Hassen_Sprites
advertisement
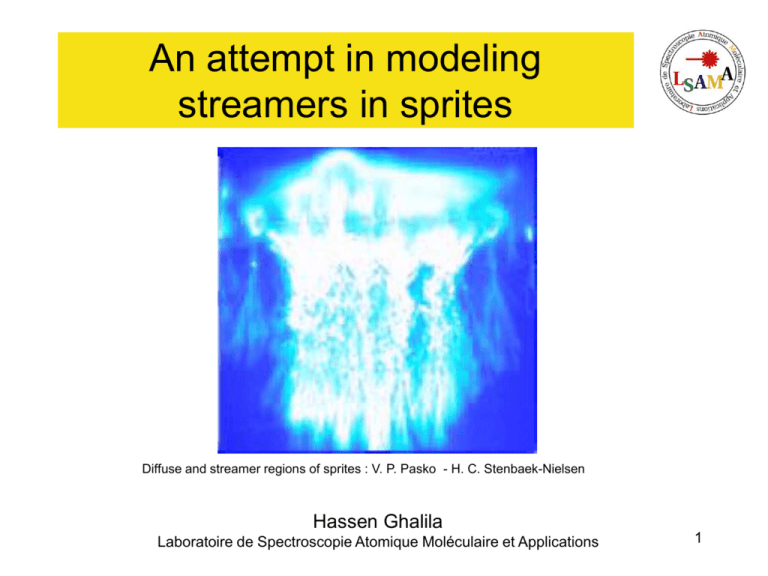
An attempt in modeling streamers in sprites Diffuse and streamer regions of sprites : V. P. Pasko - H. C. Stenbaek-Nielsen Hassen Ghalila Laboratoire de Spectroscopie Atomique Moléculaire et Applications 1 References Sprites produced by quasi-electrostatic heating and ionization in the lower ionosphere V.P. Pasko, U.S. Inan, T.F. Bell and Y.N. Taranenko Monte Carlo model for analysis of thermal runaway electrons in streamer tips in transient luminous events and streamer zones of lightning leaders G. D. Moss, V. P. Pasko,N. Liu and G. Veronis Effects of photoionization on propagation and branching of positive and negative streamers in sprites. N. Liu and V. P. Pasko 2 Quasi-Electrostatic Field 100KmIonosphere Mesosphere E 50Km Streamers Stratosphere 10Km Troposphere ++ + + + ------++ + + + 3 Geometry Schema 60 km Perfect Conductors 90Km Gaussian distribution Lightning : Exponential decline of the charge Time ≈ 1ms 4 Numerical Modeling Why modeling and why PIC Monte-Carlo ? PIC code already ready : Cylindrical 2D1/2 and relativistic Interaction of free electrons with External and Self Electromagnetic field Monte Carlo partially ready : Nitrogen’s Cross Section : Elastic, First state excitation and First ionization Homogeneous ambient medium = vacuum : =1 =0 S/m 5 Ambient electrical properties Neutral density profile Electron density profile 0.100E+03 0.100E+03 Profile 1 2 3 0.800E+02 0.800E+02 0.600E+02 0.600E+02 H(km) H(km) 0.400E+02 0.400E+02 0.200E+02 0.200E+02 0.000E+00 0.100E+14 0.100E+16 0.100E+18 0.100E+20 0.100E+22 N(cm-3) 0.000E+00 0.100E-04 0.100E-02 0.1 10 Ne(cm-3) 1000 0.100E+06 G. Bainbridge and U. S. Inan - 2003 Atmospheric Handbook 1984 Ion conductivity profile 0.100E+03 Profile 1 2 3 0.800E+02 0.600E+02 H(km) 0.400E+02 0.200E+02 0.000E+00 0.100E-12 0.100E-10 0.100E-08 Sigma(S/m) 0.100E-06 0.100E-04 V.P. Pasko , U.S. Inan and T.F. Bell - 1997 6 Ambient electrical properties a N0 E N a N0 E N 1.62 10 < 1.62 10 +3 +3 V/m a 2 a Log e N = 50.970 + 3.0260 Log E / N + 0.08473 Log E / N V /m e N = 1.36 N 0 N0 and N are from Neutral density profile N0 = Neutral density at the ground 7 Expected results - Ambient E field Sprites produced by quasi-electrostatic heating and ionization in the lower ionosphere V.P. Pasko, U.S. Inan, T.F. Bell and Y.N. Taranenko Variable constante: r = 0.000 m Trace au temps: 0.3518E+04 ns 80 1.00E+07 1s 60 Altitude (km) 1.00E+05 Ez ( V/m ) 0,5 s 0,501 s 40 Expected Ek 1.00E+03 20 1.00E+01 0.000E+00 0.170E+05 0.340E+05 0.510E+05 0.680E+05 z en m Last results 0.850E+05 0 101 103 | Ez| (V/m) 105 107 t = 0,5 s lightning t = 0,501 s sustained field after 1ms t = 1 s relaxed field 8 PIC-MonteCarlo modeling Macro particles and Microscopic process a 9 Particle In Cell K E E K A A Discretization z z Q*S4 Q*S1 S PIC = Particle In Cell S2 S4 Q S3 S S1 Q*S3 Q*S2 S S 10 Meshing df Central difference formula dx f x + 0,5.h Π f x Π0,5.h = h t /2 0 Temporal mesh x t nt 0,5.h Π 3! 