More details on properties of light

Describe why you think rainbows sometimes pop up after it rains.
WORK
Be able to fully explain exactly how rainbows, sunsets, sunrises, polarization, and diffraction work.
Pass up your completed labs.
If you still need lab data see me after class to arrange a time for you to come in to collect it.
The separation of white light into a spectrum of colors is called dispersion.
The violet light is refracted more than red light.
This occurs because the speed of violet light through glass is less than the speed of red light through glass.
Violet light has a higher frequency than red light, which causes it to interact differently with the atoms of the glass.
This results in glass having a slightly higher index of refraction for violet light than it has for red light.
A rainbow is a spectrum formed when sunlight is dispersed by water droplets in the atmosphere.
Sunlight that falls on a water droplet is refracted.
Each color has a different frequency so they are all refracted differently resulting in dispersion.
Although each droplet produces a complete spectrum, an observer positioned between the Sun and the rain will see only a certain frequency of light from each droplet.
The rainbow we see depends on the relative position of the Sun, the droplets, and the observer.
So technically no two people can see the same rainbow at the same time.
The second order is outside of the first.
It is also fainter and has the order of the colors reversed.
Light rays that are reflected twice inside water droplets produce this effect.
These are very rare to see
How many reflections in the water droplet of the third order?
3
From top to bottom, what are the order of the colors in a third order rainbow?
Same as a first order rainbow
The region between the first and second order rainbows is noticeably dark.
This is because at this angle the water droplets won’t reflect/refract/disperse any light back to your position.
1.
What causes rainbows?
Light is electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a fundamental phenomenon of electromagnetism, behaving as waves propagating through space, and also as photon particles traveling through space, carrying radiant energy.
Most glares are horizontally polarized light, so sunglass designers make their lenses vertical polarizers, thus block the horizontal glares from being transmitted to your eyes.
Demo
Appear blurry without glasses because you are seeing the two types of polarized light.
Each eye only needs one type of polarized light.
1.
Why can light be polarized?
2.
Why do polarized sunglasses only block horizontally polarized light and not vertically polarized light as well?
3.
Why do 3D movies look blurry without the right glasses?
A clear cloudless day-time sky is blue because molecules in the air scatter blue light from the sun more than they scatter red light.
Because the blue light is scattered we can see if from every direction.
If there was no atmosphere the sky would be black.
At a low angle most of the blue light is scattered so much it never reaches your eyes because it has more atmosphere to go through.
The extra atmosphere allows the red light to scatter more and fill up the sky.
1.
Why is the sky blue during the day?
2.
Why is the sky red during sunrise and sunset?
Why do black cars heat up faster and get hotter than white?
Black paint absorbs most of the light energy while white paint reflects and scatters most of the light energy.
This extra energy changes into excess heat inside of your car.
Scientists debated for years and years whether light was a wave or a particle.
Between 1801 and 1803, English physician
Thomas Young worked on and was able to convince nearly everyone that light was a wave.
This is known as the double slit experiment
Diffraction: the process by which a beam of light or other system of waves is spread out as a result of passing through a narrow aperture or across an edge, typically accompanied by interference between the wave forms produced.
Young took light from a small source and passed it through two closely spaced slits and produced an interference pattern.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iuv6hY6 zsd0
Diffraction depends on the wavelength of the wave, and the width of the opening.
A shorter wavelength means less diffraction
A longer wavelength means more diffraction
For example red light has a longer wavelength than blue light so it will diffract more. This means the angle between its paths of constructive interference will be greater.
Why do we still get interference through a single slit?
http://www.acoustics.salford.ac.uk/feschool s/waves/diffract3.php
Huygens Principle
Argued that a wave front is a series of wavelets
Once the wave front hits a boundary the ends act as single point waves instead of a front and cause a circular pattern.
Now there in an interference pattern created.
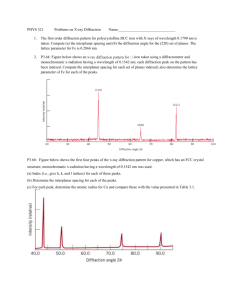
Scientist use diffraction patterns to determine the atomic structure of mystery crystals.
You can also create a diffraction pattern that produces a cool image instead of dots.
1.
What is diffraction?
2.
How does the wavelength of light effect the amount of diffraction?
So light is totally a wave right?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GzbKb5
9my3U
Uncertainty Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a8FTr2qMut
A
Go back to other PowerPoint