Intermediate Macro - Illinois State University
advertisement

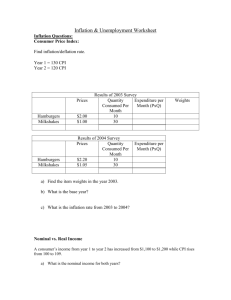
Intermediate Macro Introduction Current Events • • • • Great Recession Survival of the Euro “Lost Decade” Developing World – China – India – Sub-Saharan Africa What’s it all about? • National Economy • Micro: consumer/firm behavior • Macro variables – GDP – Inflation – Unemployment – Interest rates – Debt/deficit – exchange rates – Etc. Goals • Explain movements of and connections between macro variables. • Policy – What can the gov’t do? – What should the gov’t do Macro is hard • General Equilibrium – many variables – media coverage (yuck) • Short run vs. Long Run – Ex. new machines eliminate jobs • Many approaches to economics Plan of class • Short run – 1 to 2 years – Booms and recessions • Medium run – Why / how fast does GDP grow – equilibrium • Long run – Decades – What makes rich countries rich? – Development Our focus • Domestic economy • Short Run – Keynesian story • Classical ideas to connect to the long run Macro Flow Chart • Firms & consumers • Income and Consumtion • Government – Spending – Taxes & transfers • Savings & Investments • Imports and Exports Fiscal Policy • Government Spending – Defense – Health, Education & Welfare • Tax policy – Income tax – Capital gains tax etc. • Debt/Deficit President and Congress Monetary Policy The Federal Reserve controls • Money supply • Interest rates (one of them) • Affects firm/consumer decisions Gross Domestic Product • Why do we care so much? • GDP per capita across countries is correlated w/ – Poverty – Health – Education • Crude measure, GDP ignores – Quality of life – Environmental degradation – “Happiness” • Growth rate shows change GDP – basic facts • Rises – Population rises – Productivity rises • Except when it doesn’t – Recessions – Causes? Measurement GDP – value of all final goods and services produced over a given time Intermediate good – used as part of the production of another good Final good – sold for use by consumer/business/gov’t Note: all exports count as final goods Multiple ways to measure GDP Final or Intermediate? • Goodrich sells a tire to Ford for its new cars. • Joe buys a new tire to replace a flat on his used car. • Jean sells an extra tire in her garage to Sam. GDP example Farmer Revenue Costs Profit Supply store Revenue corn $150 seed $40 fertilizer $60 wages $25 $25 seed $40 fertilizer $60 Cost (wholesale) $70 Profit $30 GDP? 3 ways to measure GDP • Final goods – add value of all final good – $150 in corn • Value added – Sum value added for all intermediate and final goods – $40+$60+$50 = $150 – $50 is value added by farmer • Income – Sum all incomes from all production – $30+$25+$25+$70 Nominal vs. Real GDP Economy produces only corn Quantity Price 2006 6000 bushels $4 2007 8000 bushels $5 Nominal GDP(2006) = $24,000 GDP(2007) = $40,000 Growth rate = 66.6% What’s wrong with this measure? Real GDP • Measure of goods – adjusted for price changes – “in constant dollars” Using prices from 2006 real GDP(2006) = $24,000 real GDP(2007) = $32,000 Growth rate 33.3% Note: if prices rise, real GDP < nominal GDP GDP deflator Deflator = nominal GDP/real GDP Change in the deflator is a measure of inflation Deflator (2006) = 1 Deflator(2007) = 1.25 Inflation – 25% Obvious with one good….. Problem An island country in the Indian Ocean produces zebu steaks and canoes. They produced the following quantities at the following prices in the last two years. 2005 Quantity Price Steaks 800 $20 Canoes 600 $40 2006 Quantity Price 1000 $30 600 $50 Find the growth rates for nominal and real GDP, using 2005 prices as the base. Find the rate of inflation. CPI and inflation • Inflation also measured as an average of prices – Gov’t surveys – Weighted according to “typical” household expenditure Inflation • Why do we care? • Wages rise with inflation – Incomes not eroded – Exceptions • Pensions • Alimony • Disability • Distorts relative prices – Some prices adjusted faster • Uncertainty – High inflation come with volatility – Investment/consumption decisions are more difficult Unemployment Unemployed + employed = Labor force Unemployed – looking for a job Unemployment rate U = unemployed/labor force High unemployment: – Unused resources – Skills erode Not measured Discouraged workers / underemployed Real vs. Nominal GDP • Real GDP – Changes in price don’t affect it. – Measured