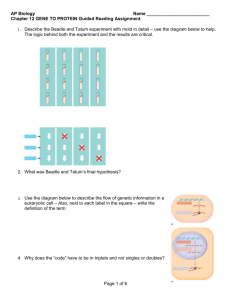
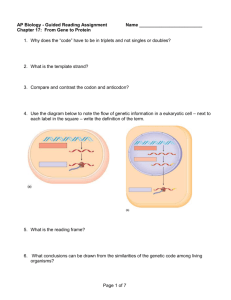
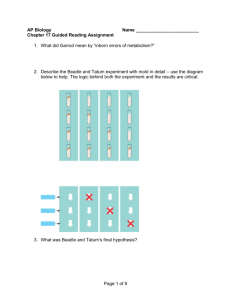
Transcription
advertisement

Transcription Gene Expression Part 1 Gene Expression • There are 4 major events that occur durin the process of gene expression – Transcription – RNA processing – Translation – Protein processing A Gene is a Transcription Unit Promoter Regulatory sequence Terminator DNA Transcription 3 mRNA 5 Start codon Ribosomalbinding site Many codons Stop codon Prokaryotic Gene Structure DNA +1 Cis-Regulatory Elements USE/Promoter /Operator ShineDelgarno box Stop Codon TAA, TAG, TGA ATG Coding Sequence = ORF 1 5’ UTR = Leader sequence Protein A Cistron 1 Regulatory Sequences ShineDelgarno box ATG Stop Codon Coding Sequence = ORF 2 Spacer = 5’UTR of 2nd cistron Protein B Cistron 2 Structural or Coding Sequences Regulatory and Coding Sequence Unit = Operon Termination sequence Prokaryotic Gene Structure DNA Shine-Delgarno Stop Codon Shine-Delgarno Stop Codon box TAA, TAG, TGA +1 box ATG ATG TAA, TAG, TGA Cis-Regulatory Coding Sequence= ORF Coding Sequence= ORF Elements USE/Promoter /Operator Protein A 5’ UTR = Leader sequence Cistron 1 Terminator sequence Cistron 2 5’ UTR = Leader sequence Polycistronic mRNA Protein B Spacer = 5’UTR of 2nd cistron Spacer ORF Protein A +1 AUG Shine-Delgarno box AUG Stop Codon Shine-Delgarno UAA, UAG, UGA box ORF Protein B Stop Codon UAA, UAG, UGA Eukaryotic Gene Structure CisRegulatory Elements Promoter/ Enhancer Stop Codon TAA, TAG, TGA Start Codon ATG Exon1 Exon2 Exon3 5’ UTR 3’ UTR Exon1 Exon2 Start Codon Exon1 5’ UTR Exon3 Stop Codon polyA tail Exon2 Exon3 AAAAAAAA 3’ UTR Transcription Proceeds Through 3 Steps Initiation • Transcription factors & RNA polymerase recognize & bind the promoter • DNA adjacent to the promoter is denatured forming the open promoter complex Elongation • RNA polymerase moves along the DNA in synthesizing a RNA transcript. Synthesis is 5’3’ – Only 1 strand of DNA is read as a template. Termination • A termination signal is reached causing RNA polymerase to dissociated from the DNA Figure 12.2 A Prokaryotic Promoter Coding strand Promoter –35 sequence 5 T TG AC A A AC T G T 3 Template strand Transcriptional start site –10 sequence +1 3 T AT AAT A A TAT TA T 5 A 5 RNA 3 Transcription Reaching A Consensus +1 Transcribed –35 region –10 region lac operon TTTACA N17 TATGTT N6 A lacI GCGCAAN17 CATGAT N7 A trp operon TTGACA N17 TTAACT N7 A rrnX TTGTCT N16 TAATAT N7 A recA TTGATA N16 TATAAT N7 A lexA TTCCAA N17 TATACT N6 A tRNAtyr TTTACA N16 TATGAT N7 A Consensus TTGACA TATAAT RNA Polymerases Structure of a bacterial RNA polymerase Structure of a eukaryotic RNA polymerase II RNA Polymerases • Differences between eukaryotes & prokaryotes • Prokaryotes – 1 enzyme with 4 subunits • 2 α’s, 1 , & 1 ’ • actual polymerase function – Sigma factors (σ ) • recognize & bind promoter DNA sequence • Eukaryotes – 3 separate holoenzymes – each has ~12 subunits • RNA Pol I – 28S, 18S, 5.8S rRNA • RNA Pol II – mRNA, snRNA • RNA Pol III – tRNA, 5S rRNA – 3 sets of basal transcription factors • recognize promoter DNA sequences The Process of Transcription • Initiation – Where/when most regulation of gene expression occurs – Different between proks & euks • Elongation – Essentially same between prokaryotes & eukaryotes – Some regulation, more in proks than euks • Termination – Different between proks & euks – Some regulation Prokaryotic Transcription Initiation Figure 12.6 Rho Dependent Termination in Prokaryotes rho utilization site Rho protein is a helicase Figure 12.8 r-dependent termination Rho Dependent Termination in Prokaryotes Figure 12.8 r-dependent termination Rho Independent Termination in Prokaryotes r-independent termination requires two sequences in the RNA – A stem-loop structure upstream of 7-9 U residues NusA Stabilizes the RNA pol pausing Figure 12.9 r-independent termination Eukaryotic Promoters Pol I • RNA Pol I – rRNA precursor UBF SL1 UCE Core 45S rRNA precursor Pol II • RNA Pol II – mRNAs, U6 snRNA • RNA Pol III – tRNA, 5S rRNA, GSTFs TFIID UAS TATA box Pol III pre-mRNA TFIIIB TFIIIC AB tRNA precursor The Pol II Transcription Initiation Complex Figure 12.12 Figure 12.12 Pol II Initiation Complex • TFIIH regulates formation of the open complex • • Has a helicase function that promotes melting of DNA Phosphorylates the carboxyl terminal domain domain of RNA pol II – RNA pol II releases TFIIB – Promoter clearance occurs RNA pol II proceeds to the elongation stage Chromatin Structure Affects Promoter Access Core histone proteins Histone acetyltransferase Histone deacetylase COCH3 COCH3 COCH3 COCH3 COCH3 COCH3 COCH 3 COCH3 COCH3 COCH3 COCH3 Acetyl group Histone acetylation ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex Change in the relative positions of a few nucleosomes Change in the spacing of nucleosomes over a long distance Chromatin remodeling