The Trophic Pyramid

Intro to ECOSYSTEMS
You will be able to comprehend how ecosystems are structured and why they are structured in a specific manner
What is the Ecology?
What is Ecology?
What is Ecology
The Trophic Pyramid
Understanding how energy is transferred between organisms in an Ecosystem
What is an Ecosystem?
• Ecosystem- the interaction between organisms and their environment
• Niche – Organism’s “job” in the
Environment
• Biome- the specific habitat organisms live in
What makes Ecosystems work ?
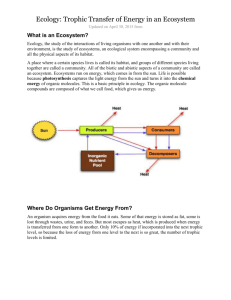
• Ecosystems dependent on the transfer of energy from one organism to another
• Energy Transfer leads to specific food relationships, which is represented by specific levels on the Pyramid
• As energy is transferred however, efficiency goes down: Only 10% of the initial energy available as you go up each level of the pyramid.
Where does Energy come from?
• Sun is the ultimate source of energy for most
Ecosystems. (not the deep sea however)
• Sunlight is converted to food energy through process known as photosynthesis
• Plants convert light energy into food energy, hence they are called the Primary Producers
• Primary Producers are the FOUNDATION of the
Pyramid; without them ecosystem fails
Construction of the Pyramid
• Primary Producers/Autotrophs- Make their own food; Placed at base of Pyramid
• Primary Comsumers: (next level up)
• Herbivores- Organisms that eat the Primary
Producers
• Scavengers- organisms that eat dead or decaying items
Construction of the Pyramid
• Secondary Consumers- small Carnivores and omnivores
• Carnivores- smallest carnivores go in this level, these are organisms that eat primarily tissue of other animals. They can not digest plant materials
• Omnivores- organisms that eat both plant and animal matter
Construction of the Pyramid
• Tertiary Consumers-
• Medium sized Carnivores
• Top Level APEX PREDATOR-
• Largest Carnivore(s) in the ecosystem.
Balancing the Ecosystem
• How the energy is transferred throughout the food chain determines the numbers of organisms that can exist in an ecosystem
• Approximately only 10 % of the energy taken in by an organism is transferred to the next organism
• 90% of the energy is lost due to the organism using the energy to grow, maintain its health, and eliminated waste
• The impact of this shows on the levels of the pyramid; organisms number go down by a power of 10 as you move up in the levels in the pyramid
Trophic Pyramid
Example
Fresh Water
Snapping Turtle (10)
Largemouth Bass (10), Trout (10)
Minnow (80), Dragonfly (90),
Bullfrog (20)
Mussel (100), Mosquito (700),
Crayfish (60)
Algae (5000), Lilly Pad
(5000)