1. SNAPSHOT 1 CH. 9 NERVOUS SYSTEM Fri. March 8 – Fri March
advertisement

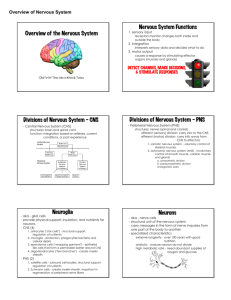
1. SNAPSHOT 1 CH. 9 NERVOUS SYSTEM Fri. March 8 – Fri March 22 PS6 Understand the organization and function of the nervous system. LT1 Describe the functions of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. LT2 Compare and contrast the structure and function of the autonomic and somatic nervous system. LT3 Describe the function for each of the 12 cranial nerves within the brain. LT4 Describe the structure and function of neurons and neuroglial cells. Fri. March 8, all classes Do Now pg. 202 Read “Deadly Mercury” and answer the following questions. What were some of the symptoms Dr. Wetterhahn experienced from coming in contact with dimethylmercury? What does dimethylmercury do to the brain? Activities 1. Complete II 9.1 Introduction through V 9.4 Neurons pages 67, 68, 69 in the packet Mon. Mar. 11 All Periods Do Now Why are neuroglial cells important for neurons? Activity 1. Go over Friday’s work. ALTERED SCHEDULE HSPE WRITING AND READING TESTING LATE ARRIVAL FOR TUES-THURS. Tues. March 12 Periods 1, 2 Wed. March 13 Periods 3, 4 Thurs. March 14 Periods 5, 6 * I HAVE FIRST LUNCH COME TO CLASS FIRST LUNCH IS AT 10:55-11:25 Tues. March 12 through Thurs. March 14 All Classes Activity: DVD “The Brain” 90 minutes by the History Channel Mon. March 18 Do Now Draw a common nerve cell and label axon, dendrite, nucleus, myelin sheath Activity: Needs to be completed in 45 minutes. 1. Answer questions on page 71 for B use 9.4 Neurons on page 206 in the textbook and C using page 208 Classification of Neurons 2. Label the neurons on the top of page 72 using your new knowledge 3. Turn to page 71 in your packet locate D. complete the chart using pages 208 and 209. 4. Define Page 210 resting potential, p. 212 threshold potential, action potential 5. Answer questions for A of VII. 9.6 Nerve Impulse on page 71 found on pages 213-214. 2. Tues. March 19 Periods 1, 2, 4, 5 and Wed. March 20 Period 6 Do Now Pg. 206 Read the blue box in the right column in the middle of the page. Explain why infant’s nervous system does not function effectively. Activity Work needs to be completed in 60 minutes. 1. C. under VII. 9.6 Nerve Impulses instead of answering C. What is the refractory period? Answer: Explain All-or-None Response at the bottom of p. 213. 2. Read Topic of Interest on page 215 Factors Affecting Synaptic Transmissions. Answer the following?’s. a. What happens when nerve impulses reach the synaptic knobs too rapidly? b. What occurs during an epileptic seizure? c. How does Dilantin work? d. Name some other substances that have an affect on synaptic transmission. 3. Page 214 9.7 Define the following words: nerve pathways, synapse, neurotransmitters, excitatory, inhibitory, acetylcholine, monamines, amino acids, neuropeptides. 4. Label the following diagram using Figure 9.13 page 215 in the textbook. 1. 2. Page 72 in packet X. 9.9 Types of Nerves (pp. 217-218) Answer A-D Label and color following directions for Figure 27.2 and Figure 27.3 on page A using page 225 in the textbook. Wed. March 20th and Periods 1 & 4 and Thurs. Periods 2, 5, 6. You have 60 minutes to complete today’s work. 3. Do Now Pg. 214 Figure 9.12 What is necessary for an impulse to continue from one neuron to another? Activity 1. Fill in the chart below using page 216 NEUROTRANSMITTER LOCATION Monoamines Norepinephrine MAJOR ACTIONS CNS Control skeletal muscle actions PNS Stimulates skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. May excite or inhibit at autonomic nervous system synapses CNS Creates a sense of feeling good; low levels may lead to depression PNS May excite or __________________________________________, ________________________________, depending on receptors. Dopamine CNS Creates a sense of ___________________; deficiency in some brain areas is associated with __________________________ PNS Limited actions in _______________________; may excite or inhibit, depending on receptors. Serotonin Primarily inhibitory; _____________________; action is blocked by ________, enhanced by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor drugs Histamine CNS Amino acids GABA Glutamic acid Neuropeptides Substance P Excitatory; pain perception CNS Gases Nitric oxide Generally inhibitory; reduce pain by inhibiting substance P release PNS CNS 2. Pg. 73 in packet XI. 9.10 Nerve Pathways pg. 118 and 219 in the textbook. Answer A and B and label the diagram using the diagram on page 219. 3. Pg. 73 & 74 XII. 9.11 Meninges ( pg. 220) Complete A & B in packet. 4. Explain what the ascending tracts and descending tracts do found on page 223 in the textbook. Fri. March 22 Do Now Pg. 210 blue box what happens to neurons that are oxygen deprived? Activity 1. Answer questions on pg. 74 for XIII Spinal Cord using pgs. 221-222 & XIV 9.13 Brain A & B. Ss 3 start here Mon. March 25 All Periods Do Now What do you know about a stroke? Activity Youtube video