presentation source
advertisement

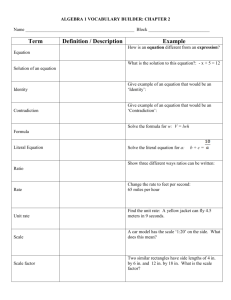
Introduction to Humanities Computing Spring 1999 Lecture Six Passport to Tour What is the important Concept from Computer Confluence Chapter 6 Devoted to spread sheets Which is transferable to The world of text analysis ? Malleable Matrix A tour Dartmouth Dante Database Project DDP is still best accessed via Telnet. The address remains: library.Dartmouth.EDU at the prompt type connect dante What is an electronic text? Can you provide examples? What type of electronic text will survive? What is a electronic text? Any string of characters Any file or document that can be read A word processing file A text file Types of Electronic Texts Literary text Linguistic corpus Hypermedia work A variety of forms WWW site (Hypermedia) Myst, Macbeth (Software, Text, and Media) MS Word formatted file (Wordprocessing) ASCII Text file (aka “Flat File”) ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange 0 Null 3 EOT (end of text) 13 CR (carriage return) 32 SP (space) 48 0 49 1 65 A 97 a, 98 b, 99 c ... Coding Standards ASCII = 7 bits per character 128 characters - 7 bits per character 32 Reserved for printing info Rest for printing characters Extended ASCII = 8 bits or 1 byte, 256 characters, upper ASCII characters used for special characters, characters with diacritical marks & ligatures UNICODE = 16 bit character set 65,000 characters - most known languages Why? Cross-Platform Long-term survival of data You can use it to encode more complex documents using markup (SGML) ASCII Text + Markup = Electronic Representation of Literary Text Encoding <html> <Head><Title>Welcome</Title></Head> <Body><H1>Welcome to 3F03</h1> This is the home page for 3F03<P> <B>Quantitative Methods in the Humanities </B> Fran&ccedil;ais </Body></html> In HTML all formatting provided by codes using ASCII characters Content Model Text Head Title Body Heading Paragraph Limits of HTML No codes for many of the features: Character, Author, Text type, Sonnet, Lines Text analysis software can’t handle it Languages other than English COCOA Markup Continuous Tags Do note require closing </tag> - change value Format: <variable value> (angled brackets < > are delimiters) Example <speaker Romeo> <scene 1> <L 1> <text-type frontmatter> <<Comments not meant to be indexed>> COCOA example <Title Misunderstanding> <<Example for Demonstration, 1997>> <t titlepage>THE MISUNDERSTANDING A PLAY IN THREE ACTS <t dedication>To my friends of the THEATRE DE L'EQUIPE <t characters>CHARACTERS IN THE PLAY: THE OLD MANSERVANT ... MARIA <t information>LE MALENTENDU (THE MISUNDERSTANDING) was presented for the first time at the Theatre des Mathurins, Paris, in 1944 Example continued <act 1> <t stagedir>Noon. The clean, brightly lit public room of an inn. Everything is very spick and span. <t play> <p mother>He'll come back. <p martha>Did he tell you so? Brief History Text Analysis Tools Text-analysis tools grew out of concordances: 1247, Concordance to the Vulgate Bible, Paris 1949, Father Busa Index Thomisticus 1970s, Batch Concordancers like OCP 1989, TACT - Interactive Concordancers 1990s, Textual Visualization What can be done... Text-analysis tools provide Speed Complex Searches Reconfigured Views Statistics Researchers can generate custom concordances interactively Concordances and Interpretation Concordances provide an alternative arrangement of the text that brings passages together into a concordantia. Interpretative strategy where answers are drawn from the text by assembling passages on the subject in question and reading this rearranged text as a meaningful whole. Concordance facilitates this rearrangement providing alternative views. Types of Text-Analysis Stylistic Describing author’s style and comparing it Authorship studies Linguistic Create representative corpus Describe linguistic use (diachronic or synchronic) Thematic Finding patterns (words & phrases) in a text Following themes through a work Comparing themes Demands a reiterative reading Problematic equations That a theme is the passages where a set of words appear Can themes be identified by key words? What about ambiguous words? That concording passages into a new text is an acceptable interpretative strategy Where does the passage start and end around a word? Is reading a rearranged text appropriate? That the distribution of words indicates the progress of a theme Do the number of hits indicate intensity of theme? What’s the connection Surface Measurement (Quantification) Interpretation (Understanding) Two Views Text-analysis is about proving things about texts Stylistic analysis provides reproducible descriptions of authors style Measurement of surface features allows us to prove more interesting points Reaction to impressionistic reader oriented literary theory Text-analysis is the rereading a text in ways that help one better understand it Text-analysis is only one of many strategies Text-analysis reveals anomalies to be researched Text-analysis is useful precisely because the computer can’t do well what human readers do well, and can do other things well E-Text Research Project Planning Prototyping Planning Phase Traditional Research Scanning or Buying Proofing Implementation Phase Markup Publication Interactive Study Research Phase Obtaining an E-text Acquire one from someone else. Oxford Text Archive Search the Internet using WWW Commercial Vendors Create it yourself Scan it using OCR software OCR = Optical Character Recognition Type it in or hire services for input Markup Validate