File
advertisement

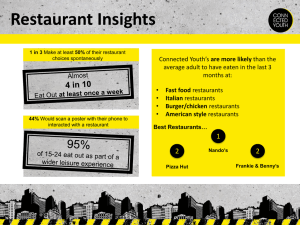
The Food Service Industry An Overview the pineapple tradition welcome friendship hospitality travel recreation lodging Hospitality managed services conventions & meetings restaurants 13 million people 14.8 million jobs by 2019 50% Spent eating out Once upon a time . . . Ancient Greeks & Romans rarely dined out, but enjoyed entertaining at home. Romans‘ desires for exotic foods and spices increased trade, stretching the Roman Empire farther east and north. Landowners, who lived in relative comfort, held large banquets almost every night. Travel was extremely dangerous. After the Moors invaded Spain in 800 AD, trade with the Far East and India came to a stop— including the shipment of spices and fine goods. Middle Ages The Renaissance through the French Revolution: – haute cuisine, an elaborate and refined system of food preparation, had its roots during this period. – Guilds, or associations of people with similar interests or professions, were organized. – Cooking guilds established many of the professional standards and traditions that exist today. In 1765, a man named Boulanger began serving hot soups called restaurers (meaning restoratives) for their health-restoring properties. He called his café a restorante, the origin of our modern word restaurant. Colonial America: - Population explosion - As early as 1634, an inn in Boston called Cole’s offered food and lodging to travelers. - Inns were typically for travelers only The Industrial Revolution: – Movement toward the cities – Lived closed to place of employment – Dining & lodging establishments increased – With the invention of the railroad in 1825, inns, taverns, and foodservice facilities located near railway stations began to grow. The Gilded Age: – Dining elegance – As a result of the California gold rush (1848–1855), people who hit the jackpot wanted to enjoy the fine dining that they knew existed in New York with their newfound wealth – Developed self-serve cafeterias for the less affluent The Twentieth Century: – More people working – During World War II = lodging industry – After World War II = the quick-service restaurant was introduced. – In the 1960s, commercial air travel became popular, and builders focused on land near airports as the next new place to situate hotels, motels, and foodservice facilities The Twentieth Century (continued): – 1970s to today = national chains boom; “eating out” as commonplace as eating at home – In the last few decades, lifestyles have moved steadily toward busier households that no longer have a dedicated daily food preparer 2 major parts: Commercial Non-commercial 80% 20% Restaurants Catering & banquet Retail Stadium Airlines & cruise ships Schools & universities Military Healthcare Business Clubs Types of Establishments Restaurants prepare and serve meals to customers. These types of business opportunities are available in restaurants. – Corporate restaurant groups – Chains – Franchisee/franchisor – Independents/entrepreneurs Types of Establishments - Catering Catering provides opportunity for creativity in menu selection and style of service. • Caterers provide foodservice for everything from special events in private homes to large-scale events such as golf tournaments, weddings, or corporate dinners. • Found in catering departments within hotels, independent catering companies, and restaurants. Types of Establishments - Retail Retail foodservice opportunities are found in businesses that offer home meal replacements and ready-made dishes. • At stadiums or sports arenas, tens of thousands of people with foodservice needs want service in a relatively small period of time. • Foodservice is provided by servers, walking vendors, cooks, and cashiers. • Stadiums also have corporate suites that offer superior service and food. • Stadiums typically have contract feeders, a unique venue with managers who specialize in managing stadium events. Types of Establishments - Convention Convention centers are specifically designed to house large-scale special events such as conventions, expositions, and trade shows. • A convention is a gathering of people, all of whom have something in common. • Expositions are large shows, open to the public, that highlight a particular type of product or service. • While expositions are open to the general public, trade shows are restricted to those involved in the industry being featured. Types of Establishments – National Parks The national park system is operated by the National Park Service, which is part of the U.S. Department of the Interior. • Many parks offer high-quality accommodations, ranging from campgrounds to hotels, as well as a wide variety of restaurants. • Most of the guest facilities in national parks are managed by private companies. Types of Establishments – Theme Parks Theme parks offer a full array of entertainment features that create an overall atmosphere of fun. • The popularity of theme parks as tourist destinations has had a major affect on all hospitality industries. • Quality of food and service is very important in this setting, as food is a major part of the guests’ experience. • Today, many theme parks worldwide offer a variety of foodservice options. Types of Establishments – Shopping Areas Shopping areas have become a major destination for travelers in the United States and other countries. • • • • Becoming more of a destination Shopping malls and plazas Outlet centers attract travelers from far away Department stores are a major segment of the retail industry • Large discount chains form another segment of the retail industry Other types of establishments • • • • • • • • Monuments Concessions Zoos Health-care facilities Schools and universities Military Correctional facilities Lodging industry Types of restaurants • Luxury • Theme or celebrityowned • Mid-scale casual restaurants • Family restaurants • Ethnic restaurants • Specialty restaurants • Quick service • • • • • Steakhouses Seafood restaurants Pancake restaurants Sandwich restaurants Family restaurants Career Pathways Front-of-the-house • Serve guests directly. Back-of-the-house • Work outside the public space. Front of the House “Curbside Appeal” Dining Room Manager Hostess Servers Bussers Back of the House Food production & restaurant systems Executive Chef Sous Chefs Cooks Runners & Dishwashers Front of the House Most important skills needed are ✔ Active Listening — Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times. Service Orientation — Actively looking for ways to help people. Social Perceptiveness — Being aware of others' reactions and understanding why they react as they do. Speaking — Talking to others to convey information effectively. Coordination — Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions. Back of the House Most important skills needed are Coordination — Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions. ✔ Monitoring — Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action. Active Listening — Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times. Problem Sensitivity — The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem. Manual Dexterity — The ability to quickly move your hand, your hand together with your arm, or your two hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble objects. SC employment outlook Cooks (restaurant) +15% Cooks (institutions) +13% Waitstaff +6% Chefs +4% Managers +2% Host/Hostesses +6% Butchers/Fish Mongers +10%