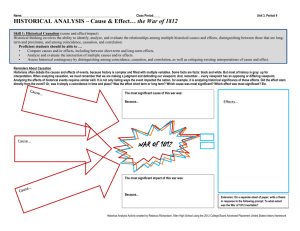
Three statistical problems Lack of independence
advertisement

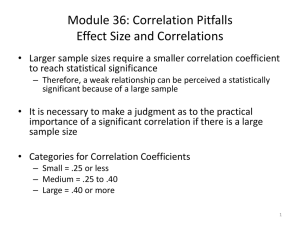
The Data Goldrush Andy Wedel Bodo Winter University of Arizona UC Merced The data revolution Griffiths, T. L. (2015). Manifesto for a new (computational) cognitive revolution. Cognition, 135, 21-23. “Data is merely the raw material of knowledge” http://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/06/technology/06stats.ht ml?_r=1& The “data science” rebranding http://drewconway.com/zia/2013/3/26/the-data-science-venn-diagram The “data science” rebranding Jeff Leek http://simplystatistics.org/2013/12/12/the-key-word-in-data-science-is-not-data-it-is-science/ Structure of this course Day 1 Day 2 (1) general statistical issues (2) cross-cultural correlational studies Andy’s day! (phonetics & phonology) Day 3 Day 4 Bodo’s day! (semantics & gesture) data-driven language contact research The course website bodowinter.com/goldrush My one slide on inferential stats assume null hypothesis p<0.05 reject null hypothesis Population Sample https://www.coursera.org/course/datascitoolbox My one slide on inferential stats cont’d Type I error = erroneously rejecting the null hypothesis demo My one slide on regression Response time (ms) 500 RT ~ Noise 400 300 0 4 8 Noise (dB) 12 16 My one slide on regression Response time (ms) 500 RT ~ Noise 400 300 0 4 8 Noise (dB) 12 16 Correlations ~ http://www.skepticalraptor.com/skepticalraptorblog.php/correlation-does-not-imply-causation-exceptwhen-it-does/ Examples of linguistic correlations Postpositions Prepositions Object-Verb 472 14 Verb-Object 42 456 Dryer, M.S. (2013). Relationship between the order of object and verb and the order of adposition and noun. WALS, http://wals.info/chapter/95 Examples of linguistic correlations ~ Examples of linguistic correlations sound change ~ Labov, W. (1990). The interaction of sex and social class in the course of linguistic change. Language Variation and Change, 2, 205-254. Eckert, P. (1989). The whole woman: Sex and gender differences in variation. Language Variation and Change, 1, 245-67. Examples of linguistic correlations ~ future tense marking Chen, M. K. (2012). The effect of language on economic behavior: Evidence from savings rates, health behaviors, and retirement assets. American Economic Review, 103, 690-731. Examples of linguistic correlations kʼ tʼ qʼ ~ Everett, C. (2013). Evidence for direct geographic influences on linguistic sounds: the case of ejectives. PloS one, 8(6), e65275. Examples of linguistic correlations ~ Everett, C., Blasi, D. E., & Roberts, S. G. (2015). Climate, vocal folds, and tonal languages: Connecting the physiological and geographic dots. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112, 1322-1327. Two types of correlations … between linguistic features … between linguistic & non-linguistic features Ladd, D. R., Roberts, S. G., & Dediu, D. (2015). Correlational studies in typological and historical linguistics. Annual Review of Linguistics, 1, 221-241. Examples of correlations Ladd, D. R., Roberts, S. G., & Dediu, D. (2015). Correlational studies in typological and historical linguistics. Annual Review of Linguistics, 1, 221-241. Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Multiple comparisons Lack of independence Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Multiple comparisons Lack of independence Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Roberts, S., & Winters, J. (2013). Linguistic diversity and traffic accidents: Lessons from statistical studies of cultural traits. PLoS one, 8(8), e70902. Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Christian Bentz Bentz, C., & Winter, B. (2013). Languages with more second language learners tend to lose nominal case. Language Dynamics & Change, 3:1, 1-27. Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation 1. L2 learning morphology 2. L2 speakers morphology 3. L2 speakers morphology confound? Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation L2 speakers morphology 4. shared history 5. chance Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation http://www.skepticalraptor.com/skepticalraptorblog.php/correlation-does-not-imply-causation-exceptwhen-it-does/ Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Steps to support causality The data must be strong. The data must be consistent. The data must be coherent. The data must be specific. The causal effect must be plausible. http://www.skepticalraptor.com/skepticalraptorblog.php/correlation-does-not-imply-causation-exceptwhen-it-does/ Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Hypothesis Data correlations increase the probability of compatible models, they decrease the probability of incompatible ones Ladd, D. R., Roberts, S. G., & Dediu, D. (2015). Correlational studies in typological and historical linguistics. Annual Review of Linguistics, 1, 221-241. Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Experiments do not provide fool-proof access to causality Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation http://blogs.discovermagazine.com/neuroskeptic/2015/05/24/fmri-of-the-amygdala-all-in-vein/ Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Multiple comparisons Lack of independence Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Multiple comparisons Lack of independence Three statistical problems Multiple comparisons https://www.sciencenews.org/article/trawling-brain Bennett, C. M., Baird, A. A., Miller, M. B., & Wolford, G. L. (2011). Neural correlates of interspecies perspective taking in the post-mortem atlantic salmon: an argument for proper multiple comparisons correction. Journal of Serendipitous and Unexpected Results, 1, 1-5. https://xkcd.com/882/ https://xkcd.com/882/ https://xkcd.com/882/ Three statistical problems Multiple comparisons Example of doing 100 tests: If α = 0.05 is taken as the significance level For 100 tests, the expected number of incorrect rejections of the null hypothesis is 5 The probability of at least one statistical result being significant is: 100 1- 0.95 = 0.994 Three statistical problems Multiple comparisons What to do? (1) Correcting for multiple comparisons (e.g., Bonferroni correction) (2) Avoid multiplicity at the design stage (Bender & Lange, 2001) Bender, R., & Lange, S. (2001). Adjusting for multiple testing—when and how?. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 54(4), 343-349. Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Multiple comparisons Lack of independence Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Multiple comparisons Lack of independence Three statistical problems Lack of independence Number of tones Three statistical problems Lack of independence 9 6 3 0 0.0 0.2 0.4 Humidity 0.6 0.8 Number of tones Three statistical problems Lack of independence 9 6 3 0 0.0 0.2 0.4 Humidity 0.6 0.8 Number of tones Three statistical problems Lack of independence 9 6 3 0 0.0 0.2 0.4 Humidity 0.6 0.8 Three statistical problems Lack of independence A simple Type I error simulation: -100 -50 0 50 100 Voice Onset Time Sample 1 Sample 2 Three statistical problems (Source code on class github repo) Lack of independence unique_items <- rnorm(nitems) unique_subs <- rnorm(nsub) resp <- unique_items[items] + unique_subs[subjects] + rnorm(nsub*nitems) 1,000 simulations Three statistical problems Type I error rate 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 Lack of independence Three statistical problems Lack of independence Type I error rate 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 accounting for independence Three statistical problems Lack of independence Type I error rate 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 accounting for independence ignoring independence Two sources of non-independence Lack of independence Language genealogy (Dryer, 1989, 1991, 1992; Cysouw, 2010; Jaeger et al., 2011) Language areas (Dryer, 1989, 2000; Maslova, 2000, Bickel, 2008; Cysouw, 2010; Jaeger et al., 2011) Bickel, B. (2008). A refined sampling procedure for genealogical control. STUF-Language Typology and Universals, 61(3), 221–233. Cysouw M. (2010). Dealing with diversity: Towards an explanation of NP-internal word order frequencies. Linguistic Typology, 14: 253–286. Dryer, M. (1989). Large linguistic areas and language sampling. Studies in Language, 13(2), 257–292. Dryer, M. (1991). SVO languages and the OV: VO typology. Journal of Linguistics, 27(2), 443–482. Dryer, M. (1992). The Greenbergian word order correlations. Language, 68(1), 81–138. Dryer, M. (2000). Counting genera vs. counting languages. Linguistic Typology, 4, 334–350. Jaeger, T. F., Graff, P., Croft, W., & Pontillo, D. (2011). Mixed effect models for genetic and areal dependencies in linguistic typology. Linguistic Typology, 15(2), 281-320. Maslova, E. (2000). A dynamic approach to the verification of distributional universals. Linguistic Typology, 4(3), 307–333. Genealogical relationships Historically Independent Cultures 1 1 0 1 Observable Cultures 4 1 0 7 Roberts, S., & Winter, J., & Chen, K. (upcoming). Future tense and economic decisions: controlling for cultural evolution. PLOS ONE. Contact relationships & =1 3 & =3 3 Borrowing Borrowing Roberts, S., & Winter, J., & Chen, K. (upcoming). Future tense and economic decisions: controlling for cultural evolution. PLOS ONE. Contact relationships & =1 3 & =3 3 Borrowing Borrowing Roberts, S., & Winter, J., & Chen, K. (upcoming). Future tense and economic decisions: controlling for cultural evolution. PLOS ONE. Contact relationships Mark Liberman http://languagelog.ldc.upenn.edu/nll/?p=3764 Two sources of non-independence Lack of independence Sean Roberts James Winters Roberts, S., & Winter, J., & Chen, K. (upcoming). Future tense and economic decisions: controlling for cultural evolution. PLOS ONE. Two sources of non-independence Controlling for area and family within a mixed effects modeling framework: Lack of independence lmer(case ~ L2prop + (1+L2prop|family) + (1+L2prop|area)) Three statistical problems Correlation is not causation Multiple comparisons Lack of independence