Chapter 12 – The Cell Cycle
advertisement

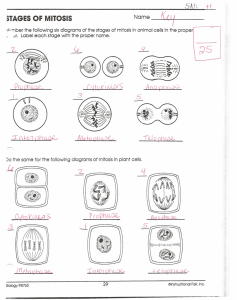
When printing slides, please use the print handout option and select black and white option. That way, you will not print black backgrounds and thus save ink! When printing slides, please use the print handout option and select black and white option. That way, you will not print black backgrounds and thus save ink! 12.1 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle 12.1 Mitotic cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells 12.2. Mitosis alternates with Interphase in the cell cycle 12.3. Not for exam Note the logarithmic scale 6.2 But first some sections of Ch. 6 Some paradigms in Biology 1. All organisms are composed of cells 2. There is a universal genetic code shared by all organisms and this code transmits information between generations. Capturing sharp images at many different planes 3D Variations in density Variations in density ~3D Electron microscopy dyes LightAdding to label molecules microscopy 6.3 6.4. Research Methods: Cell fractionation The disruption of a cell and separation of its parts by centrifugation at successively higher speeds. Bacteria, Archaea 6.5. A prokaryotic cell – lacking a true nucleus and other membrane-enclosed organelles 6.8. Animal cell Eukaryotic cell 6.8. A plant cell Eukaryotic cell DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid Chromosomes (DNA + proteins) Nucleic Acid Nucleotide Nucleosome 2 nm slinky Outline • What are cell division and eukaryotic chromosomes? • What is the cell cycle? • What is mitosis? • What is meiosis (Ch. 13)? • What are some meiotic errors (Ch. 13)? Functions of cell division: 1. Reproduction (single-celled organism) 2. Growth and development (multi-cellular organisms) 3. Renewal and repair. 12.2 Cells divide with most components equally shared among the daughter cells; but the DNA on chromosomes divides with exceptional precision! Mitosis 12.4, 12.5 Chromosome duplication and distribution during cell division 12.6. The cell cycle 12.7a. The mitotic division of an animal cell 12.7b. The mitotic division of an animal cell 12.10. Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells 12.11. Mitosis in a plant cell. Light micrographs showing mitosis in an onion root cell. Example Question • A cell containing 92 chromatids at the start of mitosis would, at its completion, produce cells containing how many chromosomes? – – – – – A) B) C) D) E) 12 23 92 16 46 12.19. Densitydependent inhibition and anchorage dependence of cell division. Cancer cells do not follow normal signals that regulate the cell cycle. They lack density-dependent inhibition (crowded cells stop dividing) and anchorage-dependence (must be attached to substrate in order to divide) and continue to divide and invade other tissues. Diving cells near the tip of an onion root. Identify a nucleus in each of the major stages of mitosis and describe major events occurring at each stage. Stages in Mitosis Fig 12.12. Bacterial cell division (binary fission) Look at Chapter 12 Review (book p. 244) • 12.1 Mitotic cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells • 12.2. Mitosis alternates with Interphase in the cell cycle • 12.3. Not for exam