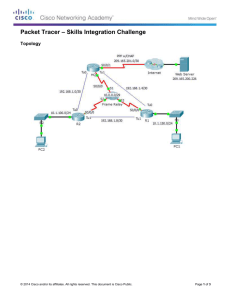
Windows Client Pro Practice Exams
advertisement

Lesson Plans LabSim Windows Client Pro Table of Contents Course Overview .................................................................................................. 3 Course Introduction for Instructors ........................................................................ 5 Section 1.1: Course Introduction ......................................................................... 11 Section 1.2: Windows as a Client........................................................................ 12 Section 1.3: Windows 7 User Interface Overview ............................................... 14 Section 1.4: Windows 8 User Interface Overview ............................................... 15 Section 2.1: Devices and Drivers ........................................................................ 17 Section 2.2: Display Management ...................................................................... 20 Section 2.3: Disk Partitions and Volumes ........................................................... 22 Section 2.4: Storage Spaces .............................................................................. 24 Section 2.5: Disk Optimization ............................................................................ 26 Section 2.6: Removable Storage ........................................................................ 28 Section 2.7: SkyDrive Storage ............................................................................ 29 Section 3.1: IPv4 ................................................................................................. 31 Section 3.2: IPv6 ................................................................................................. 33 Section 3.3: IP Address Configuration ................................................................ 36 Section 3.4: Wireless Networking Overview ....................................................... 39 Section 3.5: Wireless Networking Configuration ................................................. 42 Section 3.6: Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) .................................................. 44 Section 3.7: Windows Firewall ............................................................................ 45 Section 4.1: Desktop Applications....................................................................... 48 Section 4.2: User Account Control (UAC) ........................................................... 50 Section 4.3: Application Compatibility ................................................................. 52 Section 4.4: Application Virtualization ................................................................. 54 Section 4.5: Windows Store Applications ............................................................ 55 Section 5.1: Authentication and Authorization .................................................... 57 Section 5.2: Authentication Management ........................................................... 59 Section 5.3: Alternative Authentication Options .................................................. 61 Section 5.4: NTFS Permissions .......................................................................... 63 Section 5.5: Resource Sharing ........................................................................... 65 Section 5.6: Libraries and HomeGroups ............................................................. 67 Section 5.7: Printer Sharing and Management ................................................... 69 Section 5.8: Auditing ........................................................................................... 71 Section 5.9: Encryption ....................................................................................... 73 Section 5.10: BranchCache ................................................................................ 75 Section 6.1: Windows Versions........................................................................... 77 Section 6.2: Windows 7 Installation .................................................................... 80 Section 6.2: Windows 8 Installation .................................................................... 82 Section 6.4: Windows Upgrade ........................................................................... 84 Section 6.5: User Profile and Data Migration ...................................................... 86 Section 6.6: VHD Installation .............................................................................. 88 Section 6.7: Client-Side Virtualization ................................................................. 90 Section 7.1: System Images Overview ............................................................... 92 ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 1 Section 7.2: Image Preparation........................................................................... 93 Section 7.3: Image Capture ................................................................................ 95 Section 7.4: Manual Image Deployment ............................................................. 97 Section 7.5: Image Servicing .............................................................................. 98 Section 7.6: Domain Image Deployment........................................................... 100 Section 8.1: Network Access Protection (NAP)................................................. 102 Section 8.2: Virtual Private Network (VPN) ....................................................... 103 Section 8.3: DirectAccess ................................................................................. 105 Section 8.4: BitLocker ....................................................................................... 107 Section 8.5: BitLocker To Go ............................................................................ 109 Section 8.6: Mobile Device Security.................................................................. 111 Section 8.7: Power Management ...................................................................... 113 Section 8.8: Mobility Options ............................................................................ 115 Section 8.9: Mobile Networking......................................................................... 118 Section 9.1: Troubleshooting Tools................................................................... 120 Section 9.2: System Events .............................................................................. 122 Section 9.3: Performance Monitoring ................................................................ 124 Section 9.4: Resource Monitoring ..................................................................... 126 Section 9.5: Reliability and Performance Maintenance ..................................... 128 Section 9.6: Optimization .................................................................................. 130 Section 9.7: Remote Management.................................................................... 132 Section 9.8: Remote Assistance ....................................................................... 134 Section 10.1: System Updates .......................................................................... 136 Section 10.2: Update Deployment and Management........................................ 138 Section 10.3: System Backup ........................................................................... 140 Section 10.4: Windows 7 Data Recovery .......................................................... 142 Section 10.5: Windows 8 Data Recovery .......................................................... 144 Section 10.6: System Recovery ........................................................................ 146 Section 11.1: Application Restriction................................................................. 149 Section 11.2: Secure Boot ................................................................................ 151 Section 11.3: Internet Explorer.......................................................................... 153 Section 11.4: Internet Options .......................................................................... 156 Section 11.5: Windows Defender ...................................................................... 158 Windows Client Pro Practice Exams ................................................................. 160 MS 70-680 Practice Exams .............................................................................. 161 MS 70-687 Practice Exams .............................................................................. 162 Appendix A: Approximate Time for the Course ................................................. 163 Appendix B: Windows Client Pro Objectives ..................................................... 167 Appendix C: 70-680 TS: Windows 7, Configuring Objectives ........................... 172 Appendix D: 70-687 TS: Windows 8, Configuring Objectives ........................... 179 ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 2 Course Overview This course prepares students for TestOut’s LabSim Windows Client Pro, and Microsoft’s 70-680 and 70-687 certification exams. Module 1 – Course Introduction This module introduces the students to the objectives and content of the course. The students will learn how to use the LabSim simulator to complete lab exercises and an overview of the Windows 7 and 8 user interfaces are presented. Module 2 – Hardware Management In this module students will learn concepts about managing hardware devices such as device drivers, display options, storage devices and SkyDrive storage. Module 3 – Network Configuration This module teaches students about the elements used to configure the communication within the network: IP addresses, wireless communications, Internet Connection Sharing (ICS), and Windows Firewall. Module 4 – Application Management This module discusses managing applications both desktop and Windows store applications. Configuring User Account Control (UAC), application compatibility, and virtualization are all discussed. Module 5 – System Access This module examines elements that are used to control access to the system resources. Module 6 – Windows Installation In this module students will learn concepts about installing and upgrading a Windows operating system. Module 7 – System Images This module discusses using system images to centrally deploy Windows to computers throughout large environments. Module 8 – Mobile Computing This module discusses basic concepts of securely connecting to a network from a remote location. Module 9 – System Monitoring and Maintenance This module discusses troubleshooting tools and utilities to monitor and manage the system. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 3 Module 10 – System Protection This module examines tools that can be used to protect a system. This involves having a current system updates, and creating system backups to provide system recovery. Module 11 – Security In this module students will learn about the tools and options to secure the system. Practice Exams In Practice Exams students will have the opportunity to test themselves and verify that they understand the concepts and are ready to take the certification exam. The practice exams are divided into three separate areas and will contain examples of the types of questions that a student will find on the actual exam: Windows Client Pro Certification Practice Exams MS 70-680 Practice Exams MS 70-687 Practice Exams ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 4 Course Introduction for Instructors This course provides students with the knowledge to become industry certified as a Windows professional. This course actually meets the specifications for three different industry certification programs. It prepares the student for the following: TestOut's Windows Client Pro certification Microsoft’s 70-680 TS: Windows 7, Configuring certification Microsoft’s 70-687 TS: Windows 8, Configuring certification TestOut’s Windows Client Pro certification is a new certification which measures not just what you know, but what you can do. The TestOut Client Pro Certification measures your ability to manage install, manage, configure, monitor and troubleshoot both Windows 7 and Windows 8 client systems. The following knowledge domains are addressed: Install Windows Manage Access Manage Applications Manage Hardware Manage Storage Configure Networking Configure Printing Configure System Protection Configure Security Monitor the System Configure Virtualization Note: Windows Client Pro objectives are listed in Appendix B: Windows Client Pro Objectives. Microsoft’s 70-680 TS: Windows 7, Configuring certification measures the students’ ability to install, configure, maintain, and troubleshoot the Windows 7 operating system. The following knowledge domains are addressed: Installing, Upgrading, and Migrating to Windows 7 Deploying Windows 7 Configuring Hardware and Applications Configuring Network Connectivity Configuring Access to Resources Configuring Mobile Computing Monitoring and Maintaining System that Run Windows 7 Configuring Backup and Recovery Options ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 5 Note: MS 70-680 objectives are listed in Appendix C: 70-680 TS: Windows 7, Configuring Objectives. Microsoft’s 70-687 TS: Windows 8, Configuring certification ensures students have the skills to install, configure, maintain, and troubleshoot the Windows 8 operating system. The following knowledge domains are addressed: Install and Upgrade to Windows 8 Configure Hardware and Applications Configure Network Connectivity Configure Access to Resources Configure Remote Access and Mobility Monitor and Maintain Windows Clients Configure Backup and Recovery Options Note: MS 70-687 objectives are listed in Appendix D: 70-687 TS: Windows 8, Configuring Objectives. The section introductions in LabSim and the lesson plans list the objectives that are met for each of the exams in that section. The following icons are placed in front of lesson items in LabSim to help students quickly recognize the items in each section: = Demonstration = Exam = Lab/Simulation = Text lesson or fact sheet = Video The video and demonstration icons are used throughout the lesson plans to help instructors differentiate between the timing for the videos and demonstrations. In the lesson plans the Total Time for each section is calculated by adding the approximate time for each section which is calculated using the following elements: Video/demo times Approximate time to read the text lesson (the length of each text lesson is taken into consideration) ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 6 Simulations (5 minutes is assigned per simulation. This is the amount of time it would take for a knowledgeable student to complete the lab activity. Plan that the new students will take much longer than this depending upon their knowledge level and computer experience.) Questions (1 minute per question) Note : Appendix A: Approximate Time for the Course contains the approximate time for each section which are totaled for the entire course. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 7 Comparison of MS 70-680 and MS 70-687 Objectives Covered in LabSim Windows Client Pro The following table maps out where the MS 70-680 and MS 70-687 objectives are covered in the Windows Client Pro course. (Remember the objectives are in the appendixes.) MS 70-680 Exam MS 70-687 Exam Objectives Objectives Windows Client Pro Sections X = This section meets objectives for the identified exam. 1.0 Course Introduction 1.1 Course Introduction 1.2 Windows as a Client 403 1.3 Windows 7 User Interface Overview 1.4 Windows 8 User Interface Overview 2.0 Hardware Management 2.1 Devices and Drivers 301, 704 201 2.2 Display Management 704 603 2.3 Disk Partitions and Volumes 702 602 2.5 Disk Optimization 702 402, 602 2.6 Removable Storage 702 204 2.4 Storage Spaces 602 2.7 SkyDrive Storage 401 3.0 Network Configuration 3.1 IPv4 401 301, 303 3.2 IPv6 402 301, 303 401, 402 301 3.4 Wireless Networking Overview 403 302, 303 3.5 Wireless Networking Configuration 403 302, 303 3.5 Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) 403 3.7 Windows Firewall 404 3.3 IP Address Configuration 303 4.0 Application Management 4.1 Desktop Applications 202 4.2 User Account Control (UAC) 503 403 4.3 Application Compatibility 302 202 4.4 Application Virtualization 202 4.5 Windows Store Applications 203 ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 8 5.0 System Access 5.1 Authentication and Authorization 504 404 5.2 Authentication Management 504 404 5.3 Alternative Authentication Options 404 5.4 NTFS Permissions 502 402 5.5 Resource Sharing 501 103, 401 5.6 Libraries and HomeGroups 501 103, 401 403, 501 302, 401 5.8 Auditing 604 402 5.9 Encryption 502 402 5.10 BranchCache 505 5.7 Printer Sharing and Management 6.0 Windows Installation 6.1 Windows Versions 101 6.2 Windows 7 Installation 101 6.3 Windows 8 Installation 101 102 6.4 Windows Upgrade 102 102 6.5 User Profile and Data Migration 103 103 6.6 VHD Installation 204 102, 206 6.7 Client-Side Virtualization 204 102, 206 7.0 System Images 7.1 System Images Overview 201 7.2 Image Preparation 201 7.3 Image Capture 201 7.4 Manual Image Deployment 203 7.5 Image Servicing 202 7.6 Domain Image Deployment 203 8.0 Mobile Computing 8.1 Network Access Protection (NAP) 604 8.2 Virtual Private network (VPN) 604 501 8.3 DirectAccess 602 8.4 BitLocker 601 503 8.5 BitLocker To Go 601 503 8.6 Mobile Device Security 8.7 Power Management 8.8 Mobility Options 8.9 Mobile Networking ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 503 704 502 603, 704 501, 502 401, 502 9 9.0 System Monitoring and Maintenance 9.1 Troubleshooting Tools 703, 704 603 703 501, 603 703, 704 603 9.4 Resource Monitoring 703 603 9.5 Reliability and Performance Maintenance 403 603 9.6 Optimization 704 603 405, 604 304, 501 405 304 10.1 System Updates 701 601 10.2 Update Deployment and Management 701 601 10.3 System Backup 801 701 10.4 Windows 7 Data Recovery 803 9.2 System Events 9.3 Performance Monitoring 9.7 Remote Management 9.8 Remote Assistance 10.0 System Protection 10.5 Windows 8 Data Recovery 10.6 System Recovery 703 802 702 303 204 11.0 Security 11.1 Application Restriction 11.2 Secure Boot 403 11.3 Internet Explorer 302, 304 205, 403 11.4 Internet Options 304 205 Windows Client Pro Practice Exams X X MS 70-680 Practice Exams X 11.5 Windows Defender Certification Practice Exams MS 70-687 Practice Exams X In addition to covering everything the student needs to know for the MS 70-680 and MS 70-687 exams, this course has been designed to help students gain realworld skills that they will use every day on-the-job as a IT professional. The real world skills are what are needed to pass the Client Pro Certification exam. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 10 Section 1.1: Course Introduction Summary This section provides an introduction of the course. Basics discussed include: Three exams that the course materials prepares the student for: o Microsoft 70-680 o Microsoft 70-687 o TestOut Windows Client Pro Objectives for each certification exam Lecture Focus Questions: What are the different certifications that the Microsoft 70-680 can either fulfill the requirements for or be used as credit towards? What Windows operating system does the Microsoft 70-687 focus on? What are the major differences between the TestOut Windows Client Pro exam and Microsoft 70-680/70-687 exams? Video/Demo Time 1.1.1 Course Introduction 5:46 1.1.2 Completing Lab Exercises 9:04 Total 14:50 Total Time About 20 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 11 Section 1.2: Windows as a Client Summary This section discusses the functionality of Windows as a client. Students will become familiar with the: Networking models used with Windows operating systems: o Stand-Alone o Workgroup o Client-Server Key components of Active Directory: o Security principals o Domains o Domain controllers o Objects o Container objects o Organizational unit o Generic containers The role of GPOs GPO settings are divided into two categories: o Computer Configuration o User Configuration Key configuration settings: o Account Policies o Local Policies/Audit Policy o Local Policies/User Rights Assignment o Local policies/Security Options o Registry Policies o File System o Software Restriction Policies o Administration Templates 70-687 Exam Objectives: 403. Configure local security settings. o Configure local security policy ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 12 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the main differences between the workgroup network model and the domain network model? What might be a disadvantage of a large company using a peer-to-peer network model? When considering the two GPO categories, how are they the same? How are they different? What type of actions does the Local Policies/User Rights Assignments control? In what order are policies applied? Video/Demo 1.2.1 Windows Operating System Roles Time 11:26 1.2.2 Using Local User Accounts for Logon 6:16 1.2.3 Using Online User Accounts for Logon 2:30 1.2.5 Using Domain User Accounts for Logon 4:09 1.2.6 Group Policies 8:53 Total 33:14 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 13 Section 1.3: Windows 7 User Interface Overview Summary This section provides an overview of the Windows 7 user interface. Students will become familiar with the: Windows 7 user interface: o Desktop o Start menu o Taskbar Windows 7 keyboard shortcuts Students will learn how to: Configure the system to be more secure by requiring the screensaver to activate after the system has been idle for a defined amount of time, requiring the user to logon before the system will resume. Lecture Focus Questions: How can you quickly identify a shortcut on the desktop? What is a gadget on the desktop? On the Start menu, what is the difference between the applications listed above the horizontal line and those listed below it? What were some of the enhancements to the Start menu that were introduced in Windows 7? Which keyboard shortcut allows you to view the desktop by making all windows on the desktop transparent? Video/Demo 1.3.1 Windows 7 User Interface 1.3.2 Using the Windows 7 User Interface Total Time 8:39 10:47 19:26 Lab/Activity Use the Windows 7 User Interface Total Time About 25 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 14 Section 1.4: Windows 8 User Interface Overview Summary This section provides an overview of the Windows 8 user interface. Students will become familiar with the: Windows 8 user interface: o Start o Tiles o App Bar o Charms menu Windows 7 keyboard shortcuts Navigating Start in Windows 8 Gestures used with Windows 8 on a touch screen device Keyboard shortcuts Using the Search pane in Windows 8 Students will learn how to: Access the Charms menu. Use the Search pane to search for apps, configuration settings, and files. Configure a wireless network adapter to run in Airplane mode. Lecture Focus Questions: In the Windows 8 interface, what replaces the Start button? What different types of tiles are used and how can you differentiate them from each other? What different methods can be used to bring up the App bar? What is the difference between performing a swipe and a slide and the function of each? How would you display the on-screen keyboard within a Windows 8 app? Within a traditional Desktop app? Which keyboard shortcuts do you think you will consistently use? How does the Search pane work differently from previous versions of Windows? Video/Demo Time 1.4.1 Windows 8 User Interface 8:56 1.4.2 Windows 8 Gestures 8:13 1.4.3 Using the Windows 8 User Interface Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 10:00 27:09 15 Lab/Activity Use the Windows 8 User Interface Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 16 Section 2.1: Devices and Drivers Summary This section discusses managing devices and drivers. Basics discussed include: Categories of hardware devices: o Always present o Usually present with variable parameters o May or may not be present Considerations regarding device drivers: o Windows driver store o Driver staging Management options for device drivers: o Device Manager o Microsoft System Information o Devices and Printers o Group Policies o Reliability Monitor o Driver Verifier o Microsoft Validation Process Device driver configuration and troubleshooting details Tools to configure and troubleshoot device drivers: o Device Manager o Devices and Printers o PnPUtil o Group Policy Settings o System Information (Msinfo32) o Reliability Monitor o Driver Verifier Monitor o Driver Query o Signature Verification o DirectX Diagnostic Students will learn how to: Use the PnPUtil tool to stage a driver or remove a driver in the driver store. Use Device Manager to enable and disable devices, as well as roll back or install device drivers. Use Group Policy to manage and maintain drivers. