2007 PowerPoint - General Education
advertisement

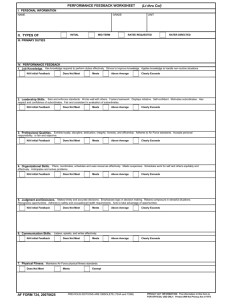
WRITING & Writing Assessment CRITICAL THINKING ASSESSMENT WRITING ASSESSMENT READERS: HONRS 150 INSTRUCTORS Number of papers read: Number of readers per paper: Number of readers: 41 2 8 (Gary Hatch, Joyce Adams, Elizabeth Crowe, Lisa Johnson, Deirdre Paulsen, Kerry Spencer, Kylie Turley) WRITING RUBRIC Paper #: Title: Traits Course: Fails Standard 1 Meets Standard 2 3 Exceeds Standard 4 5 6 Thesis and Support Lacks a clear, recognizable assertion Has a clear, recognizable assertion that provides focus and direction to the essay. Shows recognition of opposing views, multiple perspectives, or location within scholarly literature Organization Lacks clear, transparent organization. Characterized by lack of flow and coherence Clear, transparent organization. Characterized by coherence and flow within sections. Transitions may be formulaic or mechanical. Organized conceptually rather than formulaically. Consistent coherence and flow. Transitions move beyond the formulaic or mechanical. Rhetorical Knowledge Suggests a lack of awareness of rhetorical situation Demonstrates an awareness of subject, audience, occasion, and purpose. Stylistic choices are appropriate for rhetorical situation. Consistent voice (style, tone, and point of view appropriate to subject, audience, occasion, and purpose). Use of Sources Inappropriate sources that may be poorly integrated. May not consistently give appropriate credit. Uses appropriate scholarly sources that are well integrated in the essay. Sources are properly introduced. Gives appropriate credit for sources. Engages the sources. Demonstrates exceptional depth of research, such as primary research data, primary documents, or visual sources. Knowledge of Conventions Inconsistent in following standards of EAE and citation style. Generally follows accepted standards of edited American English and details of appropriate citation style. Consistent in following standards of edited American English and details of appropriate citation style. Notes (only for elements of an essay that aren’t covered by the rubric): Overall Scores by Standard N = 41 6 papers 17% 37% exceeds meets fails 16 papers 46% 19 papers Trait – Knowledge of Conventions N = 41 5 papers 13% 34% 14 papers 53% 22 papers Trait - Organization N = 41 5 papers 12% EXCEEDS 48% 20 papers MEETS 40% 16 papers FAILS Trait – Rhetorical Knowledge N = 41 8 papers 21% 41% EXCEEDS MEETS FAILS 17 papers 38% 16 papers Trait - Thesis N = 41 11 papers 9 papers 23% 26% EXCEEDS MEETS FAILS 51% 21 papers Trait – Correct Use of Sources N = 41 7 papers 16% 38% 16 papers EXCEEDS MEETS FAILS 46% 18 papers All Traits 100.00% 90.00% 80.00% 70.00% 60.00% 50.00% EXCEEDS MEETS 40.00% FAILS 30.00% 20.00% 10.00% 0.00% know organization rhetorical conventions knowledge thesis use of sources N = 41 Reader Agreement Agree 1 Split 2 Split Conventions 41.46% 51.22% 7.32% Organization 46.34% 51.22% 2.44% Rhetorical Knowledge 39.02% 53.66% 7.32% Thesis 46.34% 48.78% 4.88% Sources 43.90% 75.61% 4.88% OVERALL 43.41% 56.10% 5.37% Reader Agreement 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 2 Split 50% 1 Split 40% Agree 30% 20% 10% 0% Conventions Organization Rhetorical Knowledge Thesis Sources OVERALL Critical Thinking Assessment Critical Thinking Readers • • • • • • • Bill Baker, Management Communications Ralph Brown, Sociology Valerie Hegstrom, Spanish & Portuguese John Lamb, General Education & Chemistry Hal Miller, Psychology Karen Pierotti, General Education Robert Seegmiller, Physiology & Developmental Biology CRITICAL THINKING RUBRIC Fails Standard Trait 1 2 Meets Standard 3 4 Exceeds Standard 5 6 ● lacks clarity & focus ● fails to clarify ● articulates clearly at early point & once thereafter ● sustains the argument ● maintains focus on theme ● offers insightful, sophisticated point of view Evidence ● lacks sufficient evidence ● citations improperly applied/ inappropriate ● uses appropriate, sufficient, relevant