in prices from a single year. GDP Deflator = Nominal GDP Real GDP - measures the effect of prices Model of Demand Build a Model • How do elements on the flow chart fit? • How do changes affect GDP? • How do policy changes affect the economy? Start with Demand - goods sector - financial sector Demand Z – aggregate demand Z = C + I + G + X – IM Equilibrium condition: Z=Y Assume: X = IM (no trade imbalance) Z = C + I + G; Z=Y Does Y affect C, I, G? Consumption Function • C increasing in Y • Slope less than 1 – Some income saved • Autonomous consumption Algebraically, C = c0 + c1YD c0>0 – autonomous consumption 0<c1<1 –marginal propensity to consume (MPC) Solving Assume (for now) I and G are fixed Y = c0 + c1YD + I + G Or Y = c0 + c1(Y–T) + I + G With Y=Z Y* = (1/(1-c1))(c0 - c1T + I + G) Example c0 = 100; c1=0.75 I = $250; G = $200; T = $200 (balanced budget, for now) Y* = (1/0.25)400 = 1600 What if G rises by $50? Y* = $1800 DY > DG Why? (Keynesian cross) Multiplier • Increase in G, Yh, Ch, Yh etc…… • Why doesn’t Y explode? – Some saved every step Multiplier = 1/(1-c1) measures the extra impact on Y of a change in autonomous spending. Money Supply and Demand Liquidity Preference 2 assets: Money and Bonds W=M+B Hold bonds: better return Hold money: for transactions (liquidity) Demand for Money vs. interest rate ? Higher i greater demand for bonds lower demand for money Money S&D • Demand for money slopes down • Supply of Money is vertical – Decision of the Fed – Doesn’t respond to i – Fed can shift S to change equilibrium i What shifts Demand? • Nominal GDP – Real GDP or prices Bonds Discount bonds pays $100 in one year. price? i - yield ex. P = $80 80(1+i) = 100 so i = 25% P = 100/(1+ i) If P rises, i falls Equilibrium What if i > i* ? excess money buy bonds P i i falls to equilibrium. Questions • How would an increase in prices affect equilibrium interest rates? • What would the Fed do to lower equilibrium interest rates? LM curve For a given MS, how are Y and i related? If Y rises, MD shifts out, i* rises If Y falls……. In the financial market, Y and i are directly related LM relation Goods market How does a change in the interest rate affect aggregate expenditure? Not G – decision of gov’t Not C – income and substitution effects Investment is affected by i Deriving IS • i rises, I falls, expenditure function shifts down • Equilib. GDP (Y) falls Goods market: i and Y are inversely related IS relation Note: IS for Investment – Savings relation For a given Y, i adjusts so that S=I. Shifts in IS? IS - LM Together, they determine equilibrium Y* and i* Combines goods and financial markets Can discuss fiscal and monetary policy. Shifts in IS • Consumer confidence – Preferences – Future employment • Business confidence – Profit opportunities – Changes in technology • Fiscal policy Shifts in LM • Change in prices • Monetary Policy Fiscal Policy Increase in G Expenditure shifts up IS shifts right Y* and i* rise MD shifts right Does LM shift? No, MD shifts due to a change in Y - movement along LM Monetary Policy Fed increases MS LM shifts right Y* rises and i* falls Expenditure function shifts up Does IS shift? No, Exp shifts due to a change in i movement along IS Problem A tax cut changes consumption. Show how a tax cut would affect the IS-LM, expenditure and MS – MD diagrams. Fiscal vs. Monetary Policy Monetary Policy • Advantages – Quick decisions/implementation – Fine tune • Disadvantages – Takes time to have an effect – undirected Fiscal Policy • Advantages – Immediate impact – Directed spending • Disadvantages – Takes time to decide (politics) – Changes tend to last Real Money S&D • Equilib i determined by real money S&D • Graph looks the same • Change in P – Shifts supply of real money – Shifts demand for nominal money – P rises, i rises in both cases Note: Fed controls interest rates in the short term. Long run: prices changes affect i* IS - LM C = 100 + 0.75YD I = 100 – 1000i G = 200 T = 200 (M/P)d = 3Y – 18,000i (M/P)s = 1500 Find the IS and LM relations. Find equilibrium Y* and i*. Impulse response Decrease in Fed funds Takes 4-8 quarters to have an effect Practice Problem An island country in the Indian Ocean produces zebu steaks and canoes. They produced the following quantities at the following prices in the last two years. 