Output Device - ComputerScienceUK
advertisement

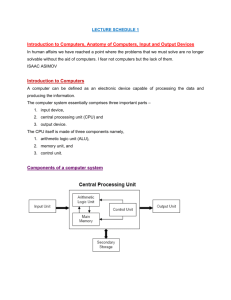
Activity 1 On your white boards explain the role of the following computer components (explain what they do): Input Device Output Device CPU RAM Hard Drive (Hard Disk) www.computerscienceuk.com Activity 1 ANSWERS to ACTIVITY 1 Input Device – A device which sends data to the CPU (e.g. mouse, keyboard etc) Output Device - A device which receives information from the CPU (e.g. monitor, speakers etc) CPU – The ‘brain’ of the computer. It does all the processing – all the thinking! RAM – This is where programs are loaded when they are open – think of this as the CPU’s ‘work station’. Hard Drive (Hard Disk) – This is the long term storage for programs and files. www.computerscienceuk.com How it all works? Introduction to Computer Hardware www.computerscienceuk.com Lesson Objectives Lesson Objectives • Remember that a computer is made up of a range of components and remember their purpose / function. • Understand the role of the CPU, RAM and Hard Drive • Understand how the CPU, RAM and Hard Drive work together. • Understand how the input and output devices work with the CPU Success Criteria • ALL: Will be able to describe the steps that take place when you open a program. • MOST: Will be able to describe the steps that take place when you are using a program. • SOME: Will be able to produce and annotate a diagram to show how the Input & Output devices, CPU, RAM and Hard Drive work together. Literacy – Key Words CPU Central Processing Unit – the brain of the computer. RAM Random Access Memory – where programs are loaded when they are in use. I/O Devices The input devices send data to the CPU, the output devices receive information from the CPU. Hard Drive The computer’s long term storage for programs and files www.computerscienceuk.com Learning Habits This topic will look at computers and their hardware. To be successful in this unit you will need to make use specific learning habits… which ones will you use? Adapting : Reflecting and making changes Noticing details Empathising… …with feelings and views Effective use of time Questioning: Asking questions to get below the surface Imagining… …how things could be and seeing a range of possibilities Listening… …to understand Collaboration: Working effectively with others Independence: Working effectively alone Making links… …and recognising relevance Reasoning: Thinking rigorously, methodically and giving explanations. Distilling… …what you have learnt and what you need to learn Meta Learning: Talking about how you have been learning Managing distractions… …and sustaining concentration Perseverance: Overcoming frustration and difficulty Imitation: Picking up good habits from others Capitalising: Using resources purposefully Planning… …your learning in advance www.computerscienceuk.com So how do all of these devices work together…? How does the computer actually work? www.computerscienceuk.com The CPU, RAM and I/O Devices Double Click Icon to Open Program. 1. Instruction to open program sent to the CPU. 2. CPU sends request for program to be loaded from hard drive onto the RAM. 3. Hard drive loads program onto the RAM. CPU now ready to work with the program! www.computerscienceuk.com The Office Desk Comparison When you open a program on your computer, you send a message to the CPU (brain of the computer) to deal with the request. The CPU will look for the program on the hard disk – imagine this as the draws of a desk – long term storage. It will then take the program and load it on the RAM – imagine this as the desktop – the program is now ready to use. Hard Drive www.computerscienceuk.com The CPU, RAM and I/O Devices Type a letter when ‘Word’ is open. 1. Instruction to display letter is sent to the CPU. 2. CPU asks RAM for instructions on how to display a letter. 3. RAM sends program instructions onto CPU. 6. CPU instructs Monitor to display a letter on the screen. www.computerscienceuk.com The Office Desk Comparison When you are using a program, you use an input device (keyboard, mouse, etc.) If you click on a menu (for example) you are sending to the CPU your request to see the menu. The CPU will ask the RAM for the program’s instructions on how to display the menu. When the CPU receives the instructions, it will then be able to process them and send a message to the monitor to update the screen with the menu showing. Hard Drive www.computerscienceuk.com Your Main Task Today Remind yourself of your target level… …based on your target level you must pick an appropriate task. RULES • If your target level is a level 3 or a 4, you can pick any worksheet • If your target level is a level 5 or 6, you can only pick worksheet 2 REMEMBER – using the appropriate Learning Habits will help you with this task Choice of tasks on next slides… www.computerscienceuk.com Task – Complete the appropriate worksheet 1) Open and Complete the L3-4 Worksheet. Use the presentation to help you! 2) Open and Complete the L5-6 Worksheet. Use the presentation to help you! www.computerscienceuk.com