TYPES OF ENGLISH CIVIL LAW
advertisement

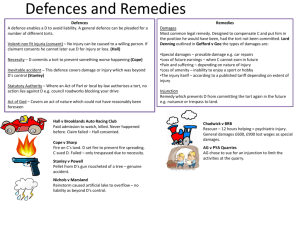
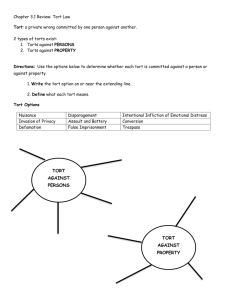
TYPES OF ENGLISH CIVIL LAW Unit 29 Preview Contract: definition Requirements for a valid English contract Forms of contract Void and voidable contracts Breach of contract Torts: definition Types of tort Legal terms Exercise English Civil Law Law of Contract Law of Tort Definition of Contract “A legally binding agreement made between two or more persons, by which rights are acquired by one or more acts or forbearances on the part of the other or others” Agreement arises as a result of offer and acceptance Forebearance A deliberate failure to exercise a legal right (e.g. to sue for debt) Requirements for a valid contract 1. Offer, acceptance, consideration 2. Intention to create legal relations 3. Contractual capacity 4. Formal legal requirements Offer An indication of willingness to do or refrain from doing something that is capable of being converted by acceptance into a legally binding contract Offer It is made by an offeror to an offeree and is capable of acceptance only by an offeree who knows of its existence Acceptance Agreement to the terms of an offer that converts the offer into a legally binding contract Acceptance must involve some action on the part of the offeree Consideration The price, in money, goods, or some other reward, paid by one person in exchange for another person promising to do something, which is an essential element in the formation of a contract Consideration Kompenzacija, poravnanje, protuizvršenje; kod ugovora potrebno je preuzimanje obveze, ali i razmjena vrijednosti Contractual capacity Competence to enter into a legally binding agreement Persons lacking this capacity: minors, the mentally disordered, etc. Forms of contract oral, written, partly oral and partly written, or implied from conduct Void contract A contract that has no legal force from the moment of its making Lack of capacity to contract, mistake, illegal contracts Voidable contract Liable to be set aside by one of the parties on such grounds as misrepresentation or undue influence Breach of contract Failure by a party to perform his obligations under that contract Areas Shipping contracts, hire purchase, sale of goods, etc. Definition of Tort Wrongs committed by one citizen against another, serious enough to merit the award of compensation to the injured person, but not serious enough to amount to the breaking of the criminal law Tort Civil liability Less serious wrongs which are not punished by the state Tort A wrongful act or omission for which damages can be obtained in a civil court by the person wronged, other than a wrong that is only a breach of contract Tort Compensation in the form of damages is awarded to the injured party, after the offender (tort-feasor) has been sued by the person he has injured Definition of tort Sir John Salmond: “A tort is a civil wrong for which the remedy is a common law action for unliquidated damages, and which is not exclusively the breach of a contract or a breach of a trust or other merely equitable obligation.” Damages A sum of money awarded by a court as compensation for a tort or a breach of contract The claimant is entitled to full compensation for his losses Types of damages Liquidated d. : a sum fixed in advance by the parties to a contract as the amount to be paid in the event of breach Unliquidated d: the amount fixed by the court Law of tort Concerned with providing compensation for personal injury and property damage caused by negligence Protects other interests, such as reputation, personal freedom, title to property, enjoyment of property, commercial interests Law of tort: types Negligence Nuisance Trespass Defamation (libel and slander) Negligence 1. Carelessness amounting to the culpable breach of a duty; failure to do sth that a reasonable person would do 2. A tort consisting of the breach of the duty of care resulting in damage to the claimant Nuisance Something that causes harm or inconvenience to someone or to property Tresspass The tort of interfering with the land or goods of another person Tresspass 1. tresspass to goods (harming or interfering with goods which belong to someone else) 2. tresspass to land 3. tresspass to person (assault, false imprisonment) Defamation The act of injuring someone’s reputation by maliciously saying or writing things