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 4.0 Hardware o Manage devices in Device Manager by doing the following: ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 17 Install, uninstall, and rollback device drivers. Disable and enable hardware devices. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 301. Configure devices. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Updating, disabling, and uninstalling drivers o Signed drivers o Conflicts between drivers o Configuring driver settings o Resolving problem device driver 704 Configure performance settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Updated drivers 70-687 Exam Objectives: 201. Configure devices and device drivers. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Install, update, disable, and roll back drivers o Resolve driver issues o Configure driver settings Lecture Focus Questions: What does it mean to stage a driver? What are the advantages of placing drivers in the driver store? What does Windows do when it cannot find a driver in the driver store? How can you be assured that a driver is stable and reliable? Which tool lists drivers which do not have a digital signature? Which tool will troubleshoot problems with printers? Video/Demo 2.1.1 Device and Driver Configuration 2.1.3 Managing Devices Time 8:34 10:38 2.1.5 Troubleshooting Devices 8:13 2.1.6 Staging a Driver 5:49 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 33:14 18 Lab/Activity Manage Devices 1 Manage Devices 2 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 60 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 19 Section 2.2: Display Management Summary In this section students will learn to manage and configure a computer’s display. Concepts covered in this section include: Themes and options to modify a computer’s background, display characteristics, and sounds: o Themes o Desktop background o Window Color and Appearance o Sounds o Screen Saver Setting Settings to change the display: o Adjust size o Adjust resolution o Adjust brightness o Connect to a projector o Adjust ClearType text o Set custom text size (DPT) Adjusting visual effects on the computer Students will learn how to: Configure settings to optimize the performance of the adapter and monitor. Disable various visual effects. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 4.0 Hardware o Customize display settings. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 704. Configure performance settings. o Configuring desktop environment 70-687 Exam Objectives: 603. Monitor system performance. o Optimize the desktop environment ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 20 Lecture Focus Questions: You don't like any of the themes that are offered. What are your options for configuring a theme that is more to your liking? What are the different display options available for your desktop background? In the desktop background how would you change the order in which multiple pictures are displayed? In screen saver, what type of security does the On resume, display logon screen option provide? Video/Demo Time 2.2.1 Configuring Display Settings 10:57 2.2.2 Optimizing Video 11:56 Total 22:53 Lab/Activity Optimize Video Settings Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 21 Section 2.3: Disk Partitions and Volumes Summary This section examines managing disk partitions and volumes. Concepts covered include: Benefits of using multiple volumes on a disk or multiple disks Actions to perform after installing a new disk Partitioning schemes: o Master Boot Record (MBR) o Globally unique identifier (GUID) Partition Table (GPT) Disk types: o Basic o Dynamic Considerations when managing partitions and volumes Students will learn how to: Use Disk Management to create and resize a volume. Use Disk Management to create simple, spanned, striped, and mirrored volumes. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 5.0 Storage o Add storage to a Windows system by doing the following: Add storage devices to the system. Create, format and mount volumes. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 702. Manage disks. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Managing disk volumes o RAID 70-687 Exam Objectives: 602. Manage local storage. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Manage disk volumes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 22 Lecture Focus Questions: In which circumstances do you need multiple partitions on a single disk? What is the difference between the Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) Partition Table (GPT) and the Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning schemes? What is the difference between a partition and a volume? When working with volumes, when would you choose a basic disk over a dynamic disk? Which details should you consider when converting from a dynamic disk to a basic disk? What is the difference between a spanned volume and a striped volume? Video/Demo 2.3.1 Disk Preparation Time 9:55 2.3.2 Volume Management 11:10 2.3.3 Creating and Resizing Volumes 15:24 Total 36:29 Lab/Activity Create Volumes Add Space to an Existing Volume Resize Existing Volumes Create a Mount Point Number of Exam Questions 12 questions Total Time About 75 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 23 Section 2.4: Storage Spaces Summary This section provides information about managing storage spaces. Concepts covered include: Components of storage space : o Devices o Pools of storage o Storage spaces Benefits of using storage spaces: o Ease of adding space o Data resiliency: Simple Two-way mirror Three-way mirror Parity o Thin provisioning (overbooking) Students will learn how to: Use the Storage Spaces tool to create a pool from multiple storage devices and then define a storage space from the pool of storage. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 5.0 Storage o Add storage to a Windows 8 system by doing the following: Define storage pools. Create storage spaces. 70-687 Exam Objectives: 602. Manage local storage. o Manage storage spaces Lecture Focus Questions: What components are used to create storage spaces? What is the difference between a storage pool and a storage space? Which hardware devices can be used to make storage pools? What are the benefits of using storage pools? You are comparing the hardware required for two-way mirroring and threeway mirroring. What is the minimum number of disks required for each data resiliency type? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 24 How does thin provisioning allow you to allocate more storage space to users than is available in the pool? Video/Demo Time 2.4.1 Storage Spaces 11:42 2.4.2 Creating Storage Spaces 10:37 Total 22:19 Lab/Activity Implement Storage Spaces Overbook Storage Spaces Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 25 Section 2.5: Disk Optimization Summary This section discusses the following methods for optimizing a disk drive: Disk Cleanup Disk Defragmenter Check Disk Quotas Students will learn how to: Defragment the files on a disk to optimize the performance of the disk. Create a hard quota that does not let a user exceed a specified amount of disk space. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 5.0 Storage o Manage storage on a Windows system by doing the following: Optimize storage devices Check storage devices and file systems for errors 70-680 Exam Objectives: 702 Manage disks. o Managing disk volumes o Managing file system fragmentation 70-687 Exam Objectives: 402 Configure file and folder access: o Configure disk quotas 602 Manage local storage. o Manage disk volumes o Manage file system fragmentation ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 26 Lecture Focus Questions: How does the Disk Defragmenter optimize the performance of a hard drive? What kind of functions does the Disk Cleanup utility perform? How can you delete restore points with the Disk Cleanup utility? What does Check Disk attempt to do with orphaned files? How can you monitor and restrict disk usage by users? What is the difference between a hard quota and a soft quota? Video/Demo Time 2.5.1 Disk Optimization 5:11 2.5.2 Configuring Defragmentation and Disk Quotas 9:58 Total 15:09 Lab/Activity Perform Disk Maintenance Enable Disk Quotas Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 27 Section 2.6: Removable Storage Summary This section examines how to control reading and writing to removable storage device. Students will learn how to: Use Group Policy to manage removable media permissions. 70-680 Exam Objectives: Use Group Policy to manage removable media permissions. 70-687 Exam Objectives: 204 Control access to local hardware and applications. o Configure access through Group Policy or local security policy o Manage installation of removable devices Lecture Focus Questions: How can you prohibit the removal of sensitive data from the network? When would you use a Custom Classes policy? How can you immediately enforce removable media settings in Group Policy? Video/Demo 2.6.1 Removable Storage Policies Time 1:11 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 5 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 28 Section 2.7: SkyDrive Storage Summary In this section students will explore using SkyDrive which is Microsoft’s cloud storage service to upload files to cloud storage folders. Students will learn how to: Copy files to your SkyDrive account using a Microsoft user account. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Share system resources on a Windows system by doing the following: Use SkyDrive to store files. (Windows 8 only) 70-687 Exam Objectives: 401 Configure shared resources. o Setup and configure SkyDrive Lecture Focus Questions: What type of files can you upload to SkyDrive? What are the benefits of using SkyDrive? How can you add space to your SkyDrive account? How would you access SkyDrive if you are using Windows 7? What kind of functions does file and folder syncing in SkyDrive provide? How can you remotely access files from a computer or device with the SkyDrive app installed? Video/Demo Time 2.7.1 SkyDrive 4:03 2.7.2 Configuring SkyDrive 7:11 Total 11:14 Lab/Activity Configure SkyDrive Storage ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 29 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 30 Section 3.1: IPv4 Summary This section provides an overview of Ipv4 address concepts. IPv4 is a 32-bit binary number represented by four octets (four 8-bit numbers) that can represented as: o Decimal o Binary Converting from binary to decimal Subnet mask Default address classes Networking services o Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) o Domain Name System (DNS) o Network Address Translation (NAT) Considerations for IPv4 addresses Subnetting Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Given a network diagram, configure network settings on a Windows system by doing the following: Configure an appropriate IPv4 address, subnet mask, default gateway address, and DNS server address. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 401 Configure IPv4 network settings. o Connecting to a network o Configuring name resolution o Setting up a connection for a network o Network locations o Resolving connectivity issues o APIPA 70-687 Exam Objectives: 301 Configure IP settings. o Configure name resolution o Connect to a network o Configure network locations o Resolve connectivity issues ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 31 303 Configure and maintain network security. o Configure network discovery Lecture Focus Questions: What is the function of the subnet mask? How can you divide a large network into smaller networks? What does the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation represent? What does it mean if a Windows client has an IP address of 169.254.0.3 with the subnet mask of 255.255.0.0? What is the advantage of using NAT? How can you determine if individual computers are on the same network? How do Windows clients resolve host names to IP addresses? Video/Demo Time 3.1.1 IPv4 Addresses 10:57 3.1.3 IPv4 Subnetting 6:34 Total 17:31 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 32 Section 3.2: IPv6 Summary This section discusses the basics of IPv6 addresses. Concepts covered include: IPv6 features not included in IPv4: o Address space o Header improvements o Route aggregation o Built-in security features o Built-in Quality of Service (QoS) o Neighbor Discovery (ND) o Geographic assignment of addresses o Multiple IP addresses per device IPv6 address is a 128-bit binary number which contains two parts: o Prefix o Interface ID IPv6 identifies the following types of addresses: o Reserved o Unicast Global unicast Link-local Unique local o Multicast o Anycast o Loopback o Unspecified Considerations about IPv6 Strategies for deploying IPv6: o IPv4-mapped address Tunneling: IPv4-compatible address Intra-site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) 6-to-4 tunneling Teredo tunneling Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Given a network diagram, configure network settings on a Windows system by doing the following: Configure IPv6 settings. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 33 70-680 Exam Objectives: 402 Configure IPv6 network settings. o Configuring name resolution o Connecting to a network o Setting up a connection for a network o Network locations o Resolving connectivity issues o Link local multicast name resolution 70-687 Exam Objectives: 301 Configure IP settings. o Configure name resolution o Connect to a network o Configure network locations o Resolve connectivity issues 303 Configure and maintain network security. o Configure network discovery Lecture Focus Questions: Why doesn't IPv6 require NAT and PAT? Which portion of an IPv6 address represents the prefix, and which portion represents the interface ID? What is the difference between a link-local and a unique local unicast address? What is the difference between a unicast address and an anycast address? When implementing IPv6, which transition methods incorporate an IPv4 address? Video/Demo Time 3.2.1 IPv6 Features 3:18 3.2.3 IPv6 Addresses 4:29 3.2.5 IPv6 Implementations 2:59 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 10:46 34 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 35 Section 3.3: IP Address Configuration Summary In this section students will learn about configuring and troubleshooting IP addresses. Concepts covered include: Options for assigning IPv4 addresses and other IPv4 configuration values: o Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) o Static (manual assignment) o Automatic Private IPv4 Addressing (APIPA) o Alternate IPv4 configuration Methods to configure an IPv6 address: o Static full assignment o Static partial assignment o Stateless autoconfiguration o DHCPv6 Tools to troubleshoot network problems: o Event Viewer o Windows Network Diagnostics o Ipconfig o Ping o Tracert o Pathping o Unified tracing o Nslookup o Netstat o Netsh o Network and Sharing Center Students will learn how to: Configure a computer with a static address. Configure an IPv4-compatible address while transitioning to IPv6. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Given a network diagram, configure network settings on a Windows system by doing the following: Configure an appropriate IPv4 address, subnet mask, default gateway address, and DNS server address. Configure IPv6 settings. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 36 70-680 Exam Objectives: 401. Configure IPv4 network settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Connecting to a network o Configuring name resolution o Setting up a connection for a network o Network locations o Resolving connectivity issues o APIPA 402. Configure IPv6 network settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring name resolution o Connecting to a network o Setting up a connection for a network o Network locations o Resolving connectivity issues 70-687 Exam Objectives: 301 Configure IP settings. o Configure name resolution o Connect to a network o Configure network locations o Resolve connectivity issues Lecture Focus Questions: When would you choose to manually assign IPv4 addressing information for a network adapter? How is IP addressing different for APIPA versus DHCP? When would you choose to use DHCP to assign IP addresses? When using IPv6 stateless autoconfiguration, how do the clients learn the addresses of other clients on the network? What is the difference between the two modes of DHCPv6? Video/Demo Time 3.3.1 IP Address Configuration 2:13 3.3.4 TCP/IP Troubleshooting Tools 4:02 3.3.5 Configuring and Troubleshooting IPv4 9:26 3.3.7 Configuring and Troubleshooting IPv6 6:47 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 22:28 37 Lab/Activity Configure IPv4 Settings Configure IPv6 Settings Number of Exam Questions 14 questions Total Time About 55 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 38 Section 3.4: Wireless Networking Overview Summary This section provides an overview of wireless networking. Concepts covered include: Details of a wireless networking architecture: o Devices o Connection Method Ad hoc Infrastructure o SSID (Service Set Identifier) Comparison of specification of the following standards: o 802.11a o 802.11b o 802.11g o 802.11n Technologies used by 802.11n to improve the speed or the distance of wireless transmissions: o Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) o Channel bonding Facts regarding the wireless networks Methods to authenticate to wireless networks: o Open o Shared key o 802.1x Standards for security for wireless networking: o Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) o Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) o Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) or 802.11i Practices to provide a level of security for a wireless network: o Change the administrator account name and password o Change SSID from defaults o Update the firmware o Enable the firewall on the access point o Disable DHCP o Enable MAC address filtering o Enable IPSec ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 39 Students will learn how to: Identify the architecture used by a given wireless network. Identify the correct hardware required to connect to a given wireless network. Determine the correct security method required to connect to a given wireless network. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Enable networking on Windows by doing the following: Install a wireless network interface and configure it to do the following: Securely connect to a wireless access point. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 403. Configure networking settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Adding a physically connected (wired) or wireless device o Connecting to a wireless network o Configuring security settings on the client o Set preferred wireless networks o Configuring network adapters 70-687 Exam Objectives: 302. Configure network settings. o Connect to a wireless network o Manage preferred wireless networks o Configure network adapters 303. Configure and maintain network security. o Manage wireless security Lecture Focus Questions: What type of devices are used in a wireless network? When could you use an ad-hoc wireless network? What are the advantages of using an infrastructure wireless network? How does channel bonding increase the performance of wireless transmissions? How does 802.1x provide greater authentication security than other authentication methods? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 40 Video/Demo 3.4.1 Wireless Networking Time 8:53 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 41 Section 3.5: Wireless Networking Configuration Summary This section discusses configuring wireless connections. Concepts covered include: Tools for managing wireless network connections: o Wireless network icon o Network and Sharing Center o Netsh wlan command Considerations when having trouble establishing or keeping a wireless connection: o Incorrect configuration o Range and obstructions o Access point placement o Channel interference o Automatic switching (roaming) Students will learn how to: Create and connect to an ad-hoc wireless network. Connect to an infrastructure wireless network. Manually connect to a network whose SSID is not being broadcast. Create and save a wireless profile. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Enable networking on Windows by doing the following: Install a wireless network interface and configure it to do the following: Securely connect to a wireless access point. