Coding - Amazon Web Services
advertisement

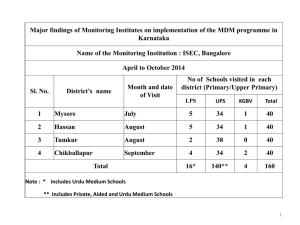
Coding and Billing in the ICD-10 Era Daniel A. Ostrovsky, MD FAAP FACP Chief Coding Consultant Duke Pediatrics Assistant Professor, Internal Medicine Pediatrics Duke University Medical Center Objectives Understand what an ICD-10 Code and CPT code are. Understand how to appropriately choose Evaluation and Management codes Understand how to appropriately document for chosen E&M codes What We Know Providers tend to underestimate the services they provide. Provider education on the “Business” of medicine is poor. Fear of auditing leads to under coding. Ambiguous guidelines lead to significant variance in how providers code for services. ICD-10 Designed to increase specificity of disease characterization and better characterize illness severity Better codified data means – More accurate identification of patients for research – More accurate characterization of provider case mix index – More accurate characterization of patient severity of illness – Better reimbursement and fewer claims denials ICD-9 vs. ICD-10 Anatomy of an ICD-10 Code What does this mean for you? Most providers currently use a relatively small code set of diagnoses regularly (approximately For most, selecting appropriate codes won’t seem 20-50) very different! For many codes in ICD-9 there is a single matching code in ICD-10. The biggest expansion of codes are in surgical or procedural specialties where site, location, laterality, and phase of care lead to lots of possible combinations. Reminders for Documentation ICD-10 specificity requires documentation of the following whenever possible/relevant – – – – – Acuity (acute or chronic) Site Specificity (anatomic location) Laterality (right, left, bilateral) Timing of Care (initial, subsequent, sequela) Manifestations ( “due to”- secondary manifestations of or external cause of a primary disease or injury) – Staging (eg. CKD stage II) – Status (History/Resolved/Remission) – Type (eg. DM II, bacterial/viral, simple/complex) ICD-10 “Extras” “Additional” Codes – Coding for tobacco exposure in most chronic respiratory conditions. – Coding for insulin usage in Type II DM – Coding external causes of injury “Combination” Codes – Eg. Mild intermittent asthma with exacerbation as opposed to mild intermittent asthma + wheezing – Type II DM with diabetic nephropathy, etc.. – Allergic rhinitis due to pollen Guidance for Code Selection In many cases, your documentation may be more specific than an available ICD-10 code. Choose the most specific! Don’t select “unspecified” options unless they are truly clinically unknown Pick age and sex appropriate codes Code all documented conditions that coexist at the time of the encounter/visit, and require or affect patient care treatment or management. Make sure those specific codes appear in your documentation Coding Uncertain Diagnoses Professional Coding Do not code diagnoses documented as “probable”, “suspected,” “questionable,” “rule out,” or “working diagnosis” or other similar terms indicating uncertainty. Rather, code the condition(s) to the highest degree of certainty for that encounter/visit, such as symptoms, signs, abnormal test results, or other reason for the visit. Hospital Coding If the diagnosis documented at the time of discharge is qualified as “probable”, “suspected”, “likely”, “questionable”, “possible”, or “still to be ruled out” or other similar terms indicating uncertainty, code the condition as if it existed or was established. Abnormal findings (laboratory, x-ray, pathologic, and other diagnostic results) are not coded and reported unless the provider indicates their clinical significance. Make sure these are part of your clinical documentation! Just like before… You should be DOCUMENTING as specifically as possible including relevant clinical detail Code the diagnoses you are managing and change/modify them as appropriate Keep problem lists updated Use appropriate codes that are age and sex appropriate Have documentation that supports the selected codes So what’s changed??? Now insurance companies have more specific diagnoses to decide whether to pay or deny your claim! Value Based Care is knocking at the door and failure to document and code thoroughly and specifically will have multiple downstream ramifications EMR’s have been a double-edged sword – Pulls data quickly together but is the data accurate? – Allows efficiency shortcuts but are they accurate? We all have to do our part! Excellent FREE Resources ICD-10 lookup by code or text word – http://www.icd10data.com/ CMS ICD-10 Pediatrics Resource Page – http://www.roadto10.org/example-practice-pediatrics/ ICD 10 Consult 2016 Free (Free App for mobile devices by Evan Schoenberg) Level of Service Coding/Billing Advanced Practice Providers – When Billing for Services Bill independently – The Supervising MD does not need to be in the office suite Bill