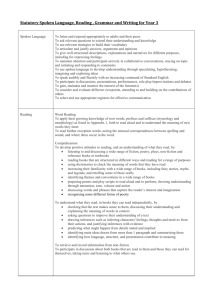
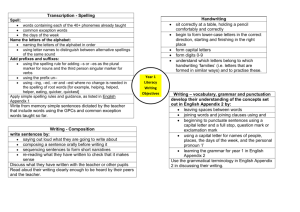
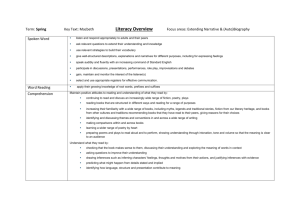
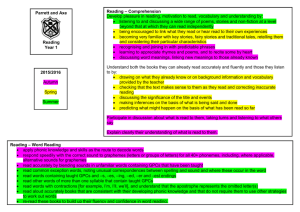
Draft computing scheme of work from the St Marks Teaching School
advertisement

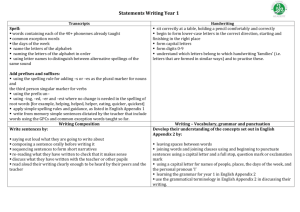
MARK CROSS CE PRIMARY SCHOOL English scheme of work Revised September 2014 Reading Writing Speaking and Listening Strand Reading: Word Reading 1 Apply phonic knowledge to decode words. Use graphaphonic knowledge for all 44 phonemes. 2 Continue to apply phonic knowledge as the primary strategy to decode. In addition children should be taught: Blend for reading the taught GPC’ and endings: –s, -es, -ing, –ed –er -est Read contractions exception words as well as words with more than one syllable. Read decodable books aloud, applying phonic skills as the primary strategy. Reread for fluency and confidence. Blending sounds including alternative sounds for graphemes. Reading words of two or more syllables. Common suffixes Common exception words. To read most words without overt sounding and blending. Read decodable books matched to their improving phonic knowledge. 3 4 Apply growing knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes. Read further exception words. Note unusual correspondences between spelling and sound and where these apply in words. 5 6 Apply growing knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes. Read aloud with understanding of new words they meet. 1 Strand 1 2 Reading: Comprehension To develop pleasure in reading, motivation to read, vocabulary and understanding by: Develop pleasure in reading, motivation to read, vocabulary and understanding by: Listening to and discussing a wide range of texts – poetry, stories and nonfiction texts Becoming familiar with a range of stories, retelling them and joining in with repeated and predictable phrases. Learning to appreciate rhymes and poems and recite some by heart Discussing meanings of new and unfamiliar words To understand books they read and listen to by: Drawing on what they already know or on information provided Checking the text for sense and self – correcting Making inference from the text, discussing the title and events. Predict what may happen Listening to, discussing and expressing views about a variety of text forms, including those beyond that which they can read independently Discussing a sequence of events in books, and become familiar with and retell a wider range of stories Being introduced to different forms of non-fiction books Discussing and clarifying the meanings of words and discuss favourite words or phrases. Continue to build up a repertoire of poems learnt by heart and recite with appropriate 3 4 Develop positive attitudes to reading and understanding by: Listening and discussing a wide range of fiction, poetry, non-fiction, reference and text books, identifying themes and conventions Reading for a range of purposes; discussing words and phrases that capture the imagination Read aloud and perform poems and playscripts Checking for sense, explaining the 6 Maintain positive attitudes to reading and understanding of what the read, by: Listen to and discussing a wide range of genre types. Read books and poems that have different structures and forms; reading for a range of purposes. Recommend books to their peers, giving reasons for choices. Participating in discussions and challenging views courteously, including formal presentations and debates. Identify and discuss themes and conventions in and across a wide range of writing. Make comparisons within and across books. Preparing poems and playa to read aloud and to perform, showing Use dictionaries Understand what they read when reading independently: 5 2 and explain their understanding of the text Participate in discussions, listening and responding to others. intonation Understand the books they read and listen to by: Drawing on what they know or on provided information and vocabulary Checking for sense and self-correcting inaccurate reading Making inference , asking and answering questions Participate in discussions about books and other works that are read to them, taking it in turns and listening to what others say. Explain and discuss their understanding of texts that they read and that they listen to meaning of words in context Ask questions and draw inferences understanding through intonation, tone, volume so that meaning is clear to an audience. Check that books make sense to them, discussing content and meaning of words. Ask questions to improve understanding. Draw on inferences such as character feelings, thoughts and motives, providing evidence and justifying reasoning. Make predictions from details stated and implied and summarise information and key events. Identify how language, including