AP Chemistry WS 11.2 Acid-Base Equilibria HOCl, HOBr, HOI Draw
advertisement

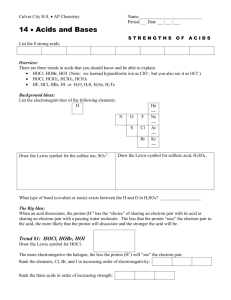
AP Chemistry WS 11.2 Acid-Base Equilibria 1. HOCl, HOBr, HOI Draw the Lewis structure for HOCl. (a) Rank the elements, Cl, Br, and I in increasing order of electronegativity: (b) Rank the three acids (from #1) in order of increasing strength: 2. HOCl, HClO2, HClO3, HClO4 Draw the Lewis structure for these acids: HOCl HClO2 HClO3 HClO4 (a) Which element has the lowest electronegativity value in these molecules? _________ (b) Each oxygen atom is very electronegative and attracts electrons. In which acid will the H + be most likely to attach to a passing water molecule? ___________ (c) Rank the four acids in order of increasing strength: 3. HF, HCl, HBr, HI (a) Rank the halogens in order of increasing electronegativity: (b) Rank the halogens in order of increasing size: (c) Rank the acids in order of increasing strength: (d) Which characteristic (size or electronegativity) is more important in explaining the strength of these acids? _______________ 4. Consider the acids, H2O, H2S, H2Se and H2Te. Rank these acids in order of increasing strength: 5. 6. Complete the chart for a 1 M solution of acid. Ionization reaction % ionization HCl(g) ⇆ H+ + Cl- 100 % HF(g) ⇆ H+ + F- 8% HCHO2 ⇆ H+ + CHO2- 4% Rank the following acids from strongest to weakest: Acid HBrO HClO Rank [HX] HClO2 [H+] [X-] HIO 1 7. Complete the chemical equation and write the Ka expression for the following weak acids. Ka expression Equation HC2H3O2(aq) ⇆ H2PO4- ⇆ H2CO3(aq) ⇆ HCO3-(aq) ⇆ 8. Ka1 for H2SO3 is 1.3 x 10-2 and Ka2 is 6.3 x 10-8. Write each dissociation equation and the overall equation. Calculate K for the reaction H2SO3 ⇆ 2 H+ + SO32-. 9. Complete the chemical equation and write the Kb expression for the following weak bases. Kb expression Equation F-(aq) + H2O ⇆ CH3NH2(aq) + H2O ⇆ 10. Classify the salts as acidic, or basic. NaCl Cu(NO3)2 KNO2 NH4Cl NaClO BaCl2 Na(C2H3O2)2 LiF 11. Write the dissociation equation that describes what happens when CH 3NH3Cl(s) is added to water. 12. Write the equation that describes the acidic character of CH3NH3+(aq), (salt hydrolysis reaction). 13. Predict the products when KCN(s) is added to water. Will the pH of the solution formed when the salt is added to water be greater or less than 7? 14. Consider the weak acid, HC2H3O2. Ka = 1.8 x 10-5 a. Write the acid dissociation equation for acetic acid. 2 b. What is the conjugate base of acetic acid? ____________________ c. A base is a proton ___________ (donor/acceptor). d. Finish this equilibrium equation (salt hydrolysis) : C2H3O2 e. + H2O Write the Kc expressions for the following reactions: The equation in “a”, the Ka The equation in “d”, the Kb Kw f. What is the relationship among these three expressions? g. Calculate the value of the Kb for the acetate ion. h. A 0.10 M solution of sodium acetate would have a pH __________ (>7, 7, <7). i. Calculate the [OH ] for a 0.10 M solution of sodium acetate. C2H3O2 H2O(l) HC2H3O2 OH Initial Change Equilibrium j. What is the pOH of the solution? _____ What is the pH of the solution? _____ 15. Cyanic acid HOCN has a Ka = 3.5 x 10 , what is the Kb for the cyanate ion OCN 16. Calculate the pH of a 0.35 M solution of potassium cyanide. Ka for HCN = 4.0 x10 . 3