evidence ● cites sources properly ● makes effective use of strong, well-placed, extensive, and relevant resources Logic ● uses weak, narrow, shallow argumentation ● does not make connections ● does not recognize assumptions, inferences ● uses faulty logic ●demonstrates reasonable development, discernible connections, coherent thinking ● recognizes assumptions/ inferences ● brings argument to a logical conclusion ● achieves strongly reasoned development ● provides analysis of assumptions or inferences ● makes strong connections ● provides compelling commentary or synthesis Alternative Points of View ● presents biased, unbalance, or narrow thinking ● reflects poor awareness of critical context ● presents counterarguments/ alternatives ● recognizes weakness(es) of own viewpoint ● shows sensitivity to other perspective ● locates argument within current critical discourse (context) ● reflects mature balance in point of view Main idea/claim/ argument/hypothesis NA Trait - Ideas Main idea/claim/argument/hypothesis 1 paper 5% 2 papers N = 11 27% Exceeds Meets Fails Not Applicable 68% 8 papers Trait - Evidence 1 paper N = 11 5% 32% Exceeds 7 papers 3 papers Meets Fails Not Applicable 63% Trait – Logic/Assumptions 1 paper N = 11 9% Exceeds 32% 59% 7 papers 3 papers Meets Fails Trait – Alternative Points of View N = 11 0% 1 paper 9% 32% 3 papers 59% 7 papers Exceeds Meets Fails N/A All Traits 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% Exceeds Meets 50% Fails 40% Not Applicable 30% 20% 10% 0% Ideas Evidence Logic/ Assumptions Counter Arguments All Traits: Writing & Critical Thinking Writing Critical Thinking 100.00% 100% 90.00% 90% 80.00% 80% 70.00% 70% 60.00% 60% 50.00% EXCEEDS MEETS 50% 40.00% FAILS 40% 30.00% 30% 20.00% 20% 10.00% 10% 0.00% Exceeds Meets Fails Not Applicable 0% know organization rhetorical conventions knowledge thesis N = 41 use of sources Ideas Evidence Logic/ Assumptions N = 11 Counter Arguments Critical Thinking & Writing Assessment In the future Assessment via Final Exams Collecting final exam information during FGEC Reviews A copy of a final exam Student performance on final exam Purpose Verify that the exams line up with the foundation documents and learning outcomes. Assessment via Advanced Writing During Fall and Winter semesters, the GE office will collect about 150 papers from different departments who teach advanced writing. Paper Criteria 1. Single-author papers and some collaborative papers (when using collaborative papers we would need to know how the collaboration was set up for the collaborative groups.) 2. A paper using library resources that has real research associated with it 3. The paper should be about 8-15 pages long, double-spaced. 4. There should be no mark up on the papers by instructors 5. Preferably the paper should be in electronic format (Word program is preferred.) Assessment via Advanced Writing Course Choice GE office will collect papers from various departments – 75% of the papers will come from different sections of courses in the English, Philosophy and Management Communication departments; – the other 25% will come from other departments that teach only one or two sections of a course, e.g. Chem 391. Choosing Papers GE Office will request a chosen course’s class roll to randomly pick 5 juniors or seniors in the course GE will provide release/permissions sheets to the chosen students so we have permission to use their papers for the study. Assessment via Advanced Writing Submitting the Papers Electronically to Karen Pierotti, Administrative Assistant, General Education Distribution of Papers to Assessment Committee Student’s name, instructor’s name, and course will be eliminated from the paper Paper will receive a number before it is given to the committee Assessment During spring term, two committees will assess the papers for writing and critical thinking GE Web Site Statistical Results Annotated copies of papers for both writing & critical thinking WRITING & Writing Assessment CRITICAL THINKING ASSESSMENT