consumers of the final commodity ai = ratio of cost of imported input to the price of the final commodity without tariffs ti = nominal tariff rate on the imported input Tariff arguments • Creates revenue for government • Infant industry protection • Dumping – of foreign goods at low prices to kill off competition • Cheap labour – protection from cheap foreign labour • Strategic trade policy – ↑ national welfare at the cost of other nations • Externalities – protect industries from foreign competition in order for them to capture benefits of R&D Trade Policy • Analyze the most common reasons for countries to protect certain industries • Discuss the mechanisms used to provide protection Introduction • Since the end of WWII, average tariff rates around the world have fallen substantially • By 2001, average nominal rates were 4% in US, 5.1% in Japan, 3.9% in EU • However, all nations have higher levels of protection in particular industries they deem “sensitive” • In addition to tariffs and quotas, many countries provide generous subsidies to some of their agricultural producers, particularly among developed nations Main Arguments behind Trade Barriers 1 • Labor: Protection must be used against imports from countries where wages are much lower – Problem: Does not consider differences in productivity between different workforces: as productivity rises, so will wages Main Arguments behind Trade Barriers 2 • Infant industry: Developing countries have nascent industries that must be protected against competition from industrial countries – Assumes: (1) market forces do not allow for the development of a certain industry and (2) the industry has positive externalities—spillover benefits (valuable linkages to other industries or technologies) – Problems: (1) may increase inefficiency and result in negative linkage effects and (2) technological externalities are difficult to measure—which industries should be protected? Main Arguments behind Trade Barriers 3 • National security: Certain industries must be protected in order to guard national security (military security, cultural values) – Problems: (1) Vital mineral resources, for example, can be purchased cheaply abroad during peacetime; and (2) how to assess the effects of, say, U.S. television programs on Canadian culture? Main Arguments behind Trade Barriers 4 • Retaliation: Another country´s trade barriers must be countered with trade barriers – Problems: Although retaliation can provide an incentive for trade negotiations, it can also lead to escalating trade wars Other arguments behind Trade Barriers • Dumping: occurs when an exporter sells a product at a price below the one it charges in its home market