The Teenage Brain
advertisement

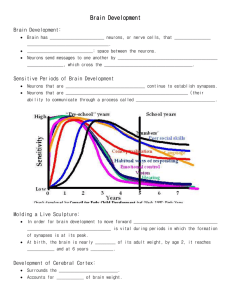
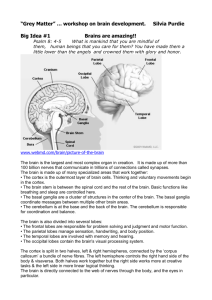
The Adolescent Brain David H. Vawter (vawterd@winthrop.edu) Dave Vawter, B.S., M.Ed., Ph.D, D.A.D “ This too shall pass” Brainy Facts: What do we know about the brain? • Adult = 3 pounds • 2% of our body weight but consumes 20% of our calories • 70% water, it consumes 30% of the water we drink The brain develops from the back towards the front. Beginning at the Cerebellum, then the Amygdala, the Basal Ganglia, the Corpus Callosum and then last the Prefrontal Cortex. Dr. Jay Giedd, Neuroscientist • Used MRI to scan the brains of nearly 1000 healthy children ages 3-18. • Between ages of birth2 and 9-10= tremendous growth of neurons • Ages 2-3 and 11+= massive pruning During adolescence… use it or lose it • Fewer but faster connections • The grey matter continues to thicken, • Used connections will flourish, unused will die. Brain Break • Rally Robin Frontal Lobe • • • • • • Problem solving Judgment Planning Organization Self-monitoring Emotions • Attention • Concentration • Awareness of abilities • Self-control • “do the right thing” The CEO of the Brain • The frontal lobes: executive decisions and moral/ethical control • Development continues from back to front through early 20’s • “It’s sort of unfair to expect teens to have adult levels of organizational skills or decision-making before their brains are finished being built.”- Dr. Giedd Misread signals Everything is not as it seems to them….. • Teens relied on the amygdala, associated with emotion and gut reactions • Teens see anger when it was not intended But what if the student is very smart? • ..\body\brain\Emotion_(Amygdala)_and_Int ellect_(Frontal_Cortex)__Analyzing_the_B rain_of_a_Teenage_Genius.asf Catching ZZZZZZs • They need 9 ¼ hrs… • They get…6-7….! • The biological clock shifts in the teen years Sleep deprivation can have a major negative effect on learning and memory! Turn off backlit devices an hour before bed “Teen Brain” or ADD/ADHD? ADD/ADHD? Does the teen have…… • Ability to "hyperfocus" • Above average intelligence or higher • Creative thinking • The inability to focus causing problems with grades, relationships, safety, self-esteem • Famous people: Albert Einstein, Will Smith, Walt Disney, Ben Franklin, Whoopie Goldberg How do you help the ADD/ADHD student? • Remove clutter even from walls • Allow movement, sit in the back or side • Do not get angry at their behavior; that will never fix the problem • Give extra time if noticeably distracted • Keep a stash of their materials in your room; help them with organization During adolescence… period of high risk • Drugs and alcohol can alter normal development of the brain • Teens who drink are exposing their brains to the toxic effects of alcohol at a critical time of brain development Image from Susan Tapert, PhD, University of California, San Diego http://www.sfn.org/skins/main/images/brainbriefings/bb_Oct2002_large.gif . What about students from poverty? TEACHERS MAKE A DIFFERENCE!! Neurogenesis-the birth of new neurons • Evident in the hippocampus and perhaps in the cerebral cortex. • New neurons develop from neural stem cells that remain in our brains throughout life. • Continual turnover of neurons - old ones die and new ones are born - and these new neurons can participate in circuits that underlie learning. Common Factors in the Lives of Low SES Kids! Neurogenesis is the raw material for learning! Chronic Stress … 1. Creates emotional problems (Burgess et al. 1995) 2. Lowers IQ, reading scores (Delaney-Black, et al. 2002) 3. Causes Memory loss (Lupien, et al. 2001) 4. Shortens dendrites (Cook and Wellman, 2004), (Brown, et al. 2005) 5. Causes neuron death (De Bellis, et al. 2001) 6. Fosters inappropriate attachments Schore, A. 2002) “What were you thinking?” Under High Stress, Brains Engage in Bottom-Up DecisionMaking for a More Reflexive Strategy Arnsten AF. (2010) Stress signaling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function Teachers who criticize, hold negative attitudes and use sarcasm as classroom discipline will activate the fear and stress areas of the student’s brain. This activation alters the student’s ability to think and learn. What does this mean for EDUCATORS? • Crucial time in brain development • Willful pigheadedness? • Making mistakes • Providing structure, helping them get organized, making our content relevant, getting them involved in learning SUMMARY: Brains Can Change for the Better Brains physically change every day Targeted classroom teaching can make dramatic changes in days DNA is not your destiny Teachers are the strongest change agent in student’s lives Brain Break The Adolescent Brain -Part Two: Strategies for the Classroom WHICH OF THESE FACES WALKS OUT OF YOUR ROOM? Movement Relevance Relationships Use ART, DRAMA, MUSIC! MOVEMENT, ENGAGEMENT, FEEDBACK, COMMUNICATION STATIONS Work in Groups! • Plan • Select with partial choice • Let them use GoogleDocs to create presentations • They create the assessment Novelty • Dress Up • Change the room around • Go outside!!! Speed Teaching! The Six R’s • Reflexes • Reflection • Review • Reteaching • Relevancy • Ready for what is next Reflexes • TPR – Hand Checks – Movement Reflection • Long term retention Review • Not how many times….. Reteaching • Differentiation Relevancy • Two Kinds – To their lives – Why Ready • Cognitive Dissonance • Anticipation When they get to be about 25, they’ll realize their parents and teachers were pretty smart people.