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 403. Configure networking settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Adding a physically connected (wired) or wireless device o Connecting to a wireless network o Configuring security settings on the client o Set preferred wireless networks o Configuring network adapters ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 42 70-687 Exam Objectives: 302. Configure network settings. o Connect to a wireless network o Manage preferred wireless networks o Configure network adapters 303. Configure and maintain network security. o Manage wireless security Lecture Focus Questions: What type of information does a wireless profile contain? How can a Windows system connect to a wireless network? What could cause a Windows system to disconnect intermittently from a wireless network? What materials can block a wireless network's radio signals? Video/Demo Time 3.5.1 Managing Wireless Connections in Windows 7 9:59 3.5.2 Managing Wireless Connections in Windows 8 9:16 3.5.6 Wireless Network Troubleshooting 2:51 Total 22:06 Lab/Activity Connect to a Wireless Network Configure a Wireless Profile Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 43 Section 3.6: Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) Summary This section discusses Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) which allows multiple computers to share a single Internet connection. Details include: Configuring Internet Connection Sharing (ICS): o Configuring the ICS host o Configuring ICS clients Considerations when using ICS Students will learn how to: Configure an ICS host. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 403. Configure networking settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring network adapters Lecture Focus Questions: What are the advantages of using ICS in a small network? What are the differences between an ICS host and an ICS client? How many network adapters are required before you can implement ICS? Which network adapter on the ICS host will have 192.168.137.1 as the IP address? Video/Demo 3.6.1 Configuring ICS Time 5:17 Lab/Activity Configure ICS Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 15 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 44 Section 3.7: Windows Firewall Summary In this section students will learn the basics of configuring Windows Firewall. Concepts covered in this section include: The role of Windows Firewall Two main types of firewalls: o Network firewalls o Host-based firewalls Concepts for implementing a Windows Firewall: o Types of Windows Firewall o Network Location Awareness (NLA) o Configuring Windows Firewall Firewall exceptions: o File and Print Sharing o Network Discovery o Performance Logs and Alerts o Routing and Remote Access o Windows Remote Management o Remote Assistance o Remote Desktop o Windows Management Instrumentation o Windows Media Player o Windows Media Player Network Sharing Service Windows Firewall with Advanced Security (WFAS) types of rules: o Program o Port o Predefined o Custom Connection security rule types: o Isolation o Authentication exemption o Server-to-server o Tunnel o Custom Rule scope options to apply to traffic: o Allow the connection o Block the connection o Allow the connection if it is secure o Override block rules Connection security rule types: o Isolation o Authentication exemption o Server-to-server ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 45 o Tunnel o Custom Options to configure the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security: o Firewall state o Inbound connections o Outbound connection Windows Firewall considerations Students will learn how to: Configure the Windows Firewall to protect the computer from outside sources. Create inbound and outbound rules using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security snap-in. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: Configure Windows Firewall and Windows Firewall with Advanced Security rules. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 404. Configure Windows Firewall. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring rules for multiple profiles o Allowing or denying an application o Network-profile-specific rules o Configuring notifications o Configuring authenticated exceptions 70-687 Exam Objectives: 303 Configure and maintain network security. o Configure Windows Firewall o Configure Windows Firewall with Advanced Security o Configure connection security rules (IPSec) o Configure authenticated exceptions o Configure network discovery ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 46 Lecture Focus Questions: How does Windows Firewall protect users from intrusion attempts? Why does Windows Firewall provide a list of predefined firewall exceptions? When would you choose to use the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security snap-in over the Windows Firewall control panel? What type of connection security rule protects traffic based on IP addresses? Video/Demo 3.7.1 Windows Firewall 3.7.2 Configuring Windows Firewall Time 7:17 10:40 3.7.5 Windows Firewall with Advanced Security (WFAS) 6:31 3.7.6 Configuring WFAS 7:25 3.7.7 Configuring an IPSEC Connection in WFAS 8:38 Total 40:31 Lab/Activity Configure the Windows Firewall Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 65 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 47 Section 4.1: Desktop Applications Summary This section discusses considerations when installing and managing desktop applications. Details include: Actions to take before installing a desktop application Accessing Control Panel in Windows 7 and Windows 8 Options for managing applications in Programs and Features: o Change o Repair o Uninstall Students will learn how to: Install and manage desktop applications. Associate a file type or protocol with a program. Set default programs for file types and protocols. Repair a desktop application using either Programs and Features in Control Panel or msi.exe at the command line. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 3.0 Applications o Manage Windows applications by doing the following: Install a standard Windows application using Windows Installer. 70-687 Exam Objectives: 202 Install and configure desktop applications. o Install and repair applications by using Windows Installer o Configure default program settings o Modify file associations Lecture Focus Questions: How can you install a desktop application using msi.exe? How can you manage a desktop application installed on a Windows system? What steps should you take before installing a desktop application? Why would you associate a file type with a specific program? How can you repair a desktop application that isn't functioning properly? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 48 Video/Demo Time 4.1.1 Desktop Applications 9:35 4.1.2 Managing Desktop Applications 8:44 4.1.3 Modifying File Associations 6:28 4.1.4 Repairing Desktop Applications 7:36 Total 32:23 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 49 Section 4.2: User Account Control (UAC) Summary This section provides basic information about the User Account Control (UAC) tool. Concepts covered include: Standard user account Administrator account UAC concepts: o Privilege elevation o Admin Approval Mode The role of the access token Notification level settings: o Always notify o Notify me only when programs try to make changes to my computer o Notify me only when programs try to make changes to my computer (do not dim the desktop) o Never notify Students will learn how to: Manage Secure Desktop and UAC notification levels. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: o Configure User Account Control (UAC) rules. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 503. Configure user account control (UAC). This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring local security policy o Configuring admin vs. standard UAC prompt behaviors o Configuring Secure Desktop 70-687 Exam Objectives: 403 Configure local security settings. o Configure User Account Control (UAC) behavior ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 50 Lecture Focus Questions: What is the recommended UAC notification level setting? Why? How does UAC determine the type of actions that a user can perform on the system? How does privilege elevation work? What is the purpose of the Secure Desktop? How would you identify when Secure Desktop is activated? Under which circumstances would you use Group Policy to configure UAC settings? Video/Demo 4.2.1 User Account Control (UAC) 4.2.2 Configuring UAC Settings Total Time 5:33 11:15 16:48 Lab/Activity Configure UAC Settings 1 Configure UAC Settings 2 Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 51 Section 4.3: Application Compatibility Summary In this section students will learn compatibility methods to use when using older applications with new versions of Windows. Options covered include: Program Compatibility Application Compatibility Toolkit (ACT) Windows XP mode Group policies Students will learn how to: Use the Program Compatibility Troubleshooter utility to handle application compatibility issues. Manually configure the compatibility mode in the properties of an application. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 3.0 Applications o Manage Windows application by doing the following: Run an application in Compatibility Mode 70-680 Exam Objectives: 302. Configure application compatibility. o Setting compatibility mode o Implementing shims 70-687 Exam Objectives: 202. Install and configure desktop applications. o Set compatibility mode Lecture Focus Questions: What are the requirements for Windows XP Mode? What must you do to use Windows XP Mode? What tools are available to solve application compatibility problems with Windows? What is the best long-term application compatibility solution? Which program compatibility feature should you use for known incompatible programs? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 52 Video/Demo Time 4.3.1 Application Compatibility 13:51 4.3.2 Using the Program Compatibility Troubleshooter 10:07 Total 23:58 Lab/Activity Configure Application Compatibility Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 53 Section 4.4: Application Virtualization Summary This section discusses the Microsoft application virtualization solution to allow client systems to access and run applications from a virtual application server. Concepts covered include: Methods to implement App-V. Considerations when installing the App-V client on a Windows workstation. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 3.0 Applications o Manage Windows application by doing the following: Manage App-V applications 70-687 Exam Objectives: 202. Install and configure desktop applications. o Manage App-V applications Lecture Focus Questions: How does App-V virtualize applications? How does an App-V solution help to reduce costs to an organization? What two methods can be used to implement App-V? How does the App-V solution increase security on a system? How does App-V make applications easier to manage? Video/Demo Time 4.4.1 Application Virtualization with App-V 5:07 4.4.2 Managing App-V Applications 6:18 Total 11:25 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 15 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 54 Section 4.5: Windows Store Applications Summary This section compares Windows Store apps to traditional desktop applications. Also covered are the tasks associated with Windows apps: Installing Windows Store Apps Starting and managing an app Switching between running apps Positioning Apps Uninstalling an app Controlling access Sideloading apps Using location-aware apps Common Windows 8 apps contracts: o Search o Settings o Printing o Share Client Pro Exam Objectives: 3.0 Applications o Manage Windows Store apps on a Windows 8 system by doing the following: Install, manage, and uninstall apps from the Windows Store. Configure location settings for location-aware apps. 70-687 Exam Objectives: 203. Install and configure Windows Store applications. o Install, reinstall and update Windows Store applications o Restrict Windows Store content o Add internal content (side loading) o Disable Windows Store Lecture Focus Questions: You have a Windows Store application installed and running. How would you pin it to the task bar? How do you update an installed Windows Store application? How do you switch between running apps using gestures? using a mouse? What methods can be used to snap an app? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 55 What types of apps are sideloaded? What are the most commonly used contracts for Windows 8 apps? How would you control access to the Windows store for juvenile family members? Video/Demo Time 4.5.1 Windows Store Applications 5:21 4.5.2 Managing Windows Store Applications 9:35 Total 14:56 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 56 Section 5.1: Authentication and Authorization Summary This section provides information about using authentication to validate user identity and authorization to access system resources. Concepts covered include: Authentication features: o Kerberos v5 o Windows NT LAN Manager (NTLM) o Certificates o Smart cards o Biometrics o Online Identity Integration Authorization terms: o Permission o Policy o Right Built-in groups: o Administrators o Backup Operators o Cryptographic Operators o Event Log Readers o Hyper-V Administrators o Network Configuration Operators o Performance Log Users o Performance Monitor Users o Users o Power Users o Remote Desktop Users Students will learn how to: Determine the most appropriate authentication mechanism for a given Windows system. Use groups to grant users the appropriate level of access to a Windows system. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: Configure authentication restrictions. Configure password policies. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 57 70-680 Exam Objectives: 504. Configure authentication and authorization. o Resolving authentication issues o Managing credentials o Managing certificates o Smart cards with PIV o Elevating user privileges o Multifactor authentication 70-687 Exam Objectives: 404. Configure authentication and authorization. o Configure rights o Manage credentials o Manage certificates o Configure smart cards o Configure biometrics Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between authentication and authorization? Why does the Power Users group exist as a built-in group? When considering authorization, what is the difference between a permission and a right? Video/Demo 5.1.1 Authentication and Authorization Time 5:46 Number of Exam Questions 2 questions Total Time About 10 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 58 Section 5.2: Authentication Management Summary This section discusses managing authentication. Concepts covered include: Tools to manage authentication: o Credential Manager o Runas o Account Policies Students will learn how to: Use PC Settings to create new local user accounts and assign passwords. Use the Local Security Policy to configure password policy and account lockout policies. Use Credential Manager to manage and maintain credentials. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 2.0 Access o Manage users and groups by doing the following: Create new users. Create new groups and add members. Manage user passwords. Manage user account types. 9.0 Security o Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: Configure authentication restrictions. Configure password policies. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 504. Configure authentication and authorization. o Resolving authentication issues o Managing credentials o Managing certificates o Smart cards with PIV o Elevating user privileges o Multifactor authentication 70-687 Exam Objectives: 404. Configure authentication and authorization. o Configure rights o Manage credentials ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 59 o Manage certificates o Configure smart cards o Configure biometrics Lecture Focus Questions: Under which circumstance is Credential Manager unnecessary? What is the difference between the account lockout duration and the account lockout threshold? How can you force users to create and use unique passwords? Video/Demo 5.2.1 Authentication Management 5.2.2 Using Credential Manager Time 8:41 10:06 5.2.5 Using Run As with Desktop Applications 7:12 5.2.6 Using Run As with Windows 8 Apps 4:41 5.2.7 Managing User Rights and Account Policies 5:53 Total 36:33 Lab/Activity Create a New User Manage User Passwords Manage Account Policies Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 65 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 60 Section 5.3: Alternative Authentication Options Summary This section examines using Windows 8 alternative authentication options for logging into a system: Picture password PIN number Students will learn how to: Use PC Settings to create and configure a new Microsoft user account. Use PC Settings to associate a local user account with an online user account. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 2.0 Access o Link a local user to a Microsoft account. (Windows 8 only) 70-687 Exam Objectives: 404. Configure authentication and authorization. o Configure picture password o Configure PIN o Set up and configure Microsoft Account Lecture Focus Questions: What gestures can you use to make a picture password? Why is a PIN number not as secure as a picture password? When should you create a Microsoft user account for a user? Video/Demo Time 5.3.1 Alternative Authentication Options 4:04 5.3.2 Using Alternative Authentication Options with Windows 8 6:37 5.3.3 Using a Windows Live ID with Windows 8 6:22 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 17:03 61 Lab/Activity Create a New Online User Account Associate a Local User with an Online User Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 62 Section 5.4: NTFS Permissions Summary This section discusses the basics of using NTFS permissions. Details covered include: Levels of permissions: o NTFS file permissions are available only on NTFS volumes or partitions o Shared folder permissions are assigned to a shared folder Considerations concerning standard NTFS permissions Standard NTFS permissions: o Full control o Modify o Read & execute o List folder contents o Read o Write Concepts concerning setting up or managing NTFS permissions: o Explicit vs inherited permissions o Copying or moving files o Using icacls Special permissions Students will learn how to: Restrict access to files and folders using NTFS permissions. Apply Special Permissions to provide specific control over files and folders. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 2.0 Access o Restrict access to files and folders on a Windows system using NTFS permissions. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 502. Configure file and folder access. o Configuring NTFS permissions o Resolving effective permissions issues o Copying files vs. moving files. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 63 70-687 Exam Objectives: 402. Configure file and folder access. o Encrypt files and folders using EFS o Configure NTFS permissions Lecture Focus Questions: What are the six standard NTFS permissions? How does an object receive explicit permissions versus inherited permissions? How are effective permissions determined? Which permissions take precedence when both share and NTFS permissions apply to a folder? How does copying or moving files with NTFS permissions affect the permissions on the file or folder? Video/Demo 5.4.1 Standard NTFS Permissions 5.4.2 Configuring Standard NTFS Permissions Time 9:30 10:09 5.4.5 Special Permissions 3:59 5.4.6 Configuring Special Permissions 8:02 Total 31:40 Lab/Activity Configure NTFS Permissions Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 64 Section 5.5: Resource Sharing Summary In this section students will explore resource sharing. Details about the following concepts will be covered: The role of the Network and Sharing Center o Location types: Domain Public Private o Networking services: Network discovery File and printer sharing Public folder sharing Media streaming File sharing connections Password protected sharing HomeGroup connections Methods to control access to shared content: o Network File and Folder Sharing o Advanced Sharing o Public folder sharing Details about folder sharing configuration Students will learn how to: Create a shared folder. Configure share permissions on a shared folder. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Share system resources on a Windows system by doing the folder: Share a folder. Restrict access to a shared folder or printer using share permissions. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 501. Configure shared resources. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Shared folder permissions ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 65 70-687 Exam Objectives: 401. Configure shared resources. o Configure shared folder permissions Lecture Focus Questions: Under what circumstances would you choose to enable the Public Folder Sharing networking service? What are the differences between domain, public, private, work, and home network profiles? When using public folder sharing, where are the public files located? How can you create an administrative share? How do share permissions relate to NTFS permissions? Video/Demo Time 5.5.1 Setting Advanced Sharing Options 7:39 5.5.3 Resource Sharing 6:38 5.5.4 Implementing Shared Folders Total 10:14 24:31 Lab/Activity Share and Secure Folders Number of Exam Questions 13 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 66 Section 5.6: Libraries and HomeGroups Summary In this section students will learn about libraries and HomeGroups. Details about the following concepts will be covered: Libraries section in Windows Explorer (File Explorer in Windows 8) Folder redirection Using Group Policy to configure the Folder Redirection Group Policy HomeGroups Students will learn how to: Create a HomeGroup to share specific types of files with other Windows systems. Join a HomeGroup to share a library of files. Configure folder redirection. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Share system resources on a Windows system by doing the folder: Configure HomeGroup sharing. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 501. Configure shared resources. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Folder Virtualization o Shared folder permissions o Configuring HomeGroup settings 70-687 Exam Objectives: 103. Migrate and configure user data. o Configure folder redirection. 