Active Listening Skills
advertisement

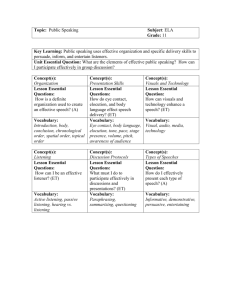
Active Listening Skills Adapted from http://www.taft.cc.ca.us/lrc/class/assignments/actlisten.html Mentoring Matters: A Practical Guide to Learning-Focused Relationships by Laura Lipton and Bruce Wellman, 2003 Attending : Pay attention to your eye contact, posture and gestures S.O.L.E.R. Five steps to attentive listening: Squarely face the person Open your posture Lean towards the sender Eye contact maintained Relax while attending Pausing Silence can be golden. Silence can also feel uncomfortable. The pace of a conversation will affects both the emotional and intellectual climate. Frequent well-placed pauses contribute to a inductee’s confidence and capacity. In order to reach higher levels of thinking, the inductee must have time to process. However, for most of us, consciously pausing to provide for space for thinking requires patience and practice. Providing wait time to think and process can be a great gift to the inductee. Pause to Enhance Thinking and Thoughtfulness Wait Time 1 Wait Time 2 Wait Time 3 Pause after asking a question Pause after a colleague responds Pause before your next question or response to allow thinking time to allow time to retrieve to model thoughtfulness and a need additional and/or related to signal support for thinking to think before responding information to demonstrate your belief in your colleague’s capacity for thinking Paraphrasing Purposeful paraphrasing signals our full attention. It lets the inductee know that we understand his or her thoughts, concerns, questions, and ideas, or we are trying to. By showing we are listening, we earn permission to inquire for details and press for elaboration. Questions may often be interpreted as interrogation. Paraphrasing helps establish a safe environment and trigger more thoughtful responses than simply asking questions alone. Paraphrasing should not slip to the low level of “parrot phrasing.” Three Types of Paraphrases Acknowledge and Clarify Summarize and Organize Shifting Levels of Abstraction (Up or Down) So, you are feeling _________ So, there seem to be two key So, a(n) ____________ for you issues here _________ and might be ____________ You’re noticing that ________ _________ Shifting up: Shifting down: In other words, ____________ - Category - Example On the one hand, there is Hmmm, you’re suggesting Value - Non-example __________ and on the other that _____________________ - Belief - Strategy hand, there is ___________ - Assumption - Choice For you then, several themes - Action are emerging _____________ - Goal - Intention - Option