EEE 302 Lecture 10
advertisement

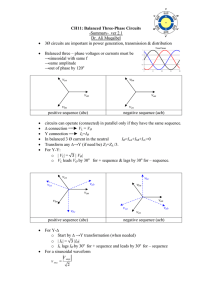
EEE 302 Electrical Networks II Dr. Keith E. Holbert Summer 2001 Lecture 10 1 Source/Load Connections • The equivalent load may be in an equivalent delta () or wye (Y) configuration – the delta load configuration has no neutral line – the current is zero in the neutral line for a balanced wye load configuration • Source/Load connections can be connected in any of the possible combinations: Ysource-Yload source-Yload Ysource-load source- load – Analysis prefers the first connection (Y-Y) Lecture 10 2 Balanced Wye-Wye Connection a Van + – b Vbn + – c Vcn ZY ZY ZY + – n Lecture 10 Load 3 Balanced Wye-Wye Connection • The line-to-line voltages (or line voltages) are Vab = VP3 30° Vbc = Vab -120° Vca = Vab -240° where VP is the magnitude of the phasor voltage between any two lines • The magnitude of the line voltage is VL = VP3 Lecture 10 4 Balanced Wye-Wye Connection • The line current for phase a is Ia = Van / ZY = Vp 0° / ZY – In a Y-Y connection the magnitude of the line current (IL) equals the magnitude of the load current (IY) • The neutral current In is In = Ia + Ib + Ic = 0 • Balanced Y-Y three-phase ac circuits may be analyzed on a per phase basis Lecture 10 5 Balanced Wye-Delta Connection Van + – Vbn + – n Vcn a Z b Z Z + – c Load Lecture 10 6 Summarizing • A very good summary appears on pages 568-9 of the textbook including a figure and table for explanation Lecture 10 7 Class Examples • Extension Exercise E10.1 • Extension Exercise E10.2 Lecture 10 8 Three-Phase Power Relationships • The real and reactive power per phase are PP VP I L cos QP VP I L sin VL I L 3 VL I L 3 cos sin • The total real, reactive, and complex powers are PT 3 PP 3 VL I L cos QT 3 QP 3 VL I L sin S T 3 VL I L Lecture 10 9 Class Examples • Extension Exercise E10.8 • Extension Exercise E10.10 Lecture 10 10