in the supervising providers number when “sharing” the visit with the provider – only allowed for inpatient, hospital based clinic, or ED settings Very Important – Procedures, Critical Care, Consultations cannot be billed as shared. The APP must bill in his/her name if s/he is performing the procedure. Shared Visit Applies only to Inpatient, hospital based clinic, or ED When an APP and their supervising physician share a visit together, the service can be billed in either the APP’s number or the supervising physician’s number. The following are the guidelines to follow when billing a shared visit: A shared visit is a medically-necessary encounter with a patient where a physician and a qualified APP each perform and document a substantive portion of the evaluation and management visit, face-to-face with the same patient on the same date of service. Each provider, the MD/DO and APP, would perform parts of the service and personally document their parts. – One cannot document for the other. – Each provider’s documentation should be separate and patient specific. Resident/Fellows cannot share visits with APP’s CPT Current Procedural Terminology Standardized codes used for billing Codes available for every type of service provided Linked to ICD codes to justify services provided. Evaluation and Management Coding Elements History Physical Exam Medical Decision Making Face to Face Time Guidelines developed by CMS (Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services) Medical Decision Making Presenting problems Number and complexity Data Type of tests How they are reviewed Risk Multidimensional assessment Problem Points Eg. Bug bite, simple strain/sprain Eg. Asthma, ADHD, Eczema Eg. Asthma, Eczema Eg. AOM, SOB, Dizziness Eg. Headache, abdominal pain Add up the points to get a total. For example, a child being seen for an exacerbation of their asthma who also has allergic rhinitis which is well controlled on current therapy would garner 2 points for the asthma with exacerbation and 1 point for the allergic rhinitis giving a problem point total of 3. Data Points •You only get 1 point for ordering/reviewing multiple lab tests •You must document your personal read of an image, tracing, or specimen to get the points for an independent review Risk Four levels – Minimal 99212 – Low 99213 – Moderate 99214 – High 99215 Three Dimensions – Presenting Problems – Management Options – Diagnostic Procedures Choose the highest level of risk!!! Medical Decision Making Putting it All Together 99212 99213 99214 99215 Two out of three factors must meet or exceed the requirements for any given level of medical decision making. “The Table” History Exam MDM Face-to-face $$ 99211 Supervision Only Supervision Only Straightforward 5 minutes $16.82 99212 HPI: 1-3 elements “Problem Focused” 1 system “Problem Focused” Straightforward 10 minutes $33.50 99213 HPI:1-3 elements ROS: 1system “Expanded” 2-7 systems One element per system “Expanded” Low 15 minutes $55.94 99214 HPI: 4+ elements ROS: 2-9 System 1/3 P/F/SHx “Detailed” 2-7 systems At least one of the systems having at least 2 elements noted “Detailed” Moderate 25 minutes $84.29 99215 HPI: 4+ elements 8+ systems Single element from each acceptable “Comprehensive” High 40 minutes $114.00 Or Status of 3 active or inactive problems ROS:10+ system 2/3 P/F/SHx “Comprehensive” Billing for Time Counseling To be used when >50% of the visit is spent in teaching/counseling the patient in regard to the presenting issue. This is different then extended face to face time. Documentation Statement – eg. For 99213 “I spent 15 minutes face to face with the patient and family in which 10 minutes were spent counseling the parents in supportive care for URI and proper sleeping position.” Inpatient Time Based Billing Time spent must be ON THE PATIENT WARD Time includes only the EXCLUSIVE time spent in the management and care of the specific patient New Established Modifier 25 Used when a separate and identifiable procedure is performed. – Ex: Incision and Drainage of an abscess – Administration of vaccines in a non-hospital based clinic Used for a “Split visit” – Patient presents for a preventative visit but also has an acute issue which you manage and clearly document the separate issue. Need to be linked to an appropriate ICD code. Modifier 25 Examples I&D of Abscess 10060 $88 Joint Injection/aspiration 20600 $45 Wart Destruction 17110 $86 Removal of Cerumen impaction 69210 $40 Reduction Nursemaid’s elbow 24640 $93 Ganglion Cyst aspiration 20612 $48 Prolonged Services – 1st hour 99354 – Each additional 30 minutes 99355 $85 $84 Preventive Service Visits Well Child Checks have CPT codes based on the age of the patient – <1y – 1-4 y – 5-11y – 12-17y – 18-39y Need to be linked to an appropriate ICD-10 code. Z00.129 (Routine WCC without abnormal findings) You Code It!!! (Time Permitting) Hx: 5 elements ROS: At least 2 (GI, GU) P/F/SHx: 3/3 