The Higher Canadian Institute for Business
and Engineering Technology
Quality Assurance Unit
Course Specification
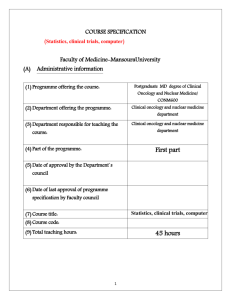
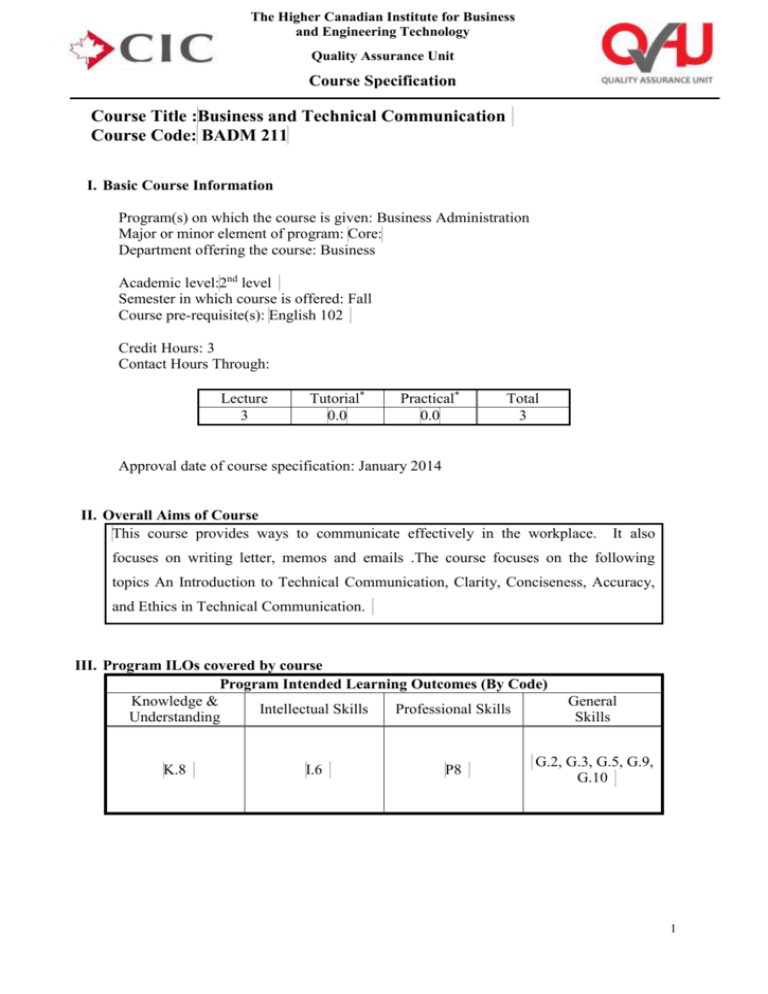
Course Title :Business and Technical Communication
Course Code: BADM 211
I. Basic Course Information
Program(s) on which the course is given: Business Administration
Major or minor element of program: Core:
Department offering the course: Business
Academic level:2nd level
Semester in which course is offered: Fall
Course pre-requisite(s): English 102
Credit Hours: 3
Contact Hours Through:
Lecture
3
Tutorial*
0.0
Practical*
0.0
Total
3
Approval date of course specification: January 2014
II. Overall Aims of Course
This course provides ways to communicate effectively in the workplace.
It also
focuses on writing letter, memos and emails .The course focuses on the following
topics An Introduction to Technical Communication, Clarity, Conciseness, Accuracy,
and Ethics in Technical Communication.
III. Program ILOs covered by course
Program Intended Learning Outcomes (By Code)
Knowledge &
Intellectual Skills
Professional Skills
Understanding
K.8
I.6
P8
General
Skills
G.2, G.3, G.5, G.9,
G.10
1
The Higher Canadian Institute for Business
and Engineering Technology
Quality Assurance Unit
Course Specification
IV. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs)
a. Knowledge and Understanding
Upon completion of the course, students should be able to:
K.1Recognize the importance of technical communication.
K.2Define terms of different types of audiences.
K.3Recognize diversity including multiculturalism and “cross-culturalism”.
K.4 Identify the difference between technical correspondences.
K.5Recall the importance of teamwork in technical communication.
b. Intellectual/Cognitive Skills
Upon completion of the course, students should be able to:
I.1 Revise sentences to delete wordiness, to achieve simplicity, and to achieve
conciseness.
I.2 Write clear details by answering reporter’s questions.
I.3 Organize their writing to help readers better understand documents.
I.4 Evaluate technical communication for clarity, accuracy and organization.
I.5 Distinguish between different types of audiences.
I.6 Revise to avoid biased and sexist languages.
I.7 Write to achieve audience involvement.
I.8 Write different types of technical correspondences.
I.9 Compare and contrast between different topics.
c. Practical/Professional Skills
Upon completion of the course, students should be able to:
P.1 Use different channels of oral and written technical communication.
P.2 Solve problems and conflicts in collaborative work.
P.3 Use business formal format in writing.
P.4 Apply the writing process to create effective technical correspondences.
d. General and Transferable Skills
Upon completion of the course, students should be able to:
G.1Synthesize in teamwork.
G.2Demonstrate their ideas and work effectively by presentations and discussions.
G.3Arrange their ideas critically.
G.4Perform successful debates
G.5Use technical terminology and synonyms effectively
V. Course Matrix Contents
Main Topics / Chapters
Chapter 1: An Introduction
to Technical Communication
Chapter 3: Clarity,
Conciseness, Accuracy, and
2Ethics in Technical
Communication
3- Chapter 4: Communicating
1-
Duration
(Weeks)
2
Course ILOs Covered by Topic
(By ILO Code)
K&U
I.S.
