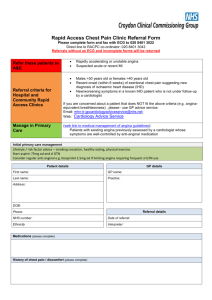
Role of Ultrasound in confirmation of ET tube position
advertisement

APPROACH TO CHEST PAIN DR. PRAKASH MOHANASUNDARAM EMERGENCY PHYSICIAN Department of Accident, Emergency & Critical Care Medicine. Vinayaka Mission Kirupananda Variyar Medical college Hospital, Salem, Tamilnadu, India. www.emergencymedicineindia.com A&E(VINAYAKA) BACKGROUND Approx 5% of all ED visits 15% - AMI 25-30% - Unstable angina 14 -34% - Other conditions Atypical presentations – common A&E(VINAYAKA) ACUTE CHEST PAIN • Recent onset, typically less than 24 h • Location described on the anterior thorax • A noxious uncomfortable sensation distressing to the patient. A&E(VINAYAKA) CATEGORISATION • Visceral pain • Pleuritic pain • Chest wall pain A&E(VINAYAKA) Typical exertional angina Atypical angina Unstable angina Acute myocardial infarction Aortic dissection Pericarditis Oesophageal reflux or spasm Oesophageal rupture Mitral valve prolapse VISCERAL PAIN A&E(VINAYAKA) Pulmonary embolism Pneumonia Spontaneous pneumothorax Pericarditis Pleurisy PLEURITIC PAIN A&E(VINAYAKA) Costosternal syndrome Costochondritis Precordial catch syndrome Slipping rib syndrome Xiphodynia Radicular syndromes Intercostal nerve syndromes Fibromyalgia CHEST WALL PAIN A&E(VINAYAKA) Etiology Quality Location Radiation Dura Asso. Asso.Symptom Onset tion Symptoms s MI MI visceral retrosternal Neck jaw shoulder arm >15 min Nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, dyspnoea variable angina Angina visceral retrosternal Neck, Jaw shoulder, arm <15 min Nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, dyspnoea gradual A&E(VINAYAKA) Etiology Quality Aortic severe dissection Location Asso. Symptoms Onset Sudden retroster Inter constant Nausea diaphoresi nal scapular s, tearing dyspnoea pleuritic lateral Pneumot pleuritic horax lateral PE Radiation Duration Neck, back constant dyspnoea sudden constant dyspnoea sudden A&E(VINAYAKA) SCENARIO - 1 • 40 year old gentleman comes to ER with h/o chest pain, breathlessness, sweating since 2 hrs • Chest pain retrosternal, crushing type, non radiating lasting for 2 hrs • H/O hypertension for the past 3 years, • Known smoker and a genetic h/o heart disease. A&E(VINAYAKA) VITALS • • • • BP-110/60 HR-104 RR-34 SPO2-95% • • • • CVS – Tachycardia RS - Tachypnoea PA - Soft CNS- NFND A&E(VINAYAKA) What r the initial assesment? DD? A&E(VINAYAKA) Immediate Assessment (<10 min) Vital signs / O2 sat IV Access ABC 12 Lead ECG Brief history Fibrinolytic checklist Physical examination Cardiac marker levels Electrolytes Coagulation studies CXR (EARLY) A&E(VINAYAKA) Describe your immediate general treatment? A&E(VINAYAKA) Immediate General Treatment OXYGEN ASPIRIN NITRATES ONAM MORPHINE A&E(VINAYAKA) Assess Initial 12-Lead ECG Classify patients with acute ischemic chest pain into 1 of 3 ECG classification groups: STEMI NSTEMI / UA Nondiagnostic or Normal A&E(VINAYAKA) ….ECG • STEMI ST elevation / presumed new LBBB 0.1mv or 1mm in 2 or more contiguous precordial leads or 2 or more adjacent limb leads. •UA/NSTEMI ST dep ≥ 0.5 mm (0.05mv) or dynamic T inversions with pain or discomfort Non-persistent or transient ST elevation >0.5mm for less than 20 mins •Nondiagnostic ST deviation <0.5 mm or T inversions <0.2 mm A&E(VINAYAKA) “ J “ POINT J point plus 0.04 second PP baseline ST-segment deviation = 4.5 mm The point at which the ST segment originates from the QRS complex is called the J point A&E(VINAYAKA) ST-T Changes A&E(VINAYAKA) How to identify LBBB • Deep S wave in V1 and a tall late R wave in lead I and/or V6,wide QRS complexes • WILLIAM • Serial Cardiac markers for confirmation A&E(VINAYAKA) ECG diagnosis of LBBB A&E(VINAYAKA) AMI Localization I lateral aVR V1 septal V4 anterior II inferior aVL lateral V2 septal V5 lateral III inferior aVF inferior V3 anterior V6 lateral A&E(VINAYAKA) INFERIOR WALL MI, RVMI A&E(VINAYAKA) Acute Inferior MI A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) True Posterior MI A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) CARDIAC MARKERS • Limited role in case of diagnostic ST elevation in ECG • Role in pts with