(railroads, Native Americans, and industry) Document Analysis
advertisement

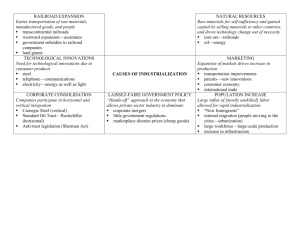
Expansion Directions: Use the political cartoons, documents, and information sheets to complete the following… EQ: How did railroads impact the United States? (Remember to come back and answer the EQ in your own words at the end of the assignment!) Growth of Railroads 1. What similarities do you see between the Railroads Map of 1890 and the Railroads Map of 1918? 2. What differences do you see between 1890 and 1918? 3. In what ways do you think the growth of railroads impacted or changed life in the U.S.? Transcontinental Railroad 1. What was the Transcontinental Railroad? Why is it significant? 2. Who built the Transcontinental Railroad? What kind of challenges did workers face? Political Cartoon #1 Title/Caption Date Description (Give a detailed description of what you see) Topic (Not just “railroads”- what about the railroads? Message- What message is the creator sending, what is he saying about the railroads? Political Cartoon #2 Title/Caption Date Description (Give a detailed description of what you see) Topic (Not just “railroads”- what about the railroads? Message- What message is the creator sending, what is he saying about the railroads? Political Cartoon #3 Title/Caption Date Description (Give a detailed description of what you see) Topic (Not just “railroads”- what about the railroads? Message- What message is the creator sending, what is he saying about the railroads? Railroads and Big Business 1. How did large railroad companies force small companies out of business? 2. What is pooling? Political Cartoon #4 Title/Caption Date Description (Give a detailed description of what you see) Topic (Not just “railroads”- what about the railroads? Message- What message is the creator sending, what is he saying about the railroads? The Battle of Wounded Knee 1. What do you think the impact of the American hunting bison for sport was on Native Americans? 2. What caused the massacre at Wounded Knee? 3. What impact would the massacre have on Native American and American relations? John D. Rockefeller and the Oil Industry 1. What is a monopoly? 2. How does horizontal integration lead to a monopoly? 3. Look at the Standard Oil Octopus Cartoon… What was the relationship between Standard Oil and the government? Andrew Carnegie and the Steel Industry 1. Why is the Bessemer Process significant and how did it contribute to the success of Carnegie? 2. What impact did the Bessemer process have on the development of the railroad industry? 3. How does vertical integration differ from horizontal integration? Growth of Railroads Railroads in 1890 Railroads in 1918 Transcontinental Railroad In 1869, the Transcontinental Railroad was completed. This was the first time that the railroad crossed the entire continent. Pacific Railway Act of 1862 – U.S. Government hired Union Pacific and Central Pacific Railway Company to extend railways across the United States. Who built the Transcontinental Railroad? Mostly Chinese immigrants, as well as Irish immigrants and desperate out-of-work Civil War veterans The working conditions were very difficult because of weather and harsh terrains. Political Cartoon #1 “A Good Square American Smile” Printed in Frank Leslie’s Weekly on June 5, 1869 Creator: Frank Bellew Political Cartoon #2 Caption: "All Hail and Farewell to the Pacific Railroad” Source/Date: Harper's Weekly, June 10, 1869 Creator: Thomas Nast Political Cartoon #3 Across the Continent: Westward the Course of Empire Takes its Way CIRCA 1868 Railroads and Big Business -Railroad companies offered rebates, or discounts, in order to keep or win customers. -This forced many small railroad companies out of business. -Large companies bought smaller ones or forced them out of business. -In order to end competition and keep prices high, railroad companies agreed to divide up business in an area and set high prices. This was known as pooling. Political Cartoon #4 Caption: The Modern Colossus of (Rail) Roads Source/Date: Puck, December 10, 1879 The sign in the foreground says "all freight seeking the seaboard must pass here and pay any tolls we demand." The flag over Field's line says "L Road; Many nickels stolen are millions gained, C. W. Field.” Wounded Knee 1890 Native Americans on the plains and American settlers were in constant conflict over land, supplies, and culture. The picture to the right portrays a mountain of bison skulls killed by whites. Americans hunted buffalo/bison for sport and drove the animals to near extinction. Throughout 1890, the U.S. government worried about the increasing influence at Pine Ridge of the Ghost Dance spiritual movement, which taught that Indians had been defeated and confined to reservations because they had angered the gods by abandoning their traditional customs. Many Sioux believed that if they practiced the Ghost Dance and rejected the ways of the white man, the gods would create the world anew and destroy all non-believers, including non-Indians. The Ghost Dance movement was viewed by U.S. government officials as aggression and preparation for an attack. On December 15, 1890, reservation police tried to arrest Sitting Bull, the famous Sioux chief, who they mistakenly believed was a Ghost Dancer, and killed him in the process, increasing the tensions at Pine Ridge. WOUNDED KNEE: CONFLICT BREAKS OUT On December 29, the U.S. Army’s 7th Cavalry surrounded a band of Ghost Dancers under Big Foot, a Lakota Sioux chief, near Wounded Knee Creek and demanded they surrender their weapons. As that was happening, a fight broke out between an Indian and a U.S. soldier and a shot was fired, although it’s unclear from which side. A brutal massacre followed, in which it’s estimated 150 Indians were killed (some historians put this number at twice as high), nearly half of them women and children. The cavalry lost 25 men. The conflict at Wounded Knee was originally referred to as a battle, but in reality it was a tragic and avoidable massacre. Surrounded by heavily armed troops, it’s unlikely that Big Foot’s band would have intentionally started a fight. Some historians speculate that the soldiers of the 7th Cavalry were deliberately taking revenge for the regiment’s defeat at Little Bighorn in 1876. Whatever the motives, the massacre ended the Ghost Dance movement and was the last major confrontation in America’s deadly war against the Plains Indians. (History.com) John D. Rockefeller and the Oil Rockefeller Rockefeller is considered a “Captain of Industry” Formed the first modern Trust/Monopoly in the oil industry = Standard Oil Was the first billionaire in the U.S. by 1900. Rockefeller used money he made selling stock in his company to buy out other oil companies, thus creating a monopoly and controlling the market. This is what is known as horizontal integration (you buy out your competition) The Standard Oil Octopus Reaches into the Economy and Government. Andrew Carnegie and the Steel Industry Andrew Carnegie was a Scottish immigrant who became a giant in the steel industry The Bessemer Process allowed Carnegie to build his empire and become the richest man in the world. Carnegie implemented vertical integration as opposed to Rockefeller, who only used horizontal integration.