against him or her that are not true 1. Libel (written d.) 2. Slander (spoken d.) Law of contract/law of tort Some torts: also breaches of contract (e.g. negligent driving by a taxi-driver that causes injury to his passenger- both tort of negligence and breach of contract to carry the passenger safely to his destination) Law of tort/criminal law Many torts are also crimes: e.g. assault, dangerous driving Assault An intentional or reckless act that causes someone to be put in fear of immediate physical harm Assault Actual physical contact is not necessary to constitute an assault (e.g. pointing a gun at someone may constitute an assault) Other areas of civil law Family law Revenue law Patents and copyrights Trade unions Administrative law Points to remember Two main areas of English civil law Definition of contract Elements of a contract Void and voidable contracts Definition of tort Types of tort Legal terms Law of contract Ugovorno pravo Tort Šteta, štetna radnja, građanski delikt Law of Torts Građansko deliktno pravo Legal terms Forebearance Nečinjenje (u građanskom pravu) Hire purchase Kupnja na kredit Legal terms Civil liability Građanskopravna odgovornost Tort-feasor Počinitelj štete; počinitelj delikta (u građanskom postupku) Sue Sudski goniti, pokrenuti postupak Legal terms Unliquidated damages Neugovorena odšteta Liquidated damages Ugovorena odšteta (zbog neizvršenja ugovora Legal terms Trust Prijenos imovine na povjerenika; fiducijarni odnos, povjereno upravljanje u korist drugog; skrbništvo Legal terms Negligence Nehaj, nemar, nepažnja Nuisance Smetnja, ometanje, uznemirivanje Tresspass Ometanje posjeda, povreda prava privatnosti, bespravno stupanje na tuđi posjed Legal terms Defamation Kleveta, uvreda Libel Pisana kleveta Slander Usmena kleveta Legal terms Family law Obiteljsko pravo Revenue law zakon o prihodima Exercise: What is a contract? Complete the text using the following: agreement, breach, capacity, consideration, damages, fraud, illegal, obligation, oral, performance, property, signed, terms What is a contract? agreement, breach, capacity, consideration, damages, fraud, illegal, obligation, oral, performance, property, signed, terms It is an agreement that creates a binding ____ upon the parties. The essentials of a contract are as follows: mutual ____; a legal ____which in most instances need not be financial; parties who have legal ____to make a contract; absence of ____or duress; and a subject matter that is not ____or against public policy. What form does a contract take? agreement, breach, capacity, consideration, damages, fraud, illegal, obligation, oral, performance, property, signed, terms In general, contracts may be either ___or written. Certain types of contracts, however, in order to be enforceable, must be written and ____. These include contracts involving the sale and transfer of _____. How does a contract end? agreement, breach, capacity, consideration, damages, fraud, illegal, obligation, oral, performance, property, signed, terms In case of a ____of contract, the injured party may go to court to sue for financial compensation (or ____), or for rescission, for injunction, or for specific performance if financial compensation would not compensate for the breach. Specific____of a contract is the right by one contracting party to have the other contracting party perform the contract according to the precise___ agreed Key: It is an agreement that creates a binding obligation upon the parties. The essentials of a contract are as follows: mutual agreement; a legal consideration which in most instances need not be financial; parties who have legal capacity to make a contract; absence of fraud or duress; and a subject matter that is not illegal or against public policy. Key In general, contracts may be either oral or written. Certain types of contracts, however, in order to be enforceable, must be written and signed. These include contracts involving the sale and transfer of property. Key In case of a breach of contract, the injured party may go to court to sue for financial compensation (or damages), or for rescission, for injunction, or for specific performance of financial compensation would not compensate for the breach. Specific performance of a contract is the right by one contracting party to have the other contracting party perform the contract according to the precise terms agreed