figurative language, structure and presentation contribute to meaning. Distinguish between fact and opinion. Retrieve, record and Predict what happens next; summarise paragraphs Identify how language, structure and presentation contribute to meaning Retrieve and record information from nonfiction text By discussing books read to them and those read by themselves 3 Year Writing: Transcription Spelling (See English Appendix 1) 1 Spell: Words containing the 44 phonemes taught. Common exception words and days of the week. Name: Letters of the alphabet in order and use letter names to distinguish between alternative spellings. Add Prefixes and suffixes: Use spelling rules for adding –s or –es. Using prefix –un Using –ing, -ed, -er, -estwhere the root word doesn’t change. Apply simple spelling rules (see appendix 1) Write from memory simple sentences dictated by the teacher including skills taught so far. 2 Spell by: Segmenting words using graph aphonics. Learning new ways of spelling homophones. Learn to spell common exception words. Learn to spell more simple contractions. Learning the possessive apostrophe (singular) Distinguishing between homophones and near homophones. (See appendix 1) 3 4 Use further prefixes and suffixes and rule for applying them. present information from non-fiction. 5 6 Use further prefixes and suffixes and rule for applying them. Spell words with ‘silent’ letters Spell further homophones. Spell words that are often misspelt. Continue to spell homophones and other words which are often confused. Place the possessive apostrophe accurately. Use knowledge of morphology and etymology in spelling. Use the first two or three letters in a word to check spellings. Use dictionaries to check spellings and meaning of words using the first 3 or four letters. Write from memory simple sentences dictated by the teacher including skills Add suffixes including –ment, - taught so far. ness, -full, -less, -ly Use a thesaurus. Apply simple spelling rules (see appendix 1) Write from memory simple sentences dictated by the teacher including skills taught so far. 4 Year Handwriting and Presentation 1 Sit correctly at a table holding a pencil comfortably and correctly. Begin to form lower case letters in the correct direction, starting and finishing in the correct place. Form capitals and form digits 1-9 Year Writing: Composition Understand which letters belong to which handwriting ‘families.’ 1 Pupils should be taught to write sentences by: Saying out loud what they are going to write about Composing a sentence orally before writing it Sequencing sentences to form short narratives Rereading what they have written to check that it makes sense Discuss what they have written 2 Form lower-case letters of the correct size relative to one another Start to use lead ins to join letters where appropriate. 3 4 Write legibly, fluently and with increasing speed by: To increase the legibility, consistency and quality of their handwriting Choosing which shape of a letter to use and deciding whether or not to join letters. Choosing the writing implement best suited to the task. Use spacing between words. 2 3 4 Plan their writing by: Consider what they are going to write before beginning, by: planning or saying out loud what they are going to write about, writing down ideas and 6 Start to use lead ins to join letters where appropriate Write capital letters and digits of correct size and orientation. To develop positive attitudes towards and stamina for writing, by writing about: personal experiences and those of others (real and fictional), real events, poetry and for different purposes. 5 Discussing similar writing to that which they are planning to write, in order to learn from its structure, vocabulary and grammar Discussing and recording ideas Draft and write by: Composing and 5 6 Plan their writing by: Identify the audience for and purpose of the writing; selecting appropriate forms and using writing as models for their own. Noting and developing ideas, drawing on reading and research. Consider who authors have developed character and settings. Draft and write by: 5 with the teacher or other pupils Read their writing aloud, clearly enough to be heard by their peers and the teacher key vocabulary and encapsulating what they want to say, sentence by sentence. Make simple additions, revisions and corrections to their writing by: rehearsing sentences orally, progressively building a varied vocabulary and increasing the range of sentence structures (Appendix 2) Using paragraphs Creating settings, character and plot Using simple organisational devices e.g. headings, sub headings Evaluating their writing with the teacher and other pupils Rereading to check that their writing makes sense and that vocabulary is used correctly and