401. Configure shared resources. o Configure shared folder permissions o Configure HomeGroup settings o Configure file libraries Lecture Focus Questions: How would you share individual files and folders within the HomeGroup? What is a library, and where are files located when displayed in a library? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 67 How does folder redirection work? Video/Demo Time 5.6.1 Implementing Libraries 6:32 5.6.2 Using Folder Redirection 9:23 5.6.4 Implementing HomeGroups Total 12:19 28:14 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 68 Section 5.7: Printer Sharing and Management Summary In this section students will learn the basics of managing printer sharing on a network. Concepts covered include: Configure printer sharing Printer permissions: o Print o Manage Printer o Manage Documents Printer management features: o Client-Side Rendering (CSR) o Driver isolation o SML Paper Specification (XPS) o Windows Color System (WCS) o Location-aware printing Students will learn how to: Create and share a printer. Manage the default printer based on the location. Manage printer permissions. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0. Networking o Share system resources on a Windows system by doing the following: Share a printer and add drivers for other operating systems. Restrict access to a shared folder or printer using share permissions. 7.0 Printing o Configure and manage printing on a Windows system by doing the following: Connect a printer to a local port and configure the appropriate drivers and utilities. Connect to a shared printer on the network and configure the appropriate drivers and utilities. Configure printer settings. Manage print jobs in the print queue. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 69 70-680 Exam Objectives: 403. Configure networking settings. o Configuring location-aware printing 501. Configure shared resources. o Printers and queues 70-687 Exam Objectives: 302. Configure networking settings. o Configure location-aware printing 401. Configure shared resources. o Configure shared printers Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between the Manage Printer and the Manage Documents printer permissions? What are the functions of the Print Management MMC snap-in? When would you choose to isolate a print driver? How does Client-Side Rendering (CSR) reduce print processing times? What is the advantage of location-aware printing? Video/Demo Time 5.7.1 Shared Printer Management 8:21 5.7.2 Sharing and Managing Printers 8:56 Total 17:17 Lab/Activity Install and Configure a Local Printer Share a Printer Configure Default Printers Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 70 Section 5.8: Auditing Summary This section explores using auditing to record when system events occur. Concepts covered include: Common audit policies: o Account logon events o Logon events o Account management o Object access o Policy change o Privilege use o System events o Process tracking o Directory service access Configuring auditing Students will learn how to: Configure auditing to track the success and failure of specified actions of a user. Create a custom view to filter tasks and manage the audit results. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 604. Configure remote connections. o Advanced security auditing 70-687 Exam Objectives: 402. Configure file and folder access. o Configure object access auditing Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between account logon and logon audit policies? As the Administrator you have requested that all users change their passwords. What audit policy would verify that all the users have complied with the request? What policy would you use to audit failed attempts to view or modify registry settings? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 71 Video/Demo Time 5.8.1 Auditing 4:23 5.8.2 Configuring Auditing 7:49 Total 12:12 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 72 Section 5.9: Encryption Summary This section discusses using encryption on a NTFS file system. Details covered include: Key features of EFS EFS considerations: o System requirements o Key generation and file encryption o Adding a DRA o EFS restrictions o Creating, moving and copying files and folders o Managing encrypted files Certificate management areas: o Key protection o Certificate validation o Certificate revocation o Crypto period o Certificate renewal o Key disposal Students will learn how to: Encrypt files and folders to protect data from unauthorized users. Back up the file encryption key. Create a Designated Recovery Agent (DRA). Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Manage Windows user certificates. o Encrypt data on a Windows system in the following ways: Encrypt files and folders on a per-file basis using Encrypting File System (EFS). 70-680 Exam Objectives: 502. Configure file and folder access. o Encrypting files and folders by using EFS 70-687 Exam Objectives: 402. Configure file and folder access. o Encrypt files and folders by using EFS ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 73 Lecture Focus Questions: Which Windows editions support Encrypting File System (EFS)? Once a folder is encrypted, which users can access the data inside the folder? Which types of files cannot be encrypted? What NTFS permission must you have to encrypt a file? What is the purpose of a PFX file? Video/Demo Time 5.9.1 Encrypting Files System (EFS) 7:29 5.9.2 EFS Tools and Management 6:20 5.9.3 Implementing EFS Total 12:23 26:12 Lab/Activity Encrypt Files Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 74 Section 5.10: BranchCache Summary This section examines using BranchCache to quickly access information in remote locations. Concepts covered include: The role of BranchCache Modes that BranchCache operates: o Hosted Cache o Distributed Cache Configuring BranchCache clients Tools to configure BranchCache on a client computer: o netsh o Group Policy o Windows Firewall with Advanced Security 70-680 Exam Objectives: 505. Configure BranchCache. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Distributed cache mode vs. hosted mode o Network infrastructure requirements o Configuring settings o Certificate management Lecture Focus Questions: Under which circumstances should you enable distributed cache mode versus hosted cache mode? How does BranchCache treat traffic while in transit? When would you choose to configure BranchCache using Group Policy rather than netsh? When BranchCache settings have been configured using both the netsh command and Group Policy, which settings take precedence? Video/Demo Time 5.10.1 BranchCache 4:32 5.10.3 BranchCache Configuration 6:47 5.10.4 Configuring BranchCache 2:24 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 13:43 75 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 76 Section 6.1: Windows Versions Summary This section reviews Windows versions, features and minimal requirements. Details covered include: Editions of Windows 7: o Starter o Home Basic o Home Premium o Professional o Enterprise o Ultimate Windows 7 features: o Windows Firewall o Action Center o Power Management o User Account Control o Internet Explorer 8 o Improved Backup and Restore o HomeGroup o Windows Media Center o Windows Aero o Encrypting File System o Remote Desktop Host o Windows XP Mode o Domain Join o Group Policies o AppLocker o DirectAccess o BranchCache o BitLocker and BitLocker To Go o Boot from VHD o Back up to a Network Features included in each Windows 7 edition Minimal requirements for the Windows 7 editions Windows 7 N-editions Editions of Windows 8: o Window RT o Windows 8 o Windows 8 Professional o Windows 8 Enterprise Features included in each Windows 8 edition Minimal requirements for the Windows 8 editions Additional requirements to use certain features ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 77 Client Pro Exam Objectives: 1.0 Windows operating system. o Given an existing system with no operating system installed, select the correct version and edition of Windows to meet end-user requirements. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 101. Perform a clean installation. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Identifying hardware requirements 70-687 Exam Objectives: 101. Evaluate hardware readiness and compatibility. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Determine whether 32 bit or 64 bit is appropriate o Determine screen resolution o Choose between an upgrade or a clean installation o Determine which SKU to install Lecture Focus Questions: What are the different editions of Windows 7? What are the different editions of Windows 8? Which editions would allow you to create or join a HomeGroup? What is the difference between the Ultimate edition and the Enterprise edition in Windows 7? What is the difference between a Professional edition and a Professional N-Edition in Windows 7? What is the difference between the Professional edition and the Enterprise edition in Windows 8? What is the difference between Windows RT and Windows 8? Video/Demo Time 6.1.1 Windows 7 Versions 5:08 6.1.3 Windows 8 Versions 11:06 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 16:15 78 Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 79 Section 6.2: Windows 7 Installation Summary This section discusses installing Windows 7. Details covered include: When to select a custom (advanced) or clean installation Options for a clean installation on a Windows 7 system: o Performing a clean installation on a new or existing system o Installing a multi-boot system Windows installation sources: o DVD o USB o ISO o Network o Windows Deployment Services (WDS) Students will learn how to: Copy Windows 7 installation files to a USB flash device. Perform a Windows 7 installation using a USB flash device. Install Windows 7. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 1.0 Windows operating system o Install the correct PC hardware to support the installation of Windows. o Select the correct version and edition of Windows to meet end-user requirements. o Perform a clean installation of Windows 7 or Windows 8 to meet end-user requirements. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 101. Perform a clean installation. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Identifying hardware requirements o Setting up as the sole operating system o Setting up as dual boot; installation methods o Boot from the source of installation, preparing the installation source: USB, CD, network share, WDS ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 80 Lecture Focus Questions: Under which circumstances should you choose a clean installation of Windows? What is the advantage of a dual-boot system? When would you choose an upgrade rather than a clean installation of Windows? What requirements must be met in order for a USB flash storage device to be used as an installation source? In which environment would you use Windows Deployment Services (WDS)? Video/Demo Time 6.2.1 Windows 7 Installation Types and Sources 6:24 6.2.3 Creating a Windows 7 USB Installation Source 4:02 6.2.5 Installing Windows 7 7:17 Total 17:43 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 81 Section 6.2: Windows 8 Installation Summary This section discusses installing Windows 8. Details covered include: When to select a custom (advanced) or clean installation Options for a clean installation on a Windows 8 system: o Performing a clean installation on a new or existing system o Installing Windows To Go o Installing a multi-boot system Windows installation sources: o DVD o USB o ISO o Network o Windows Deployment Services (WDS) Students will learn how to: Copy Windows 8 installation files to a USB flash device. Perform a Windows 8 installation using a USB flash device. Create a Windows to Go installation device for Windows 8. Install Windows 8. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 1.0 Windows operating system o Install the correct PC hardware to support the installation of Windows. o Select the correct version and edition of Windows to meet end-user requirements. o Perform a clean installation of Windows 7 or Windows 8 to meet end-user requirements. o Use Windows To Go to create a bootable USB flash storage device. 70-687 Exam Objectives: 102. Install Windows 8. o Install as Windows to Go o Install VHD ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 82 Lecture Focus Questions: Under which circumstances should you choose a clean installation of Windows? What is the advantage of a dual-boot system? When would you choose an upgrade rather than a clean installation of Windows? What requirements must be met in order for a USB flash storage device to be used as an installation source? In which environment would you use Windows Deployment Services (WDS)? Video/Demo Time 6.3.1 Windows 8 Clean Installation 7:19 6.3.2 Windows 8 Windows to Go Installation 3:51 6.3.3 Creating a Windows to Go Bootable Device 13:33 6.3.6 Creating Windows 8 Installation Sources 3:19 6.3.8 Installing Windows 8 6:41 Total 34:43 Lab/Activity Create a Windows To Go USB Drive Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 55 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 83 Section 6.4: Windows Upgrade Summary This section provides information about upgrading from one version of Windows to another. Concepts covered include: Types of upgrades available for Windows 7: o Intra-edition upgrade o Previous Windows version upgrade Windows 8 upgrade paths and options: o Migrate from XP or Vista to Windows o Migrate from Vista to Windows 8 o Upgrade from Windows 7 to Windows 8 o Upgrade edition from Windows 7 to Windows 8 o Upgrade Windows 8 intra-edition Considerations when upgrading Generic steps to the upgrade process Students will learn how to: Run the Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor tool to determine the computer's hardware readiness for Windows 7. Perform an upgrade from Windows Vista to Windows 7. Perform an upgrade from Windows 7 to Windows 8. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 1.0 Windows operating system o Given an existing Windows Vista system, upgrade to Windows 7. o Given an existing Windows 7 system, upgrade to Windows 8. o Given an existing Windows 8 system, use Windows To Go to create a bootable USB flash storage device. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 102. Upgrade to Windows 7 from previous versions of Windows. o Upgrading from Windows Vista o Migrating from Windows XP o Upgrading from one edition of Windows 7 to another edition of Windows 7 70-687 Exam Objectives: 102. Install Windows 8. o Migrate from Windows XP or Windows Vista ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 84 o Upgrade from Windows 7 to Windows 8 or from one edition of Windows 8 to another edition of Windows 8 Lecture Focus Questions: You have Windows 7 Professional installed. Which editions of Windows 7 support an upgrade from your current system? You have Windows 7 Home Premium installed. You would like the system to run the Home Basic edition. How would you make the change? When upgrading to Windows 7, what are the tasks you should complete prior to running the setup program? How does the Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor tool simplify the process of upgrading Windows 7 to a different edition? Under what circumstances must you perform a clean installation instead of an upgrade installation? You want to upgrade your Windows Vista system to Windows 8. Will your applications be retained during the upgrade? You currently use Windows 8 and want to upgrade to Windows 8 Professional. How can you do this? Video/Demo Time 6.4.1 Windows 7 Upgrade Overview 4:16 6.4.2 Upgrading to Windows 7 From Windows Vista 4:55 6.4.3 Windows 8 Upgrade Paths and Options 9:34 6.4.4 Upgrading to Windows 8 7:30 Total 26:15 Number of Exam Questions 12 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 85 Section 6.5: User Profile and Data Migration Summary This section examines preserving user profile data during an upgrade and migrating the user data back to a specified computer once the upgrade is completed. Details discussed include: User Profile data and settings preserved during migration Types of migrations: o Side-by-side o Wipe-and-load Migration tools: o Windows Easy Transfer (WET) o User State Migration Tool (USMT) The role of the C:\Windows.old\directory ScanState LoadState Students will learn how to: Use USMT to migrate user settings and profile information. On the source computer run Scanstate to save the migration user accounts to a network share. On the destination computer run Loadstate to import user migration information from a network share. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 103. Migrate user profiles. o Migrating from one machine to another o Migrating from previous versions of Windows o Side-by-side vs. wipe and load 70-687 Exam Objectives: 103. Migrate and configure user data. o Migrate user profiles o Configure folder redirection o Configure profiles ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 86 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the main differences between a side-by-side migration and a wipe-and-load migration? What types of files and data are moved during a migration? How can you save user data during a migration? When would you choose to perform a migration using the Windows Easy Transfer (WET) over the User State Migration Tool (USMT)? What are the transfer methods available when using WET to save user files? What are the different kinds of migration stores supported by USMT? Which scanstate command moves Windows XP user data files during a hard-link migration? Video/Demo Time 6.5.1 Windows 7 User Profile and Data Migration 10:56 6.5.2 Windows 8 User Profile and Data Migration 11:14 6.5.3 Using WET 11:43 6.5.4 Using USMT 6:09 Total 40:02 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 60 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 87 Section 6.6: VHD Installation Summary This section discusses using a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) to install Windows 7 Enterprise and Ultimate as well as Windows 8 Professional and Enterprise in a VHD file. Concepts covered include: Benefits of using a VHD file: o Ease of use o Bootable o Compatible with hypervisor systems o Installation General actions with a VHD file: o Create o Attach o Detach o Compact o Expand Tools to create and manage VHD files: o Disk Management o DiskPart o WIM2VHD o BCDEdit Students will learn how to: Create a VHD file and apply a Windows image to the file. Install Windows to a VHD file. Configure a computer to boot from the VHD file. Create a dual boot system using a VHD file. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 11.0 Virtualization o Create and manage virtual machines on a Windows 8 system by doing the following: Enable Client Hyper-V. Create a new virtual machine and install an operating system within it. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 204. Configure a VHD. o Creating, deploying, booting, mounting, and updating VHDs o Offline updates ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 88 o Offline servicing 70-687 Exam Objectives: 102. Install Windows 8. o Install VHD 206. Configure Hyper-V. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Create and configure virtual disks Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between a Virtual Hard Drive (VHD) and a standard Hard Disk Drive (HDD)? What are the advantages of using a VHD for Windows installations? What is the difference between a fixed disk VHD file and a dynamically expanding VHD file? Which utilities would you use to create, manage and mount VHD files? What is a native-boot VHD? Video/Demo Time 6.6.1 Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) Overview 9:44 6.6.2 Creating VHD Image Installations 12:42 6.6.4 Installing Windows 7 on a VHD 6.6.5 Creating a Windows 7 / Windows 8 Dual Boot System Total 4:07 10:40 37:13 Lab/Activity Create a VHD Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 55 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 89 Section 6.7: Client-Side Virtualization Summary This section examines Client-Side Virtualization. Concepts covered include: Client Hyper-V requirements: o Windows 8 o System Methods to implement Client Hyper-V: o External virtual networks o Internal virtual networks o Private virtual networks Actions to use Client Hyper-V on Windows 8: o Enable Hyper-V o Configure virtual networking o Create virtual machines o Start the virtual machine o Connect to the VM Students will learn how to: Enable and configure Hyper-V on a Windows 8 system. Create and manage virtual machine snapshots. Create an external virtual switch to allow a virtual machine to access a physical network. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 204. Configure a VHD. o Creating, deploying, booting, mounting, and updating VHDs 70-687 Exam Objectives: 102. Install Windows 8. o Install VHD 206. Configure Hyper-V. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Create and configure virtual machines o Create and manage snapshots o Create and configure virtual switches o Create and configure virtual disks ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 90 Lecture Focus Questions: How is Hyper-V implemented in Windows 8? What are the three different kinds of virtual switches that can be created? You have decided to implement Client Hyper-V. What version of Windows 8 is required? What is the difference between an internal virtual network and a private virtual network when implementing virtual networking using Client HyperV? Video/Demo Time 6.7.1 Virtualization Overview 9:49 6.7.2 Client-Side Virtualization in Windows 8 6:43 6.7.3 Creating Virtual Machines 9:10 6.7.4 Managing Virtual Machine Snapshots 5:24 6.7.5 Managing Virtual Networking 6:10 Total 37:16 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 91 Section 7.1: System Images Overview Summary This section provides an overview of using system images to deploy Windows to computers in a large enterprise environment. Stored as a Windows Image (WIM) file Windows Automated Installation Kit (Windows AIK) tools: o Windows Preinstallation Environment (Windows PE or WinPE) o Windows System Image Manger (Windows SIM) o System Preparation Tool (Sysprep) o ImageX o Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) o Oscdimg Types of computers required to prepare a system image: o Reference o Technician General steps to create a system image 70-680 Exam Objectives: 201. Capture a system image. Lecture Focus Questions: What are the advantages of using a system image to install Windows to computers? What is the file extension of a Windows system image file? How do you create an answer file for an automated installation? Which tools does the Windows Automated Installation Kit include to prepare or create a system image? Video/Demo 7.1.1 System Images Overview Time 3:45 Number of Exam Questions 2 questions Total Time About 10 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 92 Section 7.2: Image Preparation Summary In this section students will learn about image preparation. Details include: Basic steps to perform a normal Windows installation: o windowsPE o offlineServicing o specialize o oobeSystem Additional steps to prepare and deploy a system image: o generalize o auditSystem o auditUser Methods to run Windows Setup: o Interactive (attended) o Automated (unattended) Windows SIM General steps to create an answer file Considerations when using an answer file for automated installations Results of using Sysprep Sysprep switches: o /audit o /generalize o /oobe o /shutdown o /reboot o /quiet o /quit o /unattend Considerations when using Sysprep General steps to create, prepare, and deploy a Windows installation image: Students will learn how to: Use Windows SIM to create an answer file. Configure properties and components of the answer file to increase the automation of the installation and setup. Use Sysprep to prepare an installation before it is captured. