power point Link
advertisement

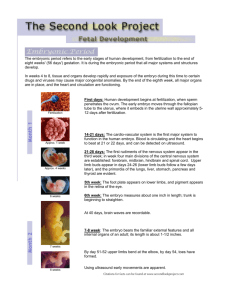
Chapter 12 Growing and Changing Lesson 5 Heredity and Human Development Click for: >> Main Menu >> Chapter 12 Assessment Teacher’s notes are available in the notes section of this presentation. Next >> chromosomes Threadlike structures that carry genes genes The basic units of heredity cell The basic unit of life tissue A group of similar cells that do a particular job organ A body part made up of different tissues joined to perform a particular function body A group of organs that work together to carry out system related tasks embryo The developing organism from two weeks until the end of the eighth week of development fetus The developing organism from the end of the eighth week until birth In this lesson, you will learn to explain how humans inherit certain characteristics. identify the basic unit of life. describe how a fetus develops. identify ways an expectant mother can care for her developing fetus. Analyzing a Graphic Levels of Body Structure Using the diagram shown here, create a concept map about the different levels of body structure. As you read the lesson, fill in the concept map. Cells Heredity When a sperm and egg unite, the newly fertilized egg has a complete set of chromosomes. chromosomes Threadlike structures that carry genes Genes carry the codes for inherited traits. genes The basic units of heredity Heredity Fertilization and Human Development How does a single cell become a person made of many cells? cell The basic unit of life Soon after fertilization, the fertilized egg begins to divide and multiply. Fertilization and Human Development Groups of cells make up tissues and tissues then make up organs. tissue A group of similar cells that do a particular job organ A body part made up of different tissues joined to perform a particular function Fertilization and Human Development Eventually, an entire body system is formed. body system A group of organs that work together to carry out related tasks Development of the Fetus A fertilized egg is called a zygote. The zygote divides to form 2 cells about 24 hours after fertilization. After one week, the zygote attaches to the lining of the uterus. After another week, the zygote is called an embryo. embryo The developing organism from two weeks until the eighth week of development Fertilization and Human Development After the eighth week, the human embryo is called a fetus. fetus The developing organism form the end of the eighth week until birth. Birth takes place about nine months after fertilization. Care During Pregnancy Eat healthful foods Don’t take unnecessary drugs Have regular checkups Positive Health Behaviors for Expectant Mothers Don’t drink alcohol Beware of infections Don’t use tobacco Lesson 5 Review What I Learned Vocabulary Define chromosomes. Lesson 5 Review What I Learned Identify List four levels of body organization from most complex to most basic. Lesson 5 Review What I Learned Describe Describe the development of a human from the point of fertilization. Lesson 5 Review What I Learned List What are four ways that a pregnant female can care for her developing baby? Lesson 5 Review Thinking Critically Apply A test of Ling’s fetus shows that its cells each have one more chromosome than normal human cells. How many chromosomes does each of her fetus cells have? Lesson 5 Review Thinking Critically Analyze Using the information given in Figure 12.9, calculate the weight that the developing fetus gains at each three month stage. During which stage does it gain the most weight? End of Chapter 12 Growing and Changing Lesson 5 Heredity and Human Development Click for: >> Main Menu >> Chapter 12 Assessment