Detailed problem focused (99214) PE: 5 Systems with at least 2 elements per system Detailed problem focused (99214) MDM: Problems: New problem with no additional w/u (3 points)=Moderate Data Points: 0 Risk: Moderate- prescription drug management 2/3 moderate or higher so moderate MDM (99214) Code: 99214 Could be based on just H&P but MDM supports as well. Split Visit •URI documentation yields 99213 linked to acute upper respiratory infection, unspecified site J06.9 Modifier 25 •4 yo WCC •CPT 99392 linked to WCC •Procedures •Vision 99173 •Hearing 92551 •Developmental Screen 96110 Hx : 2 elements, ROS 2 systems Expanded Problem Focused (99213) PE: 2 systems Detailed Problem Focused (99214) MDM: Problems: Established problem stable or improving (1 point) Data: Reviewed Throat Cx (1 point) Risk: One self-limited problem Overall MDM minimal (99212) Code: 99212 2/3 meet requirements. Hx: 4 elements, PMHx,1 ROS Expanded (99213) PE: 2 organ systems with single element in each Expanded (99213) MDM: – Problem: 1 minor, selflimited problem (1 point) – Data: 0 – Risk: Low (OTC med) Overall MDM is straightforward (99212) Code: 99213 2/3 support the dx code chosen. Hx:4+Elements, ROS 2+, PMHx, FHx Detailed (99214) PE: 5 systems Detailed (99214) MDM – – – Problem: New problem with planned further workup (4 points) Data Points: culture sent (1 Point) Risk: Prescription drug management (moderate) Overall MDM: Moderate (99214) Procedure: I&D Code: 99214 Modifier 25 with procedure 10060 linked to cutaneous abscess of buttock L02.31 Hx: 4+Elements, ROS >10 PFSHx Comprehensive (99215) PE 8+ organ systems Comprehensive (99215) MDM Moderate Persistent asthma – Problem: Established problem worsening (2 points) Low – Data: Order CXR 1 point, personal review 2 points. 1 point for Pulse ox Total=4 points High – Risk: High Moderate Persistent asthma with acute exacerbation- No clear source for exacerbation. Not responding adequately to nebs here. Will require further management in ER for his severe sx. Overall MDM=High (99215) Procedure: nebs Code: 99215 modifier 25 procedure 94640 linked to Moderate persistent asthma with exacerbation J45.41 Hx: 4+ elements, 2+ ROS 2+, 2/3 PFSHx Detailed (99214) PE: 8+ systems Comprehensive (99215) MDM: – Problem: New problem without additional workup planned (3 points) – Data: UA/Ucx (1 point) – Risk: Acute illness with systemic sx. (moderate) Overall MDM: Moderate (99214) Code: 99214 linked to Fever, unspecified R50.9 Hx: 4+ elements, ROS 3 systems, PM/SHx Detailed (99214) PE: 7 systems Detailed (99214) MDM: – Problem severity: New Problem, further workup planned. 4points – Data: UA/Ucx,1 point= minimal – Risk: Rx management=moderate Overall MDM=moderate (99214) Code: 99214 Hx and PE not suggestive of vaginitis or STD or other abdominal process. Hx: 4 elements, 1 ROS, PMHx Expanded (99213) PE: 2 Systems one with 2+ elements Detailed (99214) MDM: – Problem: Established Problem, worsening (2 points) (Low) – Data:0 – Risk: Prescription Drug Management=Moderate Overall MDM=Low (99213) Code: 99213 linked to allergic eczema L20.84 Allergic Hx: 4+ elements, 2+ ROS, P/SHx Detailed (99214) PE:8+systems Comprehensive (99215) MDM – Problem: New problem with further workup (4 points) (High) – Data: Flu PCR, 1 point – Risk: Prescription drug management (Moderate) Overall MDM: Moderate (99214) Code: 99214 linked to cough R05 Hx: 4+ elements, 2+ ROS, P/SHx Detailed (99214) PE: 7 systems Detailed (99214) MDM: – Problem: New problem no further workup (3 points) – Data:0 – Risk: acute self-limited problem=Low – Overall MDM: Low (99213) Code: 99214 linked to J06.9 Acute URI of unspecified site 2/3 support this code and the nature of the problem supports the extent of history and PE. Time Based Coding 30 min Code: 99214 linked to encounter for pregnancy test, result positive Z32.01 Link to Dan’s Medical Decision Making Calculator (Proprietary for your personal use only) Dan Ostrovsky’s Medical Decision Making Calculator (Excel) https://www.dropbox.com/s/jvq6zlwj73qhw77/MDM%20 calculator%20final.xlsx?dl=0 SPECIAL THANKS Tammy Clay, PDC Chief Compliance Officer Jessica Ferrari, Pediatrics Revenue Manager Danielle Graf, Pediatrics Revenue Manager Melissa Sangster PDC Revenue Manager References aappediatric coding newsletter. The AAP peer-reviewed coding and Nomenclature Newsletter. 2009. Vol.4, Number 10. 2-12. AAP Coding Calculator *subscription to coding newsletter required AAP NC 2007/8 Medicaid Reimbursement Survey Hearing Screening Coding Fact Sheet for Primary Care Pediatricians http://emuniversity.com Jensen PR. Coding Routine Office Visits:99213 or 99214. Family Practice Management. 2005. September. 52-57. Physicians Computer Company www.icd10data.com www.nctracks.nc.gov http://www.roadto10.org/ http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/icd/icd10cm_guidelines_2014.pdf ICD-10-CM The Complete Official Draft Code Set 2013. www.optumcoding.com