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 201. Capture a system image. o Preparing system for capture ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 93 Lecture Focus Questions: What role does the Windows System Image Manager (Windows SIM) perform during image preparation? What is the purpose of the Sysprep utility? What privileges are required to execute Sysprep? Which Sysprep option allows a user to remove all machine-specific information from an installation? What is the out-of-box experience mode? Video/Demo Time 7.2.1 Automated Installations 3:20 7.2.4 Creating an Answer File 6:07 7.2.5 Image Preparation 2:46 Total 12:13 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 94 Section 7.3: Image Capture Summary This section discusses capturing system images. Details include: The role of Windows PE Steps to create a bootable Windows PE disk for capturing system images The role of ImageX Considerations exclude specific files during the ImageX capture operation ImageX options: o /capture o /configu o /compress o /split o /apply o /apply /ref o /verify Steps to capture the reference computer’s Windows installation onto a network share Students will learn how to: Create a Windows PE boot disk. Use ImageX to capture a Windows installation. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 201. Capture a system image. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Preparing system for capture o Creating a WIM file o Automated capture o Manual capture Lecture Focus Questions: Which tool can you use to create a bootable Windows PE disc? What are the boot sources for Windows PE? Which tool is used to create an image from a reference computer? What is the purpose of the exclusion exception section of the wimscript.ini file? Which imagex.exe option checks for errors and file duplication after capturing the installation? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 95 Video/Demo 7.3.1 Image Capture 7.3.2 Capturing System Images Total Time 3:07 10:24 13:31 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 96 Section 7.4: Manual Image Deployment Summary This section discusses manually deploying an image. Concepts covered include: The process to manually deploy an image from a network share Additional details on deploying an image Students will learn how to: Manually deploy an image onto a local computer. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 203. Deploy a system image. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Manually deploying a customized image Lecture Focus Questions: What tools would you use to manually deploy an image from a network share? Why should you create two partitions on a hard drive prior to installing the image? What command at the command prompt connects a network share and maps the drive with a letter? What is the purpose of BCDBoot when deploying an image to the local hard drive? Video/Demo 7.4.1 Deploying Images with ImageX Time 2:40 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 10 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 97 Section 7.5: Image Servicing Summary In this section students will learn about using image servicing to manage and maintain previously-captured images. Concepts covered include: Mounting a previously captured image Tools to service an image: o Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) o ImageX Components of the system image that typically need servicing: o Drivers o Windows Applications and Application Patches o Windows Security Updates and Features o International Settings o Windows Editions Students will learn how to: Use ImageX to mount an image, make and save changes to the image, and dismount the image. Use DISM to mount an image, make changes to the image, gather information about the image, and dismount the image. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 202. Prepare a system image for deployment. o Inserting an application into a system image o Inserting a driver into a system image o Inserting an update into a system image o Configuring tasks to run after deployment Lecture Focus Questions: When would you choose to use ImageX over DISM to mount an image? When using DISM, how do you save changes before dismounting an image? How do you mount a read-write image with ImageX? What is the difference between an online image and an offline image? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 98 Video/Demo Time 7.5.1 Image Servicing 4:00 7.5.2 Mounting and Unmounting Images 9:45 7.5.4 Image Servicing with DISM 8:06 7.5.5 Changing Image Settings and Drivers 6:03 7.5.6 Applying Updates to Images 3:32 Total 31:26 Number of Exam Questions 14 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 99 Section 7.6: Domain Image Deployment Summary This section discusses deploying a system image. Concepts covered include: The role of the Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT 2012) Distribution methods: o Lite Touch Installation (LTI) o Zero Touch Installation (ZTI) MDT 2012 Deployment Workbench areas to manage and distribute Windows images: o Distribution share o Task sequences o Deployment point The role of Windows Deployment Services (WDS) Types of WDS images: o Install image o Boot image o Capture boot image o Discover boot image WDS requirements Files WDS uses to automate the installation process using: o Windows Deployment Services client unattend file o Image unattend file Transmission methods WDS supports to deploy images: o Unicast o Multicast Scheduled casting WDSUTIL utility Students will learn how to: Use WDS to create an installation and boot image. Image a computer with a Windows image. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 203. Deploy a system image. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Automated deployment methods ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 100 Lecture Focus Questions: What is the role of the Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT)? What is the difference between the Lite Touch Installation and Zero Touch Installation MDT distribution methods? What are the main areas of the MDT Deployment Workbench that are used to manage and distribute Windows images? What are the differences between the MDT and Windows Deployment Services (WDS)? What are the four different types of WDS images that may be used during installation? Video/Demo Time 7.6.1 Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT) 4:03 7.6.3 Windows Deployment Services (WDS) 4:35 7.6.4 Deploying Images with WDS 7:06 Total 15:44 Lab/Activity Create WDS Images Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 101 Section 8.1: Network Access Protection (NAP) Summary This section provides an overview of Network Access Protection (NAP). Concepts covered include: NAP uses the following components: o NAP client o NAP server o Enforcement Server (ES) o Remediation server Steps to configure NAP on the client computer Remediating a client that is not compliant with health requirements Exempting a computer that does not meet NAP requirements 70-680 Exam Objectives: 604. Configure remote connections. o NAP quarantine remediation Lecture Focus Questions: How does NAP determine if a client is non-compliant with specific requirements? How does a remediation server help non-compliant clients become compliant? What is the difference between the role of the enforcement server and the NAP server? Video/Demo 8.1.1 Network Access Protection (NAP) Time 2:47 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 10 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 102 Section 8.2: Virtual Private Network (VPN) Summary This section provides information about using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to establish remote connections. Concepts covered include: The role of a VPN connection Benefits provided by VPNs Common VPN security technologies: o Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) o Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) o Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) o Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) o Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) Considerations when managing VPN connections Remote access authentication protocols from least secure to most secure: o Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) o Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) o Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol version 2 (MS-CHAP v2) o Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security (EAPTLS) Students will learn how to: Use the Network and Sharing Center to create a VPN connection. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 2.0 Access o Enable remote access by doing the following: Establish a VPN connection to a remote access server. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 604. Configure remote connections. o Establishing VPN connections and authentication o Enabling a VPN reconnect o Dial-up connections 70-687 Exam Objectives: 501 Configure remote connections. o Establish VPN connections and authentication o Enable VPN reconnect ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 103 Lecture Focus Questions: Under which circumstances would you use a VPN connection? What process does a VPN use to secure IP traffic over a TCP/IP network? What types of communications can be secured using IPSec? Which protocol is the default protocol used for new VPN connections in Windows 7 and Windows 8? What benefit does VPN Reconnect provide over traditional VPN connections? Which Windows editions support VPN Reconnect? Video/Demo 8.2.1 Virtual Private Network (VPN) 8.2.2 Creating a VPN Connection Total Time 9:47 12:10 21:57 Lab/Activity Configure a VPN Connection Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 104 Section 8.3: DirectAccess Summary In this section students will learn about using DirectAccess. Details covered include: The role of Direct Access DirectAccess connection methods: o Full enterprise network access (end-to-edge) o Selected server access (modified end-to-edge) o End-to-end Basic steps for DirectAccess clients to connect to intranet resources DirectAccess requirements for Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 deployment: o Infrastructure o Server o Client DirectAccess requirements for a Windows 8/Server 2012 implementation: o Infrastructure o Server o Client o Active Directory Configuration details for DirectAccess components: o Server o Client side Tools to manage DirectAccess: o Certificates MMC snap-in o Netsh o Network Connections Client Pro Exam Objectives: 2.0 Access o Enable remote access by doing the following: Establish a connection to a DirectAccess server. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 602. Configure DirectAccess. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring client side o Configuring authentication o Network infrastructure requirements ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 105 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the advantages of using DirectAccess to access corporate file servers? What is the difference between full enterprise network access and selected server access? What are the requirements for a DirectAccess client? How does the client's IP address configuration affect how the client sends traffic to the DirectAccess server? Video/Demo Time 8.3.1 DirectAccess 9:05 8.3.2 DirectAccess Configuration Options 7:43 Total 16:48 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 106 Section 8.4: BitLocker Summary This section discusses using BitLocker to protect data on lost or stolen laptops. Concepts covered include: The role of BitLocker Components of BitLocker: o BitLocker partition o Trusted Platform Module (TPM) o Non-TPM Security o BIOS support BitLocker vs Encrypting File System (EFS) Students will learn how to: Encrypt data with BitLocker. Generate recovery keys and create a BitLocker DRA. Configure BitLocker to implement BitLocker without a TPM. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Encrypt data on a Windows system in the following ways: Enable whole-disk encryption using TPM and BitLocker. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 601. Configure BitLocker and BitLocker To Go. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring BitLocker and BitLocker To Go policies o Managing Trusted Platform Module (TPM) PINs o Configuring startup key storage o Data recovery agent support 70-687 Exam Objectives: 503. Configure security for mobile devices. o Configure BitLocker and BitLocker To Go policies o Configure startup key storage ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 107 Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between suspending protection and decrypting the drive? When implementing BitLocker, why is it a good idea to run a system check before encrypting the drive? When using BitLocker, what are the requirements of the Trusted Platform Module? How can you implement BitLocker without a TPM? What would happen if BitLocker were enabled and the USB flash device which holds the key were to be lost? Video/Demo Time 8.4.1 BitLocker 3:18 8.4.3 BitLocker Configuration 4:46 8.4.4 Configuring BitLocker Recovery Agents 4:07 8.4.5 Implementing BitLocker without a TPM 7:44 Total 19:55 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 108 Section 8.5: BitLocker To Go Summary This section discusses using BitLocker To Go to protect portable storage devices. Concepts covered include: The role of BitLocker To Go Policies that control BitLocker To Go are: o Control use of BitLocker on removable drives o Configuer use of smart cards on removable drives o Deny write access to removable drives not protected by BitLocker o Allow access to BitLocker-protected removable data drives from earlier version of Windows o Configure use of password for removable data drives o Choose how BitLocker-protected removable drives can be recovered Using the manage-bde command line tool switches to manage BitLocker and BitLocker To Go: o –status o –on / -off o –pause / -resume o –lock / -unlock o –changepin o –changepassword o -changekey BitLocker modes which determine the security level offered: o TPM-only o TPM with startup key o TPM with PIN o TPM with PIN and startup key o Without a TPM Configuring and managing BitLocker Security components of a BitLocker configuration: o TPM owner password o Recovery key o PIN o Startup key o Data volume key o Data Recovery Agent BitLocker configuration details Students will learn how to: Configure BitLocker To Go to deny write access to unauthorized USB flash devices. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 109 Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Encrypt data on a Windows system in the following ways: Enable whole-disk encryption using TPM and BitLocker. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 601. Configure BitLocker and BitLocker To Go. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring BitLocker and BitLocker To Go policies o Managing Trusted Platform Module (TPM) PINs o Configuring startup key storage o Data recovery agent support 70-687 Exam Objectives: 503. Configure security for mobile devices. o Configure BitLocker and BitLocker To Go policies o Configure startup key storage Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference in function between BitLocker and BitLocker To Go? Which editions of Windows 7 and Windows 8 allow read access to BitLocker To Go devices? Video/Demo Time 8.5.1 BitLocker To Go 3:52 8.5.2 Implementing BitLocker To Go 7:30 Total 11:22 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 110 Section 8.6: Mobile Device Security Summary This section examines providing security for mobile devices. Details include: Threats to data security that mobile devices: o Losing the device o Malware o Hacking o Lack of centralized security enforcement Security features used by Windows RT to ensure the security of data on a mobile devices: o App security o User Account Control (UAC) o Device Encryption o Strong passwords o Remote wipe o Privacy settings Students will learn how to: Configure Windows 8 privacy settings. Back up the recovery key for device encryption. Configure location settings to determine the physical location of a specified mobile device. 70-687 Exam Objectives: 503. Configure security for mobile devices. o Configure remote wipe o Configure location settings (GPS) Lecture Focus Questions: What types of threats can affect data security on mobile devices? What are the main differences between Windows RT device encryption and BitLocker to Go? Why doesn't Windows RT load app modules that are not digitally signed by Microsoft? Which methods can be used by Windows Location Providers to determine the location of a mobile device? Which is the most accurate? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 111 Video/Demo 8.6.1 Mobile Device Security Time 9:22 8.6.2 Configuring Windows Mobile Device Security 4:07 8.6.3 Location Settings 5:31 8.6.4 Configuring Location Settings 3:27 Total 22:27 Lab/Activity Configure Privacy Settings Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 112 Section 8.7: Power Management Summary In this section students will learn the basics of managing power plans to optimize the power consumption of a mobile computer. Concepts covered include: Default Power Plans: o Power saver o High performance o Balanced Basic Power Plan options: o Require password on wakeup o Choose what the power buttons do o Power buttons and lid o Display o Hard disk o Wireless adapter settings o USB settings o Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) o Multimedia settings o Processor power management o Battery Power saving states include: o Shut down o Sleep o Hibernation o Hybrid sleep Additional tools to configure power options: o Group Policy o powercfg command Students will learn how to: Use power plans to manage the power consumption of a mobile computer. Configure power plan settings to provide better performance on a mobile device. Create a custom power plan and configure it for the required situation. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 4.0 Hardware o Optimize hardware performance by doing the following: Configure power options. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 113 70-680 Exam Objectives: 704. Configure performance settings. o Configuring power plans o Configuring power 70-687 Exam Objectives: 502. Configure mobility options. o Configure power policies Lecture Focus Questions: How does a power plan help to optimize the performance and conserve energy on a laptop? What are the three default power plans in Power Options? What are the differences between hibernate and sleep power saving states? What are the differences between the sleep and the hybrid sleep power saving states? What happens to the system when the critical battery level is reached? What are the actions you can define for when the notebook lid is closed? Which power saving state does the system awaken from the fastest? Video/Demo Time 8.7.1 Power Plans 6:51 8.7.2 Configuring Power Plans 6:20 Total 13:11 Lab/Activity Edit Power Options Create a Power Plan Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 114 Section 8.8: Mobility Options Summary This section discusses options to manage mobile devices and the use of offline files. Concepts covered include: Features to use, manage and maintain Windows mobile devices: o Input Methods o Broadband connection controls o Mobility Center Options o Sync Center o SkyDrive o Presentation settings Offline file operating modes: o Online o Auto Offline o Manual Offline o Slow-link Offline Files: o Enable Offline Files on the client o Enable Offline Files on a shared folder Offline Files concepts: o Automatic synchronization o Manual synchronization o Transparent caching o Conflict resolution Considerations when working with Offline Files Students will learn how to: Configure Offline Files to allow users to access files and folders when they are disconnected from the network. Use the Sync Center on a mobile device to resolve a conflict of an offline file. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 5.0 Storage o Configure offline files. 6.0 Networking o Connect a mobile Windows system to a mobile broadband network. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 115 70-680 Exam Objectives: 603. Configure mobility options. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring offline file policies o Transparent caching o Creating and migrating power policy 704. Configure performance settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Mobile computing performance issues 70-687 Exam Objectives: 501. Configure remote connections. o Manage broadband connections 502. Configure mobility options. o Configuring offline file policies o Configure sync options Lecture Focus Questions: When would you enable Airplane Mode on a mobile device? What information can be synchronized between Windows 8 devices? What types of settings can you configure using the Mobility Center for mobile devices? What is the process of transparent caching? What are the options for resolving a synchronization conflict? How does Offline Files allow you to work with files even when you are not connected to the network? What triggers the system to go from online mode to slow-link mode in Offline Files? Video/Demo Time 8.8.1 Mobility Tools 9:51 8.8.4 Offline Files 9:37 8.8.5 Offline Files Management 4:50 8.8.6 Configuring Offline Files Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 10:25 34:43 116 Lab/Activity Manage Synchronization Settings Configure Offline Settings Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 65 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 117 Section 8.9: Mobile Networking Summary This section examines wireless technologies to provide mobile device communication. Concepts covered include: Wireless technologies: o WiFi Direct o Broadband wireless connections o Near Field Communications Students will learn how to: Configure a WiFi direct connection. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 6.0 Networking o Enable networking on Windows by doing the following: Install a wireless network interface and configure it to do the following: Securely connect to a wireless access point. Securely connect to other wireless hosts using WiFi Direct. (Windows 8 only) o Connect a mobile Windows system to a mobile broadband network. o Share system resources on a Windows system by doing the following: Use Near Field Communications to share data with mobile devices. (Windows 8 only) 70-687 Exam Objectives: 401. Configure shared resources. o Configure Near Field Communication (NFC) 502. Configure mobility options. o Configure WiFi direct ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 118 Lecture Focus Questions: What type of connections does WiFi Direct replace? What are the hardware requirements to establish a WiFi Direct connection? When using WiFi Direct what type of drivers must be used with the wireless network adapters? When would you use broadband wireless (cellular) connections? What are the requirements for using broadband wireless connections? What types of mobile devices can be used with Near Field Communications (NFC)? What is the difference between Near Field Communications and Tap and Do? Video/Demo Time 8.9.1 WiFi Direct 5:31 8.9.2 Configuring a WiFi Direct Connection 2:20 8.9.3 Broadband Wireless Connections 3:30 8.9.4 Near Field Communications 5:34 8.9.5 Tap and Do 3:32 Total 20:27 Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 119 Section 9.1: Troubleshooting Tools Summary This section discusses the following Windows Diagnostics Infrastructure (WDI) troubleshooting tools and utilities: Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool (WMDT) Windows Network Diagnostics Startup and Recovery options Startup Repair System Configuration Utility (Msconfig.exe) Service console (Services (MMC snap-in) Students will learn how to: Use the Services Console to view and manage services, such as starting, stopping, pausing, and resuming. Use the Services Console to configure the computer's response if a service fails or stops. Start and stop services from the command line. Use msconfig to view all the items that are processed during the computer startup, and disable an item if needed. Use msconfig to launch support tools for managing and maintaining a system. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 3.0 Applications o Manage running processes on a Windows system by doing the following: Configure the way services are started at boot. Manually start or stop services. Use Task Manager to view and kill running processes. 10.0 Monitoring o Monitor a Windows system by doing the following: Monitor processes and resource usage with Task Manager. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 703. Monitor systems. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Generating a system diagnostics report 704. Configure performance settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring networking performance o Configuring services and programs to resolve performance issues ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 120 70-687 Exam Objectives: 603. Monitor system performance. o Configure Task Manager Lecture Focus Questions: How would you disable a service without rebooting? Which tool would you use to scan and manage memory? Which types of network problems does the Windows Network Diagnostics troubleshoot? Which troubleshooting tools run automatically when they detect a problem? What types of missing or corrupt files does Startup Repair try to fix? Video/Demo Time 9.1.1 System Troubleshooting Tools 6:45 9.1.2 System Configuration Tools 8:04 9.1.3 Configuring Services and Startup Items Total 14:31 29:20 Lab/Activity Configure Services Configure Startup Items Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 121 Section 9.2: System Events Summary This section provides information about system events generated by the operating system and other programs. Concepts covered include: Common event logs: o Application o Security o Setup o System o Forwarded Events Features available with event logs: o Filter events o Custom views o Attach a task o Event log online help Accessing Event Viewer Event Subscriptions Subscriptions types: o Collector initiated o Source initiated Types of delivery for Event Subscriptions: o Normal o Minimized bandwidth o Minimized latency o Custom Supported Windows versions Students will learn how to: Use custom views and the properties of events to troubleshoot and diagnose issues on the system. Configure collector initiated and source initiated subscriptions. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 10.0 Monitoring o Monitor a Windows system by doing the following: Monitor system events with Event Viewer. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 122 70-680 Exam Objectives: 703. Monitor systems. o Configuring event logging o Filtering event logs o Event subscriptions 70-687 Exam Objectives: 501. Configure remote connections. o Configure remote authentication 603. Monitor system performance. o Configure and analyze event logs o Configure event subscriptions Lecture Focus Questions: What common event logs can be viewed in Event Viewer? Why would you choose to filter events in Event Viewer? What is the difference between filtering events versus using a custom view? What type of tasks can you attach to an event when a specific event occurs? When would you choose to use a collector-initiated subscription over a source-initiated subscription? Video/Demo 9.2.1 Event Viewer Time 6:47 9.2.2 Using Event Viewer 11:14 9.2.4 Event Subscriptions 10:36 9.2.5 Configuring Collector-initiated Subscriptions 2:55 9.2.7 Configuring Source-initiated Subscriptions 5:56 Total 37:28 Number of Exam Questions 12 questions Total Time About 55 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 123 Section 9.3: Performance Monitoring Summary This section discusses tools to monitor the performance of a system. Details include: The role of the Performance Information Tools Windows Experience Index (WEI) Features of the Windows Performance Monitor: o Performance Monitor o Data Collector Set (DCS) o Reports perfmon.exe logman The role of the Windows Performance Toolkit (WPT) Tools in the WPT o Windows Performance Recorder (WPR) o Windows Performance Analyzer (WPA) Students will learn how to: Use the Windows Experience Index to establish the base score of a machine. Use Performance Monitor to gather information about the performance of a computer. Create a Data Collector Set to capture information and monitor the performance of a computer. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 10.0 Monitoring o Monitor a Windows system by doing the following: Monitor processes and resource usage with Performance Monitor. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 703. Monitor systems. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Data collector sets o Generating a system diagnostics report 704. Configure performance settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring desktop environment ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 124 70-687 Exam Objectives: 603. Monitor system performance. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Monitor system resources o Optimize networking performance o Optimize the desktop environment Lecture Focus Questions: Which components does the Windows Experience Index test to determine the base score? How is the base score of the Windows Experience Index calculated? What are the key differences between Performance Monitor and Data Collector Sets? What types of performance analysis can the three tools in the Windows Performance Toolkit (WPT) perform? Video/Demo Time 9.3.1 Performance Information and Tools Console 6:46 9.3.2 Viewing the Windows Experience Index 3:29 9.3.5 Performance Monitor Console 9:12 9.3.6 Monitoring Performance 9.3.8 Windows Performance Toolkit (WPT) Total 10:02 4:10 33:39 Lab/Activity Update the Windows Experience Index Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 55 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 125 Section 9.4: Resource Monitoring Summary This section provides information about the following resource monitoring tools: Windows 7 Task Manager Windows 8 Task Manager Resource Monitor Process Explorer Students will learn how to: Use Task Manager and Resource Monitor to view and manage processes and services on a computer. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 10.0 Monitoring o Monitor a Windows system by doing the following: Monitor processes and resource usage with Task Manager. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 703. Monitor systems. 70-687 Exam Objectives: 603. Monitor systems. o Configure Task Manager o Monitor system resources Lecture Focus Questions: Under which circumstances should you use Resource Monitor versus Task Manager in Windows? What type of information is provided by a wait chain? How does processor affinity affect the use of system resources? How can you use Resource Monitor to identify which application is writing to a disk? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 126 Video/Demo Time 9.4.1 Resource Monitor and Process Explorer 5:05 9.4.2 Monitoring Resources in Windows 7 8:28 9.4.3 Monitoring Resources in Windows 8 8:55 Total 22:28 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 127 Section 9.5: Reliability and Performance Maintenance Summary This section provides information about using the Reliability Monitor and Windows Action Center to monitor the health of a Windows system. Students will learn how to: Use the Reliability Monitor to view the historical data of the operating system. Use the data in the Action Center to troubleshoot a computer. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 10.0 Monitoring o Monitor a Windows system by doing the following: Monitor system reliability with Reliability Monitor and the Action Center. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 403. Configure networking settings. o Configuring security settings on the client 70-687 Exam Objectives: 603. Monitor system performance. o Monitor system resources o Optimize the networking performance Lecture Focus Questions: What is the role of the Reliability Monitor? How is the stability index value calculated? What kind of warnings does the Action Center provide? Which service is required for Action Center to run properly? Video/Demo Time 9.5.1 Reliability Monitor and Action Center 5:46 9.5.2 Using Reliability Monitor 5:20 9.5.3 Using the Action Center 4:45 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 15:51 128 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 129 Section 9.6: Optimization Summary This section discusses optimizing the performance of a system. Concepts covered include: Features to increase the system performance: o Visual Effects o Processor Scheduling o Paging File o Data Execution Protection (DEP) o Write Caching o ReadyBoost Students will learn how to: Edit the Advanced System Settings to increase the performance of a machine. Configure the virtual memory settings to optimize the computer's performance. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 3.0 Applications o Manage running processes on a Windows system by doing the following: Adjust processor scheduling. 4.0 Hardware o Optimize hardware performance by doing the following: Optimize performance settings. Configure page file settings. 5.0 Storage o Manage storage on a Windows system by doing the following: Optimize storage devices. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 704. Configure performance settings. o Configuring page files o Configuring hard drive cache o Configuring processor scheduling o Configuring desktop environment ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 130 70-687 Exam Objectives: 603. Monitor system performance. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Monitor system resources o Optimize the desktop environment o Adjust indexing options Lecture Focus Questions: If you have a machine that is responding rather slowly, what settings could you change to increase the performance of this machine? What type of processor scheduling would you use on a desktop machine running Windows? What is a temporary solution to resolve the problem of the paging file usage nearing 100%? What is a more permanent solution? How does Data Execution Protection (DEP) help prevent damage from viruses and other security threats? What type of write caching option increases performance for internal hard disk drives? How can ReadyBoost increase system performance? How can you optimize the indexing process? Video/Demo Time 9.6.1 Optimization 5:46 9.6.2 Optimizing Performance 5:39 9.6.3 Configuring Indexing 7:27 Total 18:52 Lab/Activity Configure Virtual Memory Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 131 Section 9.7: Remote Management Summary This section discusses managing remote access. Tools discussed include: Windows remote Management (WinRM) Remote management tools for Windows computers: o Windows Remote Shell (WinRS) o PsExec o PowerShell o Computer Management MMC Students will learn how to: Enable remote management and configure trusts between clients. Execute and run commands locally and remotely on different computers using PowerShell and WinRS. Use filtering and pipelining with PowerShell to display only specific data. Configure Remote Desktop to allow a connection to a remote computer. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 2.0 Access o Enable remote access by doing the following: Configure Remote Desktop access. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 405. Configure remote management. o Remote management methods o Configuring remote management tools o Executing PowerShell commands 604. Configure remote connections. o Remote desktop 70-687 Exam Objectives: 304 Configure remote management. o Choose the appropriate remote management tools o Configure remote management settings o Modify settings remotely by using MMCs or Windows PowerShell 501. Configure remote connections. o Configure remote authentication o Configure Remote Desktop settings ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 132 Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between authenticating for remote management in a domain versus in a workgroup? How can you run PowerShell commands on a remote computer? Which Windows versions and editions support accepting incoming Remote Desktop connection requests? If you cannot connect to the remote computer when using Remote Desktop, what items should you consider and verify? What are the advantages of using RemoteApp? Video/Demo Time 9.7.1 Remote Management Tools 8:12 9.7.2 Using Remote Management Tools 6:21 9.7.4 Remote Desktop 7:30 9.7.5 Using Remote Desktop Total 13:15 35:18 Lab/Activity Configure Remote Desktop Number of Exam Questions 14 questions Total Time About 55 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 133 Section 9.8: Remote Assistance Summary This section examines details about using Remote Assistance to configure and initiate a Remote Assistance session. Students will learn how to: Use Remote Assistance to provide help and support to users. Configure a Remote Assistance invitation. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 2.0 Access o Enable remote access by doing the following: Configure Remote Assistance. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 405. Configure remote management. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Remote management methods o Configuring remote management tools 70-687 Exam Objectives: 304. Configure remote management. o Choose the appropriate remote management tools o Configure remote management settings Lecture Focus Questions: What are the differences between Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop? What are the steps required to initiate a Remote Assistance session? How can the novice take back control of his computer during a Remote Assistance session? Video/Demo Time 9.8.1 Remote Assistance 2:33 9.8.2 Using Remote Assistance 8:47 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 11:20 134 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 15 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 135 Section 10.1: System Updates Summary In this section students will explore using system updates to keep a computer secure and up-to-date. Details about the following concepts will be covered: The role of Windows Update Update considerations when using Windows Update: o Update options o Update categories o Manual download o Update history o Required user privileges o Removing updates o Updating other Microsoft products o Configuring a proxy update server Students will learn how to: Use Windows Update to manage and maintain updates. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 8.0 System Protection o Configure automatic updates on a Windows system. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 701. Configure updates to Windows 7. o Configuring update settings o Determining source of updates o Configuring Windows Update policies o Reviewing update history o Checking for new updates o Rolling back updates 70-687 Exam Objectives: 601. Configure and manage updates. o Configure update settings o Configure Windows Update policies o Manage update history o Roll back updates o Update Windows Store applications ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 136 Lecture Focus Questions: How can you manually check for updates, but not install them? How do you install optional updates? What is the difference between Microsoft Update and Windows Update? Video/Demo 10.1.1 Windows Updates Time 8:01 10.1.2 Configuring Windows Update in Windows 7 7:03 10.1.3 Configuring Windows Update in Windows 8 7:34 10.1.4 Updating Windows Store Applications Total 3:59 26:37 Lab/Activity Configure Windows Update Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 137 Section 10.2: Update Deployment and Management Summary This section discusses tools to deploy and manage updates. The following concepts will be covered: The role of a local update server Tools to centrally manage updates: o Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) o System Center Essentials o System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) o Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) Automatic Update Policies available: o Configure Automatic Updates o Specify intranet Microsoft Update service location o Enable client-side targeting o Reschedule Automatic Updates Scheduled Installations o No Auto-Restart For Scheduled Automatic Updates and Installations o Automatic Updates detection frequency o Allow Automatic Updates immediate installation o Delay restart of schedule installations o Re-prompt for restart with scheduled installations o Allow non-administrators to receive update notifications o Do not display ‘Install Updates and Shut Down’ option in Shut Down Windows dialog box Download options: o Automatic o Notification Installation Option o Automatic (Scheduled) o Notification Students will learn how to: Configure Windows clients to connect to and download updates from a Windows Server Update Server (WSUS). ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 138 Client Pro Exam Objectives: 8.0 System Protection o Configure automatic updates on a Windows system. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 701. Configure updates to Windows 7. o Configuring update settings o Determining source of updates o Configuring Windows Update policies o Reviewing update history o Checking for new updates o Rolling back updates 70-687 Exam Objectives: 601. Configure and manage updates. o Configure update settings o Configure Windows Update policies o Manage update history o Roll back updates o Update Windows Store applications Lecture Focus Questions: Under which circumstances would you choose a WSUS solution rather than a standard Windows Update solution? What types of operating system vulnerabilities are identified by the Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA)? Video/Demo 10.2.1 Update Deployment and Management 10.2.2 Configuring WSUS Clients Total Time 7:57 12:29 20:26 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 139 Section 10.3: System Backup Summary This section covers the following details about backup. Considerations when managing backups: o Types of backup; System image File backup o Backup location o Requirements for backup o Scheduling backups File History in Windows 8 Parameters to manage File History: o Save copies of files o Size of offline cache o Keep saved versions Students will learn how to: Create a complete system image of a machine. Configure and schedule backups of user files and folders on the computer. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 8.0 System Protection o Protect data on a Windows system by doing the following: Configure backups, system images, and system repair discs. Recover data using backups, system images, and system repair discs. Configure File History. (Windows 8 only) o Protect operating system files and settings on a Windows system using System Restore. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 801. Configure backup. o Creating a system recovery disk o Backing up files, folders, or full system o Scheduling backups ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 140 70-687 Exam Objectives: 701 Configure backup. o Create a system recovery disk o Back up files, folders, and full system o Schedule backups Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between the two types of backups available through Backup and Restore? Which type of file system is required for the destination when backing up a system image? When is a Backup Set folder created and what is saved to the folder? Which feature allows open files to be backed up? Video/Demo 10.3.1 Windows 7 System Backup Time 11:23 10.3.2 Implementing System Backups in Windows 7 6:18 10.3.3 Windows 8 Backup Tools 6:02 10.3.4 Protecting Data in Windows 8 9:19 Total 33:02 Lab/Activity Back Up the Computer Number of Exam Questions 16 questions Total Time About 60 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 141 Section 10.4: Windows 7 Data Recovery Summary In this section students will learn about recovering files in Windows 7. Details include: Windows 7 locations that previous versions of files exist: o Backup o Shadow copies o System images Students will learn how to: Restore and recover files from a backup. Manually create a restore point and configure a schedule to create future restore points. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 8.0 System Protection o Protect data on a Windows system by doing the following: Recover data using backups, system images, and system repair discs. Restore files by configuring previous file versions. Configure File History. (Windows 8 only) 70-680 Exam Objectives: 803. Configure file recovery options. o Configuring file restore points o Restoring previous versions of files and folders o Restoring damaged or deleted files by using shadow copies o Restore user profiles Lecture Focus Questions: When would you configure the System Protection settings to automatically save files but not system settings? What is the difference between a shadow copy and a file which is in the Backup Set folder? Which tools allow you to restore individual files? What options are given when attempting to restore a file to a location where a file with the same name already exists? What must you do to restore files from a Complete PC Backup VHD file? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 142 Video/Demo Time 10.4.1 Windows 7 Data Recovery 4:16 10.4.2 Recovering Files from Backups in Windows 7 2:18 10.4.3 Recovering Files from Shadow Copies in Windows 7 6:59 Total 13:33 Lab/Activity Recover a File from Previous Versions Copy a Folder from Previous Versions Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 143 Section 10.5: Windows 8 Data Recovery Summary In this section students will learn about recovering files in Windows 8. Details include: Backup methods: o File History o System image Students will learn how to: Configure File History. Recover previous file versions using File History. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 8.0 System Protection o Protect data on a Windows system by doing the following: Recover data using backups, system images, and system repair discs. Restore files by configuring previous file versions. Configure File History. (Windows 8 only) 70-687 Exam Objectives: 703. Configure file recovery options. o Configure file restore points o Restore previous versions of files and folders o Configure File History Lecture Focus Questions: What are the key differences between System Protection on Windows 7 and on Windows 8? What must you do to configure File History on Windows 8? How do you restore files using File History? Video/Demo Time 10.5.1 Windows 8 Data Recovery 2:09 10.5.2 Recovering Data in Windows 8 9:32 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 11:41 144 Lab/Activity Configure File History Recover a File from File History Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 145 Section 10.6: System Recovery Summary This section discusses information about system recovery. Details include: Tools to assist in system recovery: o System Restore (restore point) o System Recovery Options o Boot Configuration Data (BCD) o Refresh your PC o Reset your PC The role of a recovery drive Startup modes for Windows 7: o Repair Your Computer o Safe Mode o Safe Mode with Networking o Safe Mode with Command Prompt o Enable Boot Logging o Enable low-resolution video (640x480 256 colors) o Last Known Good Configuration o Debugging mode o Disable automatic restart on system failure Changes from Windows 7 startup modes to Windows 8 startup modes Recommendations to troubleshoot startup errors with the advanced boot options Students will learn how to: Boot a system into a variety of modes for troubleshooting purposes. Perform a system restore using restore points. Use a system image to restore system settings after a volume failure. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 8.0 System Protection o Protect data on a Windows system by doing the following: Configure backups, system images, and system repair discs. Recover data using backups, system images, and system repair discs. o Protect operating system files and settings on a Windows system using System Restore. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 146 70-680 Exam Objectives: 802. Configure system recovery options. o Configuring system restore points o Restoring system settings o Last known good configuration o Complete restore; driver rollback 70-687 Exam Objectives: 702. Configure system recovery options. o Configure system restore o Determine when to choose last known good configuration o Perform a complete restore o Perform a driver rollback o Perform a push button refresh or reset o Configure startup settings Lecture Focus Questions: When your system is having significant problems, what are your alternate boot mode options? What types of drivers and services are loaded when you boot in Safe Mode? When would you choose to use the Last Known Good Configuration? What types of events trigger automatic restore points to be created? Which tool can delete all restore points except for the last restore point? How can you get a system running again as quickly as possible after a disk holding the operating system fails? Video/Demo 10.6.1 Windows 7 System Recovery Time 11:26 10.6.2 Using System Recovery in Windows 7 6:54 10.6.3 Windows 8 System Recovery 6:43 10.6.4 Windows 8 Refresh and Reset System Recovery 6:16 10.6.5 Using the Advanced Options Menu in Windows 8 12:52 10.6.8 Using System Recovery in Windows 8 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 9:14 53:25 147 Lab/Activity Create a Restore Point Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 80 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 148 Section 11.1: Application Restriction Summary This section provides students with an overview of application restriction. Concepts covered include: Software restriction policies restrict the execution of specific: o Applications o Installation files o Scripts o Dynamic-Link Library (DLL) files Application restriction rules (listed most specific to least specific) o Hash o Certificate o Path o Network Zone o Default AppLocker policies AppLocker rule types: o Executable o Windows Installer o Script o DLL o Packaged App AppLocker rules have the following conditions: o Publisher o Path o Hash Considerations when managing AppLocker Students will learn how to: Configure a local software restriction policy for a specific user. Create an application control policy. Client Pro Objectives: 3.0 Applications o Manage Windows applications by doing the following: Use AppLocker to secure installed applications. Use Group Policies to control access to applications. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 149 70-680 Exam Objectives: 303. Configure application restrictions. o Setting software restriction policies o Setting application control policies o Setting through group policy or local security policy 70-687 Exam Objectives: 204. Control access to local hardware and applications. o Configure AppLocker o Configure access through Group Policy or local security policy Lecture Focus Questions: How are software restriction policies managed, and in what order are they applied? How does a hash rule identify one application from another? Does the same hash value always apply after the application receives a software update? What are the advantages of using AppLocker over software restriction policies? If software restriction policies and AppLocker policies are configured on the same object, which rules take precedence? Video/Demo Time 11.1.1 Application Restriction Overview 1:36 11.1.2 Software Restriction Policies 6:57 11.1.3 Implementing Software Restriction Policies 12:37 11.1.5 AppLocker 11.1.6 Implementing AppLocker Total 7:07 12:25 40:43 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 55 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 150 Section 11.2: Secure Boot Summary This section provides information about using Secure Boot. Details include: Considerations when using Secure Boot o Hardware requirements o Software requirements o Choosing boot options o Secure Boot databases o Manually updating or turning off Secure Boot o Recovery processes Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: Protect against malware by configuring Secure Boot. (Windows 8 only) 70-687 Exam Objectives: 403. Configure local security settings. o Configure Secure Boot Lecture Focus Questions: How does Secure Boot fix the problem of rootkits overwriting the boot loader on the hard disk drive? What are the hardware requirements for Secure Boot? software requirements? What is the role of the signature database? the revoked signature database? What happens when the system has problems when trying to boot while using Secure Boot? Video/Demo 11.2.1 Secure Boot ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro Time 5:38 151 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 15 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 152 Section 11.3: Internet Explorer Summary This section discusses configuring security settings for Internet Explorer. Details include: InPrivate Mode features: o InPrivate Browsing o InPrivate Filtering/Tracking Protection Controlling InPrivate Mode through Group Policy settings Features that enhance Internet Explorer security: o SmartScreen Filter o Delete Browsing History o Pop-Up Blocker o AutoComplete o Per User Per Site ActiveX Control o Cross-Site Scripting Filter o Data Execution Prevention o Content Advisor o Advanced Settings Components to configure the Compatibility View: o Compatibility View button o Compatibility View Settings o Group Policy Managing Internet Explorer Add-ons Categories for Add-ons: o Toolbars and Extensions o Search Providers o Accelerators o InPrivate Filtering/Tracking Protection Details when using Manage Add-ons Group Policies to restrict the add-ons: o Add-on List o Deny all add-ons unless specifically allowed in the Add-on List o All Processes o Process List o Do not allow users to enable or disable add-ons Students will learn how to: Use InPrivate Mode to protect privacy. Use accelerators to quickly access, share, search, translate or obtain additional information about a topic. Add additional accelerators to provide additional functionality. Configure Compatibility View ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 153 Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: Configure Internet Explorer security settings. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 302. Configure application compatibility. o Compatibility issues with Internet Explorer 304. Configure Internet Explorer. This objective may include but is not limited to: o Configuring compatibility view o Configuring security settings o Configuring providers o Managing add-ons o Controlling InPrivate mode 70-687 Exam Objectives: 205. Configure Internet Explorer. o Configure compatibility view o Configure security settings o Manage add-ons o Configure websockets 403. Configure local security settings. o Configure SmartScreen filter Lecture Focus Questions: How does the SmartScreen Filter detect phishing Web sites and Web sites that dispense malware? How do the InPrivate Mode features protect a user's privacy? When would you choose to disable an add-on? What function does the Compatibility View provide for users? How can you clear previously-saved passwords saved in Internet Explorer? ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 154 Video/Demo Time 11.3.1 Internet Explorer Security Configuration 7:02 11.3.4 Compatibility View and Add-ons 4:44 11.3.7 Using IE 10 Features 9:55 11.3.8 Using InPrivate Browsing 5:18 11.3.9 Using SmartScreen Filter 3:45 11.3.10 WebSocket 7:42 Total 38:26 Number of Exam Questions 14 questions Total Time About 60 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 155 Section 11.4: Internet Options Summary In this section students will learn about settings for the Internet Explorer web browser. Concepts covered include: Internet Options tabs containing preference settings: o General o Security o Privacy o Content o Connections o Programs o Advanced Security Level Protected Mode Security zones o Local intranet o Trusted sites o Restricted sites o Internet Students will learn how to: Configure advanced security settings, zone membership, and privacy settings for IE. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: Configure Internet Explorer security settings. 70-680 Exam Objectives: 304. Configure Internet Explorer. o Configuring security settings o Certificates for secure Web sites 70-687 Exam Objectives: 205. Configure Internet Explorer. o Configure security settings ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 156 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the different kinds of security zones? What is the difference between the default security level and the default protected mode assigned to security zones? What is the difference between a root CA and a subordinate CA? Video/Demo Time 11.4.1 Internet Options 4:30 11.4.2 Configuring Internet Options 9:11 11.4.3 Configuring Security Zones 4:04 Total 17:45 Lab/Activity Modify Zone Memberships Configure Privacy Settings Configure Advanced Security Settings Restore Advanced Settings Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 157 Section 11.5: Windows Defender Summary This section discusses using Windows Defender to protect against security threats caused by spyware and other unwanted software. Details include: Windows Defender components : o Automatic scanning o Real-time protection o Alert action o SpyNet Community Considerations when working with Windows Defender Students will learn how to: Configure Windows Defender to scan a system for malware. Configure the Windows Defender protection settings to run automatic scans. Client Pro Exam Objectives: 9.0 Security o Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: Protect against malware by configuring Windows Defender. Lecture Focus Questions: What are the differences between the three types of Windows Defender automatic scans? What is the difference between the remove and quarantine action in Windows Defender? What is a heuristic and how can it help identify possible threats to your computer? Video/Demo Time 11.5.1 Windows Defender 2:51 11.5.2 Configuring Windows Defender 8:27 Total ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 11:18 158 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 159 Windows Client Pro Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the Windows Client Pro Certification exam. Students will have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exam. Students will typically take about 5-10 minutes (depending upon the complexity and their level of knowledge) to complete each simulation question in the following practice exams. There is no time limit on the amount of time a student can take to complete the practice exams for the following domains. Windows Client Pro Objective 1: Windows Operating System Installation (2 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 2: Access (7 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 3: Applications (2 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 4: Hardware (6 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 5: Storage (9 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 6: Networking (10 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 7: Printing (1 simulation question) Windows Client Pro Objective 8: System Protection (7 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 9: Security (10 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 10: Monitoring (2 simulation questions) Windows Client Pro Objective 11: Virtualization (0 simulation questions) The Windows Client Pro Certification Practice Exam consists of 15 simulation questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time the Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 160 MS 70-680 Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the MS 70-680 exam and to register for the exam. Students will have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exam. Students will typically take about 1 minute to complete each question in the following practice exams. There is no time limit on the amount of time a student can take to complete the practice exams for the following domains. Objective 100. Installing, Upgrading, and Migrating to Windows 7 (38 questions) Objective 200. Deploying Windows 7 (51questions) Objective 300. Configuring Hardware and Applications (53 questions) Objective 400. Configuring Network Connectivity (74 questions) Objective 500. Configuring Access to Resources (69 questions) Objective 600. Configuring Mobile Computing (65 questions) Objective 700. Monitoring and Maintaining Systems that Run Windows 7 (91 questions) Objective 800. Configuring Backup and Recovery Options (31 questions) The 70-680 Certification Practice Exam consists of 50 questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time the Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. The Certification Practice Exam has a time limit of 2 hours and 10 minutes. A passing score of 95% should verify that the student has mastered the concepts and is ready to take the real certification exam. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 161 MS 70-687 Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the MS 70-687 exam and to register for the exam. Students will have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exam. Students will typically take about 1 minute to complete each question in the following practice exams. There is no time limit on the amount of time a student can take to complete the practice exams for the following domains. Objective 100. Install and Upgrade to Windows 8 (29 questions) Objective 200. Configure Hardware and Applications (73 questions) Objective 300. Configuring Network Connectivity (65 questions) Objective 400. Configure Access to Resources (84 questions) Objective 500. Configure Remote Access and Mobility (54 questions) Objective 600. Monitor and Maintain Windows Clients (80 questions) Objective 700. Configure Backup and Recovery Options (17 questions) The 70-687 Certification Practice Exam consists of 50 questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time the Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. The Certification Practice Exam has a time limit of 2 hours and 10 minutes. A passing score of 95% should verify that the student has mastered the concepts and is ready to take the real certification exam. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 162 Appendix A: Approximate Time for the Course The total time for the LabSim Windows Client Pro course is approximately 65 hours and 49 minutes. The time is calculated by adding the approximate time for each section which is calculated using the following elements: Video/demo times Approximate time to read the text lesson (the length of each text lesson is taken into consideration) Simulations (5 minutes assigned per simulation) Questions (1 minute per question) The breakdown for this course is as follows: Module Sections Time Minute HR:MM 1.0 Course Introduction 1.1 Course Introduction 1.2 Windows as a Client 1.3 Windows 7 User Interface Overview 1.4 Windows 8 User Interface Overview 20 50 25 30 125 2:05 60 40 75 40 35 5 20 275 4:35 40 30 55 20 45 15 65 270 4:30 2.0 Hardware Management 2.1 Devices and Drivers 2.2 Display Management 2.3 Disk Partitions and Volumes 2.4 Storage Spaces 2.5 Disk Optimization 2.6 Removable Storage 2.7 SkyDrive Storage 3.0 Network Configuration 3.1 IPv4 3.2 IPv6 3.3 IP Address Configuration 3.4 Wireless Networking Overview 3.5 Wireless Networking Configuration 3.6 Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) 3.7 Windows Firewall ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 163 4.0 Application Management 4.1 Desktop Applications 4.2 User Account Control (UAC) 4.3 Application Compatibility 4.4 Application Virtualization 4.5 Windows Store Applications 40 35 45 15 30 165 2:45 10 65 35 50 50 40 45 20 45 30 390 6:30 35 30 55 40 60 55 50 325 5:25 10 30 25 10 50 35 160 2:40 5.0 System Access 5.1 Authentication and Authorization 5.2 Authentication Management 5.3 Alternative Authentication Options 5.4 NTFS Permissions 5.5 Resource Sharing 5.6 Libraries and HomeGroups 5.7 Printer Sharing and Management 5.8 Auditing 5.9 Encryption 5.10 BranchCache 6.0 Windows Installation 6.1 Windows Versions 6.2 Windows 7 Installation 6.3 Windows 8 Installation 6.4 Windows Upgrade 6.5 User Profile and Data Migration 6.6 VHD Installation 6.7 Client-Side Virtualization 7.0 System Images 7.1 System Images overview 7.2 Image Preparation 7.3 Image Capture 7.4 Manual Image Deployment 7.5 Image Servicing 7.6 Domain Image Deployment 8.0 Mobile Computing 8.1 Network Access Protection (NAP) 8.2 Virtual Private Network (VPN) 8.3 DirectAccess 8.4 BitLocker 8.5 BitLocker to Go ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 10 40 30 35 20 164 8.6 Mobile Device Security 8.7 Power Management 8.8 Mobility Options 8.9 Mobile Networking 35 35 65 30 300 5:00 50 55 55 35 20 35 55 15 320 5:20 65 80 275 4:35 55 15 60 50 20 200 3:20 9.0 System Monitoring and Maintenance 9.1 Troubleshooting Tools 9.2 System Events 9.3 Performance Monitoring 9.4 Resource Monitoring 9.5 Reliability and Performance Maintenance 9.6 Optimization 9.7 Remote Management 9.8 Remote Assistance 10. System Protection 10.1 System Updates 10.2 Update Deployment and Management 10.3 System Backup 10.4 Windows 7 Data Recovery 10.5 Windows 8 Data Recovery 10.6 System Recovery 70 60 11.0 Security 11.1 Application Restriction 11.2 Secure Boot 11.3 Internet Explorer 11.4 Internet Options 11.5 Windows Defender Practice Exams Client Pro Practice Exams Obj. 1: Windows Operating System Installations (2 simulation questions) Obj. 2: Access (7 simulation questions) Obj. 3: Applications (2 simulation questions) Obj. 4: Hardware (6 simulation questions) Obj. 5: Storage (9 simulation questions) Obj. 6: Networking (10 simulation questions) Obj. 7: Printing (1 simulation question) Obj. 8 System Protection (7 simulation questions) Obj. 9 Security (10 simulation questions) ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 10 35 10 30 45 50 5 35 50 165 Obj. 10: Monitoring (2 simulation questions) Obj. 11: Virtualization (0 simulation questions) Client Pro Certification Practice Exam 10 0 15 295 4:55 522 8:42 452 7:32 3949 65:49 MS 70-680 Practice Exams Obj. 100: Installing, Upgrading, and Migrating to Windows 7 (38 questions) Obj. 200: Deploying Windows 7 (51 questions) Obj. 300: Configuring Hardware and Applications (53 questions) Obj. 400: Configuring Network Connectivity (74 questions) Obj. 500: Configuring Access to Resources (69 questions) Obj. 600: Configuring Mobile Computing (65 questions) Obj. 700: Monitoring and Maintaining Systems that Run Windows 7 (91 questions) Obj. 800: Configuring Backup and Recovery Options (31 questions) 70-680 Certification Practice Exam (50 questions) 38 51 53 74 69 65 91 31 50 MS 70-687 Practice Exams Obj.100: Install and Upgrade to Windows 8 (29 questions) Obj. 200: Configure Hardware and Applications (73 questions) Obj. 300: Configuring Network Connectivity (65 questions) Obj. 400: Configure Access to Resources (84 questions) Obj. 500: Configure Remote Access and Mobility (54 questions) Obj. 600: Monitor and Maintain Windows Clients (80 questions) Obj. 700: Configure Backup and Recovery Options (17 questions) 70-687 Certification Practice Exam (50 questions) 29 73 65 84 54 80 17 50 Total Time ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 166 Appendix B: Windows Client Pro Objectives The Windows Client Pro certification exam covers the following: # 1.0 Exam Objective Windows operating system installation Install the correct PC hardware to support the installation of Windows. Select the correct version and edition of Windows to meet end-user requirements. Perform a clean installation of Windows 7 or Windows 8 to meet end-user requirements. Upgrade an existing Windows Vista system to Windows 7. Upgrade an existing Windows 7 system to Windows 8. Use Windows To Go to create a bootable USB flash storage device. 