nondiagnostic ECG changes – Early diagnosis – Missed MI – Early risk stratification Requires Serial Measurements rather than single (every 2-3 hours) A&E(VINAYAKA) …CARDIAC MARKERS CK : – Levels twice upper limit of normal = abnormal – Rises within 4-8hrs & falls within 3-4 days – False + results CK-MB isoenzyme: – More specific – False + AST : rise 18-36hrs post MI LDH : rise 24-36hrs post MI A&E(VINAYAKA) …CARDIAC MARKERS TROPONINS TnI more sensitive and specific in serial testing & not at presentation. Starts to rise by 6 hrs & persists upto 7-10 days. (diagnose late MI) Also elevated in myocarditis ,CM & pericarditis A&E(VINAYAKA) DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA (ANY TWO OUT OF THREE) • Typical history • ECG changes • Cardiac enzyme elevation CK CKMB TROPONIN A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) Goals of treatment • Door to needle time < 30 mins (thrombolysis) • Door to balloon time < 90 mins (reperfusion) A&E(VINAYAKA) SCENARIO - 2 • A 40 year male, brought to ER with h/o sudden onset chest pain & breathlessness since 2 hrs. • Pleuritic pain, constant over the anterior thorax • Has travelled from USA to INDIA 3 hrs back • Chronic smoker A&E(VINAYAKA) VITALS • • • • • BP-100/60; HR-146; RR-42; SPO2-88% TROPONIN I – not raised • • • • CVS- tachycardia RS – tachypnoea PA – soft CNS - NFND A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) PULMONARY EMBOLISM Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches, usually occuring when a venous thrombus becomes dislodged from its site of formation and embolizes to the arterial blood supply of one of the lungs. A&E(VINAYAKA) FACTS • > 50 % pts with DVT are associated with PE • > 50 % cases do not have any signs or symptoms • Common presentation can be unexplained tachycardia, tachypnoea, hypoxemia or mere anxiety • Diagnosis and suspicion is purely clinical A&E(VINAYAKA) Clinical Features Symptoms in Patients with Angio Proven PTE Symptom Dyspnea Chest Pain, pleuritic Anxiety Cough Hemoptysis Sweating Chest Pain, nonpleuritic Syncope Percent 84 74 59 53 30 27 14 13 A&E(VINAYAKA) Clinical Features Signs with Angiographically Proven PE Sign Tachypnea > 20/min Rales Accentuated S2 Tachycardia >100/min Fever > 37.8 Diaphoresis S3 or S4 gallop Thrombophebitis Lower extremity edema Percent 92 58 53 44 43 36 34 32 24 A&E(VINAYAKA) ECG – Most Common Findings: • Tachycardia or nonspecific ST/T-wave changes – Acute cor pulmonale or right strain patterns • Tall peaked T-waves in lead II (P pulmonale) • Right axis deviation • RBBB • S1-Q3-T3 (occurs in only 20% of PE patients) – Atrial fibrillation / Atrial flutter A&E(VINAYAKA) Chest X ray • Westermark’s sign focal oligemia / cut off sign • Hampton’s hump peripheral wedge shaped density above the diaphragm • Palla’s sign enlarged right descending pulmonary artery ALMOST ALWAYS NORMAL CHEST X-RAY A&E(VINAYAKA) WESTERMARK’S SIGN HAMPTON’S HUMP PALLA’S SIGN ALMOST ALWAYS NORMAL CHEST X-RAY A&E(VINAYAKA) Pulmonary Angiography (GOLD STANDARD) • Arrow indicates abrupt termination of a pulmonary artery. • Www.brighamrad.Harvard.edu/case s/bwh/images. A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) RISK STRATIFICATION A&E(VINAYAKA) Heparin / LMWH / Warfarin • Heparin 80 U/kg iv bolus foll by 18 U/kg/hr • Enoxaparin 1 mg/kg twice daily / 1.5 mg/kg daily • Tinzaparin 175 mg/kg OD • Fondaparinux <50 kg receive 5 mg, 50–100 kg patients receive 7.5 mg >100 kg receive 10 mg. • Warfarin – 2.5 to 10 mg Target INR – 2.0 TO 3.0 A&E(VINAYAKA) THROMBOLYSIS • Recombinant tPA 100 mg iv infusion over 2 hours • Streptokinase 250,000 U iv over 30 mins foll by 100,000 U/hr for 24 hrs • Urokinase 4,4OO U/kg iv over 10 mins foll by 4,000 U/kg/hr for 12 hrs • Alteplase 15 mg iv bolus foll by 2 hr infusion of 85 mg ( discontinue heparin during infusion) A&E(VINAYAKA) EMBOLECTOMY Indicated in pts with risk of thrombolysis • Surgical embolectomy • Catheter embolectomy A&E(VINAYAKA) SCENARIO - 3 • A 30 year man brought to ER with h/o fall from a two wheeler 10 mins back • Severe chest pain, breathlessness since then. • Chest pain & breathlessness increasing rapidly • No external