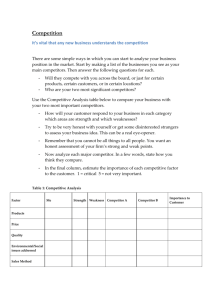
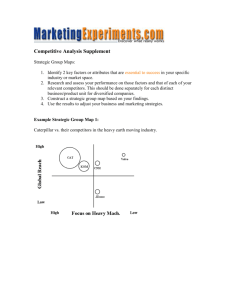
Competitor Analysis - Presentation (Download in
advertisement

Measuring Marketing • Difficulties – Requires specific, analytical skill set – Difficult to measure some areas, ie advertising’s effect on sales: • Lag effect • Multiple distribution channels • Intervening Variables Measuring Marketing • Benefits – Improved product or service – Determination of new customer segments – Increased information on those things that influence sales – Overall increases opportunity – Must be considered as “means to an end” Market Characteristics • Industry: Set of all actual sellers of a product or service • Market: Set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service – Available market is set of buyers with interest income and access to product – Served market is that part of the available market a company has decided to pursue – Penetrated market is that set of consumers who have already bought the product or service Market Demand • Market Demand is the total volume that would be bought by a defined customer group in a defined market environment under a defined level or mix of industry marketing effort • Mkt Demand is a function of a set of conditions, not a fixed, solid concrete number, and those conditions are constantly changing – Economics – Technology – Socio-cultural factors Markets • Potential – who might be a candidate • Available – who is not currently connected to another brand or substitute product • Qualified available – who has access and income • Served – which segment(s) of all possible candidates are you able to reach • Penetrated – who are currently your customers Market Characteristics, cont’d • Expandable markets: Size is strongly affected by level of industry marketing expenditures/efforts – Opportunity to build Primary Demand for product or service category • Non-expandable: Size is not much affected by level of industry marketing effort. – Need to increase selective demand for that particular service or brand Competitive Environment • Market Share is that % of the total penetrated market (buyers) held by a particular company, product or brand. • Mkt Share allows comparison with competitors within reason: – Differences in served markets Competitor Analysis: Industry Perspective • • • • • • • Industry Structure Entry Barriers Mobility Barriers Exit/shrinkage Barriers Industry Cost Structures Vertical Integration Global Reach Competitor Analysis: Industry • Slow Growth market • High Growth market • Strategic shift signals – – – – – – R & D efforts Relationship Building Geographic refocusing Management changes Changes in Spending Realignment of SBU’s Competitor Analysis: Market Perspective • Segments by Customer Needs – Segments by Geography • Who is selling a product where? – Substitute Products • What else meets the same need? • How is it alike or different? Competitor Analysis • Assess Strengths and Weaknesses (Competitive SWOT) • Estimate Competitor Reaction Patterns – – – – Laid back & complacent? Selective, pick their battles? Tigers, aggressive fighters for markets? Stochastic, unpredictable? • Determine Own Company’s Strategy based on own SWOT and above information Competitive Strategies • Cost Leadership: low COST (not price) Producer • Differentiation: differentiated product line(s) or unique customer benefits • Focused: narrow concentration on a small segment of a larger market • M-O-R or Unfocused: Non-specific customer base or no clear strategy • Value Leadership: superior customer value – Cost, operational or product quality leadership – Strong customer relationships Competitive Positions • Market Leader – largest market share • Market Challenger – runner up which is poised to overtake leader • Market Follower – runner up which is maintaining share or status quo • Market Nicher – serves small segments other overlook or choose to ignore Market Leader Strategies • Expand Total Market – New users, new uses, increased usage of product or service – Benefit from increased sales • Protect Market Share – Defensive strategies • Expand Market Share – Aggressively pursue available markets or competitor’s share Defensive Strategies • • • • • • Position Defense Flanking Defense Pre-emptive Defense Counteroffensive Mobile Defense Contraction Defense Position Defense • Attempt to Maintain Status Quo in Mkt Share • May require significant commitment in company resources • Inherent problems – Competitor Innovation – Changing Customer needs/tastes/expectations Flanking Defense • If Competitors choose weak areas of business to attack • Shore up weaker flanks: – Expansion of product lines – Product improvements – Image management for company, products or brands Pre-emptive Defense • Competitor Scanning • Anticipate competitor strategies and actions • Reposition ahead of time to prevent loss of share/sales • “No need to outrun any one you can outsmart” - Garfield Mobile Defense • Approach customers from a broader perspective than competitors – Adjust products/services accordingly – Identify and pursue new, additional markets with same or modified product • Diversify Counteroffensive • Assess damage fro a competitive attack • Respond with a stronger impact Contraction Defense • Controlled, intentional reduction of market activity • Reduce operational demands • Refocus efforts, perhaps on more core businesses Challenger Strategies • First define target and strategic actions: – Attack – Avoid – Acquire • Choose an attack strategy if required: – Frontal, flanking, encircling: attack leading, weak or all products – Bypass: use technological innovation to leapfrog – Guerilla: sporadic, unexpected attacks to draw focus Follower Strategies • Clone – Closely copy all or part of competitors marketing mix • Imitate – Copy some aspects but differentiate in others • Adapt – Build on, improve competitor’s offerings Nicher Strategies • • • • • • • • End Use Specialist Vertical Level Specialist Customer Size Specialist Customer Specific Specialist Geographic Specialist Product/Feature Specialist Quality/Price Specialist Service Specialist