2.0 Access Manage users and groups by doing the following: o Create new users. o Create new groups and add members. o Manage user passwords. o Manage user account types. Link a local user to a Microsoft account. (Windows 8 only) Restrict access to files and folders on a Windows system using NTFS permissions. Enable remote access by doing the following: o Configure Remote Desktop access. o Establish a connection to a DirectAccess server. o Establish a VPN connection to a remote access server. o Configure Remote Assistance. 3.0 Applications Manage Windows applications by doing the following: o Install a standard Windows application using Windows Installer. o Run an application in Compatibility Mode. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro Module.Section 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 8.2 8.3 9.7 9.8 4.1 4.3 4.4 4.5 9.1 9.6 11.1 167 o Use AppLocker to secure installed applications. o Use Group Policies to control access to applications. o Manage App-V applications. Manage running processes on a Windows system by doing the following: o Configure the way services are started at boot. o Manually start or stop services. o Use Task Manager to view and kill running processes. o Adjust processor scheduling. Manage Windows Store apps on a Windows 8 system by doing the following: o Install, manage, and uninstall apps from the Windows Store. o Configure location settings for locationaware apps. 4.0 Hardware Manage devices in Device Manager by doing the following: o Install, uninstall, and rollback device drivers. o Disable and enable hardware devices. Customize display settings. Optimize hardware performance by doing the following: o Configure power options. o Optimize performance settings. o Configure page file settings. 5.0 Storage Add storage to a Windows system by doing the following: o Add storage devices to the system. o Create, format, and mount volumes. Add storage spaces to a Windows 8 system by doing the following: o Define storage pools. o Create storage spaces. Manage storage on a Windows system by doing the following: o Optimize storage devices. o Check storage devices and file systems for errors. Configure offline files. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 2.1 2.2 8.7 9.6 2.3 2.4 2.5 8.8 9.6 168 6.0 Networking Enable networking on Windows by doing the following: o Install a wired network interface and connect it to a network switch. o Install a wireless network interface and configure it to do the following: Securely connect to a wireless access point. Securely connect to other wireless hosts using WiFi Direct. (Windows 8 only) Connect a mobile Windows system to a mobile broadband network. Given a network diagram, configure network settings on a Windows system by doing the following: o Configure an appropriate IPv4 address, subnet mask, default gateway address, and DNS server address. o Configure IPv6 settings. Share system resources on a Windows system by doing the following: o Share a folder. o Share a printer and add drivers for other operating systems. o Restrict access to a shared folder or printer using share permissions. o Configure HomeGroup sharing. o Use SkyDrive to store files. (Windows 8 only) o Use Near Field Communications to share data with mobile devices. (Windows 8 only) 7.0 Printing 2.7 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 5.5 5.6 5.7 8.8 8.9 5.7 Configure and manage printing on a Windows system by doing the following: o Connect a printer to a local port and configure the appropriate drivers and utilities. o Connect to a shared printer on the network and configure the appropriate drivers and utilities. o Configure printer settings. o Manage print jobs in the print queue. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 169 8.0 System Protection Protect data on a Windows system by doing the following: o Configure backups, system images, and system repair discs. o Recover data using backups, system images, and system repair discs. o Restore files by configuring previous file versions. o Configure File History. (Windows 8 only) Protect operating system files and settings on a Windows system using System Restore. Configure automatic updates on a Windows system. 9.0 Security Manage Windows user certificates. Encrypt data on a Windows system in the following ways: o Encrypt files and folders on a per-file basis using Encrypting File System (EFS). o Enable whole-disk encryption using TPM and BitLocker. Harden a Windows workstation by doing the following: o Configure Internet Explorer security settings. o Configure authentication restrictions. o Configure password policies. o Configure User Account Control (UAC) rules. o Configure Windows Firewall and Windows Firewall with Advanced Security rules. o Protect against malware by configuring Secure Boot. (Windows 8 only) o Protect against malware by configuring Windows Defender. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 3.7 4.2 5.1 5.2 5.9 8.4 8.5 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 170 10.0 Monitoring Monitor a Windows system by doing the following: o Monitor processes and resource usage with Task Manager. o Monitor processes and resource usage with Performance Monitor. o Monitor system events with Event Viewer. o Monitor system reliability with Reliability Monitor and the Action Center. 11.0 Virtualization 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 6.7 Create and manage virtual machines on a Windows 8 system by doing the following: o Enable Client Hyper-V. o Create a new virtual machine and install an operating system within it. ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 171 Appendix C: 70-680 TS: Windows 7, Configuring Objectives The certification exam measures your ability to install, configure, maintain, and troubleshoot the Windows 7 operating system. Before taking the exam, you should be proficient in the skills listed below: # Objective 100 Installing, Upgrading, and Migrating to Windows 7 (14%) 101 Perform a clean installation. This objective may include but is not limited to: Module.Section 6.1 6.2 Identifying hardware requirements Setting up as the sole operating system Setting up as dual boot; installation methods Boot from the source of installation, preparing the installation source: USB, CD, network share, WDS 102 Upgrade to Windows 7 from previous versions of Windows. This objective may include but is not limited to: 6.4 Upgrading from Windows Vista Migrating from Windows XP Upgrading from one edition of Windows 7 to another edition of Windows 7 103 Migrate user profiles. This objective may include but is not limited to: 6.5 Migrating from one machine to another Migrating from previous versions of Windows Side-by-side vs. wipe and load ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 172 200 Deploying Windows 7 (13%) 201 Capture a system image. This objective may include but is not limited to: 7.1 7.2 7.3 Preparing system for capture Creating a WIM file Automated capture Manual capture 202 Prepare a system image for deployment. This objective may include but is not limited to: 7.5 Inserting an application into a system image Inserting a driver into a system image Inserting an update into a system image Configuring tasks to run after deployment 203 Deploy a system image. This objective may include but is not limited to: 7.4 7.6 Automated deployment methods Manually deploying a customized image 204 Configure a VHD. This objective may include but is not limited to: 6.6 Creating, deploying, booting, mounting, and updating VHDs Offline updates Offline servicing 300 Configuring Hardware and Applications (14%) 301 Configure devices. This objective may include but is not limited to: 2.1 Updating, disabling, and uninstalling drivers Signed drivers Conflicts between drivers Configuring driver settings Resolving problem device driver ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 173 302 Configure application compatibility. This objective may include but is not limited to: 4.3 11.3 Setting compatibility mode Implementing shims Compatibility issues with Internet Explorer 303 Configure application restrictions. This objective may include but is not limited to: 11.1 Setting software restriction policies Setting application control policies Setting through group policy or local security policy 304 Configure Internet Explorer. This objective may include but is not limited to: 11.3 11.4 Configuring compatibility view Configuring security settings Configuring providers Managing add-ons Controlling InPrivate mode Certificates for secure Web sites 400 Configuring Network Connectivity (14%) 401 Configure IPv4 network settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: 3.1 3.3 Connecting to a network Configuring name resolution Setting up a connection for a network Network locations Resolving connectivity issues APIPA 402 Configure IPv6 network settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: 3.2 3.3 Configuring name resolution Connecting to a network Setting up a connection for a network Network locations Resolving connectivity issues Link local multicast name resolution ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 174 403 Configure networking settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: Adding a physically connected (wired) or wireless device Connecting to a wireless network Configuring security settings on the client Set preferred wireless networks Configuring network adapters Configuring location-aware printing 404 Configure Windows Firewall. This objective may include but is not limited to: 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 5.7 9.5 3.7 Configuring rules for multiple profiles Allowing or denying an application Network-profile-specific rules Configuring notifications Configuring authenticated exceptions 405 Configure remote management. This objective may include but is not limited to: 9.7 9.8 Remote management methods Configuring remote management tools Executing PowerShell commands 500 Configuring Access to Resources (13%) 501 Configure shared resources. This objective may include but is not limited to: 5.5 5.6 5.7 Folder virtualization Shared folder permissions Printers and queues Configuring HomeGroup settings 502 Configure file and folder access. This objective may include but is not limited to: 5.4 5.9 Encrypting files and folders by using EFS Configuring NTFS permissions Resolving effective permissions issues Copying files vs. moving files ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 175 503 Configure user account control (UAC). This objective may include but is not limited to: 4.2 Configuring local security policy Configuring admin vs. standard UAC prompt behaviors Configuring Secure Desktop 504 Configure authentication and authorization. This objective may include but is not limited to: 5.1 5.2 Resolving authentication issues Configuring rights Managing credentials Managing certificates Smart cards with PIV Elevating user privileges Multifactor authentication 505 Configure BranchCache. This objective may include but is not limited to: 5.10 Distributed cache mode vs. hosted mode Network infrastructure requirements Configuring settings Certificate management 600 Configuring Mobile Computing (10%) 601 Configure BitLocker and BitLocker To Go. This objective may include but is not limited to: 8.4 8.5 Configuring BitLocker and BitLocker To Go policies Managing Trusted Platform Module (TPM) PINs Configuring startup key storage Data recovery agent support 602 Configure DirectAccess. This objective may include but is not limited to: 8.3 Configuring client side Configuring authentication Network infrastructure requirements ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 176 603 Configure mobility options. This objective may include but is not limited to: 8.7 8.8 Configuring offline file policies Transparent caching Creating and migrating power policy 604 Configure remote connections. This objective may include but is not limited to: Establishing VPN connections and authentication Enabling a VPN reconnect Advanced security auditing NAP quarantine remediation Dial-up connections Remote desktop Published apps 700 Monitoring and Maintaining Systems that Run Windows 7 (11%) 701 Configure updates to Windows 7. This objective may include but is not limited to: 5.8 8.1 8.2 9.7 10.1 10.2 Configuring update settings Determining source of updates Configuring Windows Update policies Reviewing update history Checking for new updates Rolling back updates 702 Manage disks. This objective may include but is not limited to: 2.3 2.5 2.6 Managing disk volumes Managing file system fragmentation RAID Removable device policies 703 Monitor systems. This objective may include but is not limited to: Configuring event logging Filtering event logs Event subscriptions Data collector sets ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 177 Generating a system diagnostics report 704 Configure performance settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: Configuring page files Configuring hard drive cache Updated drivers Configuring networking performance Configuring power plans Configuring processor scheduling Configuring desktop environment Configuring services and programs to resolve performance issues Mobile computing performance issues Configuring power 800 800 Configuring Backup and Recovery Options (11%) 801 Configure backup. This objective may include but is not limited to: 2.1 2.2 8.7 8.8 9.1 9.3 9.5 9.6 10.3 Creating a system recovery disk Backing up files, folders, or full system Scheduling backups 802 Configure system recovery options. This objective may include but is not limited to: 10.6 Configuring system restore points Restoring system settings Last known good configuration Complete restore; driver rollback 803 Configure file recovery options. This objective may include but is not limited to: 10.4 Configuring file restore points Restoring previous versions of files and folders Restoring damaged or deleted files by using shadow copies Restore user profiles ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 178 Appendix D: 70-687 TS: Windows 8, Configuring Objectives This certification exam measures your ability to install, configure, maintain, and troubleshoot the Windows 8 operating system. Before taking the exam, you should be proficient in the skills listed below: # Objective 100 Install and Upgrade to Windows 8 (10-15%) 101 Evaluate hardware readiness and compatibility. This objective may include but is not limited to: Module.Section 6.1 Determine whether 32 bit or 64 bit is appropriate Determine screen resolution Choose between an upgrade or a clean installation Determine which SKU to install 102 Install Windows 8. This objective may include but is not limited to: 6.3 6.4 6.6 Install as Windows to Go Migrate from Windows XP or Windows Vista Upgrade from Windows 7 to Windows 8 or from one edition of Windows 8 to another edition of Windows 8 Install VHD 103 Migrate and configure user data. This objective may include but is not limited to: 6.5 Migrate user profiles Configure folder redirection Configure profiles 200 Configure Hardware and Applications (15-20%) 201 Configure devices and device drivers. This objective may include but is not limited to: 2.1 Install, update, disable, and roll back drivers Resolve driver issues Configure driver settings ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 179 202 Install and configure desktop applications. This objective may include but is not limited to: 4.1 4.3 4.4 Set compatibility mode Install and repair applications by using Windows Installer Configure default program settings Modify file associations Manage App-V applications 203 Install and configure Windows Store applications. This objective may include but is not limited to: 4.5 Install, reinstall, and update Windows Store applications Restrict Windows Store content Add internal content (side loading) Disable Windows Store 204 Control access to local hardware and applications. This objective may include but is not limited to: 2.6 11.1 Configure AppLocker Configure access through Group Policy or local security policy Manage installation of removable devices 205 Configure Internet Explorer. This objective may include but is not limited to: 11.3 11.4 Configure compatibility view Configure security settings Manage add-ons Configure websockets Configure Download Manager 206 Configure Hyper-V. This objective may include but is not limited to: 6.6 6.7 Create and configure virtual machines Create and manage snapshots Create and configure virtual switches Create and configure virtual disks ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 180 300 Configure Network Connectivity (15-20%) 301 Configure IP settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: 3.1 3.2 3.3 Configure name resolution Connect to a network Configure network locations Resolve connectivity issues 302 Configure networking settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: 3.4 3.5 5.7 Connect to a wireless network Manage preferred wireless networks Configure network adapters Configure location-aware printing 303 Configure and maintain network security. This objective may include but is not limited to: Configure Windows Firewall Configure Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Configure connection security rules (IPSec) Configure authenticated exceptions Configure network discovery Manage wireless security 304 Configure remote management. This objective may include but is not limited to: 3.1 3.2 3.4 3.5 3.7 9.7 9.8 Choose the appropriate remote management tools Configure remote management settings Modify settings remotely by using MMCs or Windows PowerShell 400 Configure Access to Resources (10-15%) 401 Configure shared resources. This objective may include but is not limited to: Configure shared folder permissions Configure HomeGroup settings Configure file libraries Configure shared printers ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 2.7 5.5 5.6 5.7 8.9 181 Set up and configure SkyDrive Configure Near Field Communication (NFC) 402 Configure file and folder access. This objective may include but is not limited to: Encrypt files and folders by using EFS Configure NTFS permissions Configure disk quotas Configure object access auditing 403 Configure local security settings. This objective may include but is not limited to: Configure local security policy Configure User Account Control (UAC) behavior Configure Secure Boot Configure SmartScreen filter 404 Configure authentication and authorization. This objective may include but is not limited to: 2.5 5.4 5.8 5.9 1.2 4.2 11.2 11.3 5.1 5.2 5.3 Configure rights Manage credentials Manage certificates Configure smart cards Configure biometrics Configure picture password Configure PIN Set up and configure Microsoft Account 500 Configure Remote Access and Mobility (10-15%) 501 Configure remote connections. This objective may include but is not limited to: Configure remote authentication Configure Remote Desktop settings Establish VPN connections and authentication Enable VPN reconnect Manage broadband connections ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 8.2 8.9 9.2 9.7 182 502 Configure mobility options. This objective may include but is not limited to: Configure offline file policies Configure power policies Configure Windows to Go Configure sync options Configure WiFi direct 503 Configure security for mobile devices. This objective may include but is not limited to: 8.7 8.8 8.9 6.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 Configure BitLocker and BitLocker To Go policies Configure startup key storage Configure remote wipe Configure location settings (GPS) 600 Monitor and Maintain Windows Clients (10-15%) 601 Configure and manage updates. This objective may include but is not limited to: 10.1 10.2 Configure update settings Configure Windows Update policies Manage update history Roll back updates Update Windows Store applications 602 Manage local storage. This objective may include but is not limited to: Manage disk volumes Manage file system fragmentation Manage storage spaces 603 Monitor system performance. This objective may include but is not limited to: Configure and analyze event logs Configure event subscriptions Configure Task Manager Monitor system resources Optimize networking performance Optimize the desktop environment Configure indexing options ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.2 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 183 700 Configure Backup and Recovery Options (10-15%) 701 Configure backup. This objective may include but is not limited to: 10.3 Create a system recovery disk Back up files, folders, and full system Schedule backups 702 Configure system recovery options. This objective may include but is not limited to: 10.6 Configure system restore Determine when to choose last known good configuration Perform a complete restore Perform a driver rollback Perform a push button refresh or reset Configure startup settings 703 Configure file recovery options. This objective may include but is not limited to: 10.5 Configure file restore points Restore previous versions of files and folders Configure File History ©2013 TestOut Corporation (Rev 6/13) LabSim Windows Client Pro 184