05Cleavage
advertisement

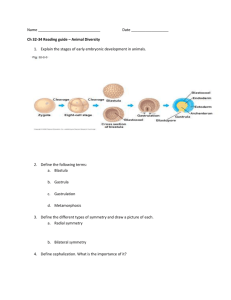
CLEAVAGE 1 Ciona intestinalis http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Garstang_Hypothesis.htm http://biodev.obs-vlfr.fr/recherche/biomarcell/ascidies/Anim-fromegg.htm http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=.07EmbIt9ELpT-YFA1rDieIO4AMQFlmlIwWj 2 3 E. G. Conklin, 1905 - In Styela partida, cells that contain yellow crescent pigment form muscle (mesoderm) http://sdb.bio.purdue.edu/AboutThisSite/conklin.article.html Swalla & Jeffery, 1995 - showed that a maternally derived mRNA was segregated into cells containing yellow crescent pigment. 4 Clear cytoplasm = ectoderm Yellow cytoplasm = mesoderm Dark gray cytoplasm = endoderm Light gray cytoplasm = neural tube and notochord. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=.0f0icUJoQpTbPzZ-do7pAF-n3I2E18sYrYZ 5 Frog 6 Second polar body 15-30 min after fertilization Frog Point of sperm fusion with egg determines: Dor Ant 1. 2. 3. 4. Position of grey crescent Major axes of embryo Position of dorsal lip Position of first cleavage furrow 5-10 min after fertilization Ven Pos Wilhelm Roux, 1885 Pronuclei will fuse 1.5 - 2 hr after fertilization L R 7 http://www.md.huji.ac.il/~yisraeli/embryology/embryo.html What do these experiments tell us? 1. In some species, the cytoplasm of the zygote is very organized. 2. That maternally derived cytoplasmic information is sequestered into specific cytoplasmic compartments. 3. The end result - maternal mRNAs end up in specific groups of cells - determines those cells eventual fate a. the cells containing the yellow pigment cytoplasm of Stylea’s embryos form muscle b. the cells of the frog embryo that contain gray crescent cytoplasm become the chordamesoderm and eventually the notochord. 8 Purposes of cleavage 1. Decrease cell size 2. Increase cell number - allows for formation of blastocoel in many species by a process called cavitation. 3. In some cases, distribution of maternal cytoplasmic information to specific groups of cells 4. Beginning of Differentiation - as cleavage proceeds, you reach a point where the blastomeres are no longer totipotent 5. Synthesis of embryo derived mRNA for direction of future development begins during cleavage. Mammals - starts after a few cleavage divisions; Frogs - starts during late blastula stage 9 10 STARFISH CLEAVAGE - EQUAL HOLOBLASTIC A Meiosis complete at ovulation Isolecithal, oligolecithal, microlecithal egg Sagittal view ~32 cell stage V View of animal pole A View of vegetal pole V II V III IV 11 UNEQUAL HOLOBLASTIC (may be meroblastic cleavage, but not always) Amphibians - meroblastic, unequal starting with 3rd cleavage division Ovulated as primary oocyte. First meiotic division completed in oviduct, second after fertilization. A cellstage stage 432 168cell cell stage 2 Sagittal view V Frog blastula 18View hr Mesolecithal vs telolecithal of animal pole A IV III II I IV 1st - 3.5 hr 2nd - 4.5 hr 3rd - 5.5 hr View of vegetal pole V http://www.luc.edu/depts/biology/dev/stages.htm 12 http://www.its.caltech.edu/~bi12/2003/movies/xclvgtop.mov Structure of the chicken (bird) shelled egg Polylecithal or megalecithal egg (huge amount of yolk) Blastodisc 13 AVIAN CLEAVAGE - DISCOIDAL 1st - 3 hr Meiosis I completed almost immediately after ovulation. Meiosis 2 completed after fertilization. 2nd - 3.5 hr 3rd - 4 hr Ovulated as primary oocyte. Yolk Looking down on the animal pole. 4th - 4.5 hr 5th - 5 hr A Discoidal cleavage is a type of meroblastic cleavage III IV II V Yolk 14 A 15 Delamination Movie of delamination in digital lab manual Polyinvagination 16 SUPERFICIAL CLEAVAGE - INSECTS Superficial cleavage is a type of meroblastic cleavage pole plasm http://www.luc.edu/depts/biology/dev/insect.htm 17 18 Human embryo cleavage and cavitation. http://www.erin.utoronto.ca/~w3bio380/lecture/Lect11/L11.htm 19