Year 12 Economics Revision Topic 1 - ais
advertisement
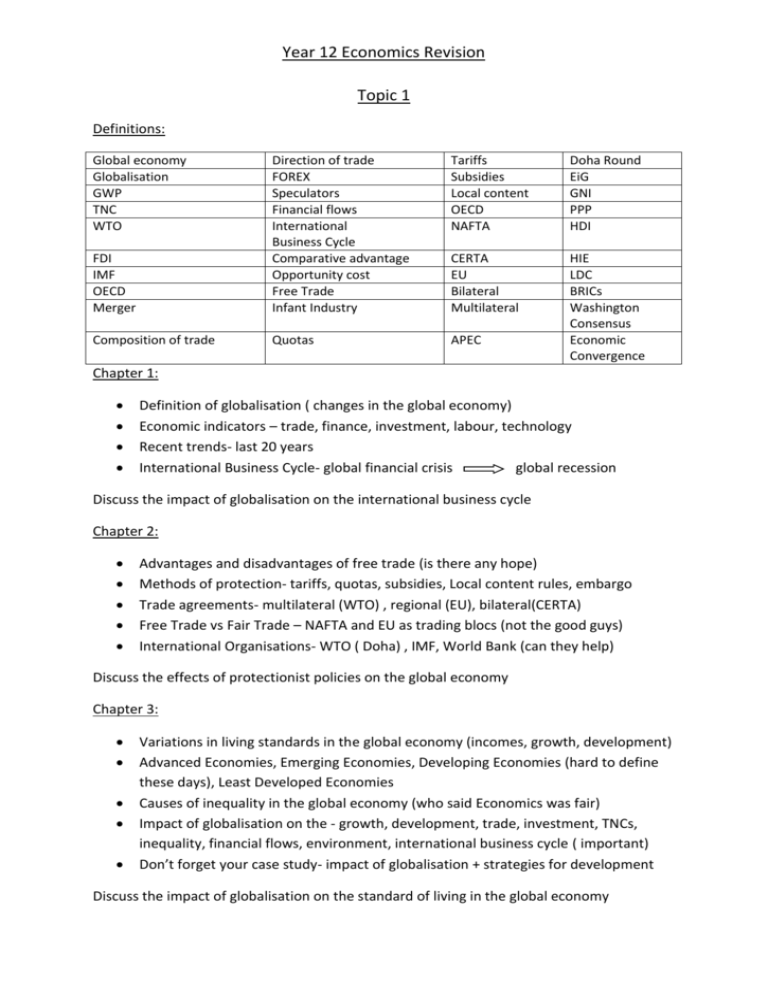
Year 12 Economics Revision Topic 1 Definitions: Global economy Globalisation GWP TNC WTO Tariffs Subsidies Local content OECD NAFTA Doha Round EiG GNI PPP HDI FDI IMF OECD Merger Direction of trade FOREX Speculators Financial flows International Business Cycle Comparative advantage Opportunity cost Free Trade Infant Industry CERTA EU Bilateral Multilateral Composition of trade Quotas APEC HIE LDC BRICs Washington Consensus Economic Convergence Chapter 1: Definition of globalisation ( changes in the global economy) Economic indicators – trade, finance, investment, labour, technology Recent trends- last 20 years International Business Cycle- global financial crisis global recession Discuss the impact of globalisation on the international business cycle Chapter 2: Advantages and disadvantages of free trade (is there any hope) Methods of protection- tariffs, quotas, subsidies, Local content rules, embargo Trade agreements- multilateral (WTO) , regional (EU), bilateral(CERTA) Free Trade vs Fair Trade – NAFTA and EU as trading blocs (not the good guys) International Organisations- WTO ( Doha) , IMF, World Bank (can they help) Discuss the effects of protectionist policies on the global economy Chapter 3: Variations in living standards in the global economy (incomes, growth, development) Advanced Economies, Emerging Economies, Developing Economies (hard to define these days), Least Developed Economies Causes of inequality in the global economy (who said Economics was fair) Impact of globalisation on the - growth, development, trade, investment, TNCs, inequality, financial flows, environment, international business cycle ( important) Don’t forget your case study- impact of globalisation + strategies for development Discuss the impact of globalisation on the standard of living in the global economy Year 12 Economics Revision Topic 2 Definitions: Trends in direction and composition of trade Net capital importer Direct Investment Portfolio Investment Structural Unemployment Debit Credit Industrialised economies Non- reversible Financial Account Current account Foreign Equity Foreign Debt Net Foreign Liabilities Debt trap Debt servicing ratio ETM Political consequences TOT Debt serving cost Flexible exchange rate expectations Dirty float Depreciation Devaluation Net TCF Structural change Micro reform Monetary policy Managed flexible peg productivity Living standards BOP Buy AUD FOREX Exchange rate Export volumes Export base Average tariffs Chapter 4: Australia’s place in global economy- trade, finance, investment BOP- current account/capital & financial account (components and trends) Debt trap cycle- Foreign debt + Foreign equity (relationship to CAD) Issues and trends in BOP (what has been happening and why) Consequences of CAD (is it all bad news or the result of globalisation) Discuss the impact of changes in the global economy on Australia’s external stability. Chapter 5: Australia’s floating exchange rate- demand and supply factors (lots of diagrams) Appreciation and depreciation of AUD (more diagrams) RBA intervention- direct and indirect intervention (diagrams again) Fixed exchange rates ( not important/ there are other alternatives) Positives and negatives of appreciation/ depreciation (most important) Explain the relationship between a country’s exchange rate and its balance of payments. Chapter 6: Government policies to reduce protection in Australia (use statistics) Implications for individuals, firms and government (some good and some bad) Future prospects for Australian industry in the global economy Explain why Australian governments have adopted a long term strategy to reduce protection. Email address = rodgerk43@yahoo.com Answers should be no more than 2 pages- answer as many as possible