2 (n+1/2) t d3 f x d3x (n+1)t P0 r 1/2 P1 Pn r n+1/2 P n+1 B0 E 1/2 B1 Bn E n+1/2 B n+1 r Spatial mesh (nzcell, nrcell) Er, Bz, Jr Ez, Br, Jz (1,j) Q, U, E, J B, r, z AXE (1,2) (1,1) (2,1) (i,1) z 11 t Cycle of the Calculations Maxwell J i,j Ei,j , Bi,j Conservation de la charge Interpolation des champs Coupling Maxwell-Lorentz Self-consistently Qi,j 1 - .E = / 2 - t B = - E 3 - t P = q ( E + v B ) 4 - .J = t 5 - t E = B - J E r, z , B r, z Interpolation de la charge Lorentz Qr, z Collisions t E = x B ΠJ t B = Π x E 4 + . J = t dP = E + v x B dt 5 . E = / 12 Monte Carlo simulation Random Collision rate P = 1 Πe ( Π t .t) 0 , e t e t , e + ex e + ex t t ,1 Excitation Diffus ion h Scattering angl_ela = angl_exc = + angl_ion = 0.5 + Ionis ation Pho t o io n i s a t i o n = P x ph ij ij N Nio 13 Cross section Adaptation to the VLF project Nitrogen , Oxygen and Argon Cross Section : Elastic, Several level of excitation and ionization Recombination, Attachment 0.178E+02 0.176E+02 0.182E+02 0.143E+02 0.141E+02 0.145E+02 0.107E+02 0.106E+02 0.109E+02 To (microsec-1) 0.713E+01 To (microsec-1) To (microsec-1) 0.705E+01 0.726E+01 0.356E+01 0.352E+01 0.363E+01 0.000E+00 0.000E+00 0.511E-04 0.604E-02 0.715E+00 0.845E+02 0.100E+05 0.511E-04 Energie (eV) Argon’s rate 0.604E-02 0.715E+00 0.845E+02 0.100E+05 Energie (eV) 0.000E+00 0.511E-04 0.604E-02 0.715E+00 0.845E+02 0.100E+05 Energie (eV) Nitrogen’s rate Oxygen’s rate Compilation of electrons cross section - Lawton and Phelps, J. Chem. Phys. 69, 1055 (1978) - Phelps and Pitchford, Phys. Rev. 31, 2932 (1985) - Yamabe, Buckman, and Phelps, Phys. Rev. 27, 1345 (1983) 14 E Results : plane electrodes z Cathode Vd (cm 100. 80. 60. 50. 40. s-1) Schlumbohm -1 Torr -1 ) Posin 5. Wagner Expérience Kline & Siambis + Nos calculs 30. 20. 70.100. 150. /p (cm 10. Anode /p (Vcm -1 Torr -1 ) 300. 600. 1000 . Drift Velocity Bowls 1. 0.5 Townsend Coefficient 0.1 Expérience Kline & Siambis Heylen 70. 100. 150. + Nos calculs /p (Vcm -1 Torr -1 ) 300. 600. 1000. 100 10 Longitudinal and Transversal coefficients 1 10 -10 10 -9 t (s) 10 -8 15 Numerical Modeling VLF propagation in the earth-Ionosphere waveguide Electromagnetic simulations : Trimpis, Tweek Works of Cummer, Poulsen, Johnson, … Transient Luminous Events PIC Monte Carlo simulations : Streamers and Runaway electrons Works of Pasko, Liu, Moss, … 16 17 18 19 Brouillon Ionospheric D region electron density profiles derived from the measured interference pattern of VLF waveguide modes G. Bainbridge and U. S. Inan 20 Discretized equations Central difference formula df x dx f x+ 0,5.h Π f x Π0,5.h = h 0,5.h Π 3! 2 d3 f x d3x Equation de Faraday B = E t r z n+1 n n+1/2 n+1/2 Br i, j = Br i, j + t ( E i+1/2, j - E i-1/2, j ) z B =- E +E B B = - 1 rE t z r r B t z r r z n+1 n n+1/2 n+1/2 n+1/2 n+1/2 =B - t ( E -E ) + t ( E -E ) i, j i, j r i+1/2, j r i-1/2, j z i, j+1/2 z i, j-1/2 z r n+1 n n+1/2 n+1/2 =B - t ( r E -rE ) z i, j z i, j j+1 i, j+1/2 j i, j-1/2 r r 0 21