injuries • No previous medical illness • Occasional smoker • What are your DD’s?????????? A&E(VINAYAKA) IN ER • Sudden altered sensorium • Airway – patent • Breathing RR- 47/min Spo2 – 86 >>>>>>65% shallow respirations • • Absent breath sounds on rt side • Tympanic note on percussion • Heart sounds heard- no muffling • Engorged neck veins Circulation BP- 70/30 mmHg HR- 156/ min CBG- 126/ min A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX A&E(VINAYAKA) Needle thoracocentesis A&E(VINAYAKA) Needle thoracocentesis • Second intercostal space, midclavicular line on the side of the tension pneumothorax. • Upper border of lower rib • Medially midclavicular line may damage the great vessels, hilar structures and the heart. • Under water seal- ICD IS A MUST. A&E(VINAYAKA) ICD IS A MUST A&E(VINAYAKA) DIAGNOSIS • • • • • Severe respiratory distress Decreased breath sounds Hyperresonance on percussion Distended neck veins Deviation of trachea to opposite side A&E(VINAYAKA) Tension pneumothorax A&E(VINAYAKA) SCENARIO - 4 • A 54 year male brought to ER with altered sensorium within 1 hour • Airway – patent • Breathing – shallow RR- 40/min Spo2- 78% • Circulation – BP-80/60 HR – 144/min CBG – 144 • GCS- 7/15 • • CVS – sinus tachycardia RS – tachypnoea crepitus over mediastinum • PA – distension & rigidity BS – not heard A&E(VINAYAKA) • k/c/o oesophageal stricture for which he underwent an endoscopy • Chronic alcoholic & smoker • While awaiting his reports he devoloped acute severe chest pain in 10 mins & sensorium deteriorated in another 10 mins • He was shifted to our hospital for further management A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) Diagnosis • Chest X ray • CT Chest • Emergency endoscopy A&E(VINAYAKA) Rx • ABC • Fluid rescuscitation • Broad spectrum parenteral antibiotics • Emergent surgical consultation surgical intervention A&E(VINAYAKA) SCENARIO - 5 • A 65 year old man comes to the ER with h/o sudden onset of chest pain . He was just about to go out for a meet with his friends • He is a K/C/O hypertension, DM for the past 10 years on medications. • He is a smoker A&E(VINAYAKA) • • • • • • • • He also c/o inability to move his lower limbs now Hoarseness of voice Dysphagia His femoral pulses are weak when correlated with his radial BP. BP – 80/60 HR – 152 RR – 32 SPO2 – 88% • CVS- tachycardia • RS – inadequate chest rise • PA – soft , BS-sluggish A&E(VINAYAKA) AORTIC DISSECTION Typical symptoms-Anterior chest pain,Neck or jaw pain, Interscapular tearing or ripping pain , Reduced perfusion- Myocardial infarction ,Neurologic symptoms, Syncope, Stroke symptoms ,Altered mental status, Hemiparesis or hemiplegia Symptoms of compression- Horner syndrome, Dyspnoea, Dysphagia ,Orthopnoea, Flank pain, and hemoptysis A&E(VINAYAKA) Investigations • Angiography is gold standard • Aortography-dissection in branch vessels,AV incompetence • Contrast problems and arranging the team • USG Thorax/ TEE • CT –fast with IV contrast. preferred in unstable • No details of branches A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) • TEE in experienced hands-useful. • CXray-thoracic Aortawidening of mediastinum, abnormal aortic contour, Pl Eff, tracheal deviation, • Intimal calcium sign. A&E(VINAYAKA) Management Reduce BP-shearing force- negative inotrope Beta blocker- esmolol, metaprolol Esmolol 500 mic/kg bolus maint 50-100 mics/kg/min Vasodilator-SNP- 0.3 mic/kg/min IV Immediate surgical referral Surgical exploration A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA) TAKE HOME MESSAGE Prompt aggressive control of ABC saves > 50% of cases Atypical presentations are common Chances of missed diagnosis is high Approach every chest pain as a life threatening disorder Serial monitoring is required GERD is a diagnosis of exclusion A&E(VINAYAKA) References Circulation 2005 ACLS Provider 2006 Textbook of emergency medicine; Judith.E.Tintinalli Harrison’s principles of Internal Medicine;17th Edition Braunwald’s Critical Care Book by Edward & Fink Rosen’s etxt book of emergency medicine ACC and AHA Guidelines 2006. Oxford hand book of cardiology. E-Medicine A&E(VINAYAKA) A&E(VINAYAKA)