P.S.
G.S.
K.1, K.4,
G.1, G.2,
P.1, P.2
K.5
G.3, G5
2
K.5
I.1, I.2,
I.3, I.4,
P.2
G.1, G.2,
G.3, G4,
G5
4
K.2, K.3
I.5, I.6,
P.2
G.1, G.2,
2
The Higher Canadian Institute for Business
and Engineering Technology
Quality Assurance Unit
Course Specification
Effectively to Your Audience
in a Multicultural World
Chapter 6: Routine
Correspondence-Memos,
4- Letters, E-Mail Messages,
Instant Messages, and Text
Messages
Net Teaching Weeks
I.7
4
K.4
G.3, G4,
G5
I.8, I.9
P.2, P.3,
P.4
G.1, G.2,
G.3, G4,
G5
12
VI. Course Weekly Detailed Topics / hours / ILOs
Week
No.
Sub-Topics
1
2
3
4
5
What is technical writing?
Communication Channels
The importance of technical
communication
The importance of teamwork
Diverse teams…Dispersed teams
Conflict resolution in
collaborative projects
What is technical writing?
Communication Channels
The importance of technical
communication
The importance of teamwork
Diverse teams…Dispersed teams
Conflict resolution in
collaborative projects
Achieving clarity in technical
communication
Simplifying words, sentenced,
and paragraph for conciseness
Organizing technical
communication
Achieving clarity in technical
communication
Simplifying words, sentenced,
and paragraph for conciseness
Organizing technical
communication
Audience recognition
Defining terms for audiences
How to communicate to different
audience levels
Total
Hours
Contact Hours
Theoretical
Practical
Hours
Hours*
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
The Higher Canadian Institute for Business
and Engineering Technology
Quality Assurance Unit
Course Specification
6
7
8
9
10
11
Avoid Biased language
Guidelines for effective
multicultural communication
Audience Involvement
Audience recognition
Defining terms for audiences
How to communicate to different
audience levels
3
Avoid Biased language
Guidelines for effective
multicultural communication
Audience Involvement
Audience recognition
Defining terms for audiences
How to communicate to different
audience levels
3
Avoid Biased language
Guidelines for effective
multicultural communication
Audience Involvement
Audience recognition
Defining terms for audiences
How to communicate to different
audience levels
3
Avoid Biased language
Avoid sexist language
Guidelines for effective
multicultural communication
Audience Involvement
Midterm Exam
The importance of memos, letters,
emails, instant messages and text
messages
Which communication channel
should you use?
The difference among routine
3
communication channels
Memos
Letters
Criteria for different types of
letters
The writing process at work
The importance of memos, letters,
emails, instant messages and text
3
messages
Which communication channel
3
3
3
3
3
4
The Higher Canadian Institute for Business
and Engineering Technology
Quality Assurance Unit
Course Specification
12
13
14
should you use?
The difference among routine
communication channels
Memos
Letters
Criteria for different types of
letters
The writing process at work
The importance of memos, letters,
emails, instant messages and text
messages
Which communication channel
should you use?
The difference among routine
3
communication channels
Memos
Letters
Criteria for different types of
letters
The writing process at work
The importance of memos, letters,
emails, instant messages and text
messages
Which communication channel
should you use?
The difference among routine
3
communication channels
Memos
Letters
Criteria for different types of
letters
The writing process at work
Final Exam
Total Teaching Hours
36
3
3
Teaching/Learning
Method
Lectures & Seminars
Tutorials
Computer lab Sessions
Practical lab Work
Reading Materials
Web-site Searches
Selected
Method
VII. Teaching and Learning Methods
Course ILOs Covered by Method (By ILO Code)
K&U
All
All
K.3
Intellectual
Skills
All
Professional
Skills
All
General
Skills
All
I.1, I.4
P.3
P.2
All
G.1, G.2,
5
The Higher Canadian Institute for Business
and Engineering Technology
Quality Assurance Unit
Course Specification
G4
Research & Reporting
Problem Solving /
Problem-based Learning
Projects
Independent Work
Group Work
Case Studies
Presentations
K.3, K.5
All
P.2
All
All
All
All
I. 9
I. 9
I. 9
All
All
All
K.5
I. 9
All
All
P.2
P. 1, P.2,
P.3, P.4
All
Simulation Analysis
Others (Specify):
Selected
Method
VIII. Assessment Methods, Schedule and Grade Distribution
Course ILOs Covered by Method
(By ILO Code)
Assessment
Method
K&U
I.S.
P.S.
G.S.
Midterm Exam
Final Exam
Quizzes
Course Work
Report Writing
Case Study
Analysis
Oral
Presentations
Practical
Group Project
Individual Project
Others (Specify):
Assignments
All
All
All
All
All
All
P.1, P.2
All
All
G.3
G.3
G.3
All
All
Assessment
Weight /
Percentage
Week
No.
20%
50%
20%
10%
IX. List of References
Required Text Books
Sharon J. Gerson, S. M. Technical Writing: Process and Product.
Pearson Custom Publishing, Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006.
Course notes
Recommended books
Periodicals, Web sites,
etc …
https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/632/01/
http://www.lupinworks.com/roche/pages/memos.php
X. Facilities required for teaching and learning
List the facilities required
6
The Higher Canadian Institute for Business
and Engineering Technology
Quality Assurance Unit
Course Specification
White board
PPTs
Data show
Course coordinator: Dr. Noha El torky
Head of Department: Dr. Dina Kreema
Date: January 2014
7