consistently. Proofreading to check Evaluate and edit by: for errors in spelling, Assessing the grammar and effectiveness of their punctuation. own and others’ Reading aloud what writing and they have written with suggesting appropriate improvements intonation to make Proposing changes to the meaning clear. grammar and vocabulary to improve consistency Proof read for spelling and Selecting appropriate grammar and vocabulary, understanding how such choices can change and enhance meaning. Précising longer passages. Use a wide range of devices to build cohesion across paragraphs. Use further organisational and presentational devices – to structure text. Evaluate and Edit: Assessing their own and others’ writing. Make changes to vocabulary, grammar, and punctuation. Ensure the consistent and correct use of tense though out a piece of writing. Ensure correct subject and verb agreement when using singular and plural, distinguishing between the language of speech and writing. Proofread for spelling and punctuation errors. Perform their own 6 punctuation errors Read their own writing aloud to a group or whole class, using appropriate intonation Year 1 2 Writing: Pupils should be taught to: Pupils should be taught to: Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation Develop their understanding of the concepts of set out in the English Appendix 2 by: Develop their understanding of the concepts set out in English app 2 by : Leaving spaces between words Joining words and joining clauses using ‘and’ Beginning to punctuate sentences using a capital letter, and a full stop, a question mark or exclamation mark Using capital letters in the appropriate places Learn the grammar for year 1 in English app 2 Learning how to use both familiar and new punctuation correctly – see English app 2, including full stops, capital letters, exclamation marks, question marks, commas for lists and apostrophes for contracted form and possessive Learn how to use: Sentences with different forms: statement , question, 4 Develop their understanding of the concepts set out in Appendix 2 Use the grammar terminology in English Appendix 2 in discussing 3 Extend the range of sentences with more than one clause by using a range of conjunctions : when, if, because, although Using the present perfect form of verbs in contrast to the past tense Choosing nouns or pronouns appropriately and to avoid repetition Use conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to express time and clause composition using reading and speaking skills. 5 6 Develop their understanding of the concepts set out in English appendix 2. Recognising vocabulary and structures that is appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms. Using passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence. Using the perfect form of verbs to mark relationships of time and cause. Using modal verbs or adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility. Using expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely. 7 their writing Year Speaking and Listening exclamation, command Expanded noun phrases to describe and specify The present and past tenses correctly and consistently including the progressive form Subordination (using when, if, that, or because) and coordination (using or, and, or but) The grammar for year 2 in English appendix 2 Some features of written standard English Use and understand the grammatical terminology in English appendix 1 2 Use fronted adverbials Learning the grammar for Years 3 and 4 in appendix 2 Indicate grammatical and other features by: Using commas after fronted adverbials Use the possessive apostrophe with plural nouns Use and punctuate direct speech Use and understand the grammatical terminology in appendix 2 3 4 Use clause beginning with question words. Learning grammar for y5 and 6 in English appendix 2. Indicate grammatical and other features by: Using commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity in writing. Using brackets, dashes or commas, and semicolons. Punctuate bullet points consistently 5 6 Listen and respond to adults appropriately Ask relevant questions Use relevant strategies to build their vocabulary Articulate and justify answers, arguments and opinions Give well structured descriptions, explanations and narratives for different purposes, including for expressing feelings Maintain attention and participate actively, staying on topic Use spoken language to develop understanding through speculating, hypothesising, imaging and exploring ideas 8 Speak audibly and fluently Participate in discussions, presentations, performances, role play and debates Gain, maintain and monitor the interest of the listener Consider and evaluate different viewpoints Select and use appropriate registers for effective communication 9