2005 Quantity Price Steaks 800 $20 Canoes 600 $40 2006 Quantity Price 1000 $30 600 $50 Find the growth rates for nominal and real GDP, using 2005 prices as the base. Find the rate of inflation. Practice Problem c0 = 100; c1=0.8 I = $150; G = $200; T = $200 Using the above, find equilibrium output/income. If autonomous consumption falls by $50, find the new level of equilibrium output. What is the multiplier? What is savings before and after the change in C? Practice Problem Let the consumption function be C = 100 + 0.9YD If autonomous consumption falls by $15, how does equilibrium output change? Show the changes on a Keynesian cross diagram. Practice Problem C = 100 + 0.75YD I = 100 – 1000i G = 200 T = 200 (M/P)D = 3Y – 10,000i M/P = 1500 Find IS Find LM Find equilibrium i and Y Practice Problem When Clinton took office in 1992, he raised taxes, and the Fed agreed to increase the money supply as long as government spending stayed constant. Show the changes on an IS-LM diagram. What happens to equilibrium output and the interest rate? When would equilibrium output rise? Problem Show the impact of a decrease in the price level on a graph of real money supply and demand and an IS-LM graph. What is the relationship between output/income and the price level? Review Problem Given the following information find the equilibrium level of output Y*. If government spending and taxes both fall by $50, how does Y* change? Show on a graph of the expenditure function with the equilibrium condition. Autonomous consumption = $300 MPC = 0.9 Investment = $100 Taxes = $150 Government spending = $150 What is savings both before and after the change in spending? Review Problem The recent recession has seen a large drop in business confidence affecting autonomous investment. The Federal Reserve has responded by increasing by increasing the money supply. Show the effect on the equilibrium on an IS-LM graph, and show the initial effects on an expenditure graph and a money S&D graph. Labor Market U.S. Labor Market • Large movements in and out of labor force and employed – Hires – Quits – Layoffs – Discouraged workers • Continental Europe - slower change – Stronger unions – More firing restrictions – Higher wages and more unemployment Wage determination Firms seem to pay higher than “competitive” wages. Why are wages higher than necessary? • Efficiency wages – Get more effort – Reduce turnover • Bargaining power – Worker skills – Depends on other options – unions Firm decision Competitive labor market W = MRP if W < MRP then firm hires more (more profit) MRP = P x MPL so marginal product = real wage (W/P) Simple version Production function: Y=L Implies MPL = 1 real wage W/P = 1 P=W “price equals marginal cost” Too simple??? - firms have “pricing power” - workers have bargaining power Wage determination formally Nominal wages negotiated according to expected prices Pe W = PeF(u,z) F(u,z) “bargaining power” u – unemployment rate z – other factors ex. labor laws worker skill Price determination Output prices also tend to be higher than wages. • Other costs • Firms have market power - monopolistic competition - monopoly - oligopoly P = W(1 + m) “markup” or W/P = 1/(1 + m) Natural rate of unemployment If price = expectations, combine equations F(u,z) = 1/(1 + m) relates the wage and price markups Determines un – natural rate of unemployment Medium run concept Graph • Price & wage determination • unemployment vs. real wage • Price setting equation constant according to markup • Wage setting, higher u means lower real wage (bargaining) Compare U.S. and France • more firing restrictions • More benefits required by law • WS curve to the right • higher un Natural rate • Medium run concept • 0% cyclical unemployment • Associated with – natural rate of employment – Natural rate of output – NAIRU • Natural rate can change over time with – labor laws – unemployment benefits – tax policy? Problem • Unions give workers extra bargaining power, but have declined in membership over the last 25 year in the U.S. Use the wage / price determination graph to show the effect on real wages and the natural rate of unemployment. Problem • Online retailing has increased competition for goods, lowering the markup firms can charge. Show how this affects the labor market and the natural rate of unemployment. Review Problem A proposed law in France would make it easier for firms to fire people. Show the effect on the natural rate of unemployment on the wage/price setting graph.