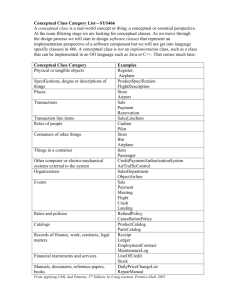
Chapter
7
Accounting Principles
Financial Accounting, Sixth Edition
Chapter
7-1
Study Objectives
1. Explain the meaning of GAAP and identify the key items
of the conceptual framework.
2. Describe the basic objectives of financial reporting.
3. Discuss the qualitative characteristics of accounting
information and elements of financial statements.
4. Identify the basic assumptions used by accountants.
5. Identify the basic principles of accounting.
6. Identify the two constraints in accounting.
7. Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
8. Explain the accounting principles used in international
operations.
Chapter
7-2
Accounting Principles
The
Conceptual
Framework of
Accounting
Objectives of
reporting
Qualitative
characteristics
Elements of
financial
statements
Operating
guidelines
Chapter
7-3
Constraints
in
Accounting
Statement
Presentation
and Analysis
Assumptions
Principles
Monetary unit
Revenue
recognition
Materiality
Conservatism
Classified
balance sheet
Matching
Summary of
conceptual
framework
Classified
income
statement
Economic
entity
Time period
Going
concern
Full
disclosure
Cost
Analyzing
financial
statements
An international
perspective
The Conceptual Framework of Accounting
Financial Statements
Various users
need financial
information
Balance Sheet
Income Statement
Statement of Retained Earnings
Statement of Cash Flows
Note Disclosure
The accounting profession
has attempted to develop
a set of standards that
are generally accepted
and universally practiced.
Chapter
7-4
Generally Accepted
Accounting
Principles (GAAP)
SO 1 Explain the meaning of GAAP and identify the
key items of the conceptual framework.
The Conceptual Framework of Accounting
Organizations Involved in Standard Setting:
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
http://www.sec.gov/
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
http://www.fasb.org/
Chapter
7-5
SO 1 Explain the meaning of GAAP and identify the
key items of the conceptual framework.
The Conceptual Framework of Accounting
Conceptual Framework - “…a constitution, a coherent
system of interrelated objectives and fundamentals.”
FASB’s conceptual framework consists of the following:
Chapter
7-6
1.
Objectives of financial reporting.
2.
Qualitative characteristics of accounting
information.
3.
Elements of financial statements.
4.
Operating guidelines (assumptions, principles, and
constraints).
SO 1 Explain the meaning of GAAP and identify the
key items of the conceptual framework.
Conceptual Framework
Objectives of Financial Reporting
a) To provide information that is useful to those making
investment and credit decisions.
b) Helpful in assessing future cash flows.
c) Identify the economic resources (assets), the claims to
those resources (liabilities), and the changes in those
resources and claims.
Chapter
7-7
SO 2 Describe the basic objectives of financial reporting.
Conceptual Framework
Review:
According to the FASB conceptual framework, the
objectives of financial reporting for business
enterprises are based on?
a. Generally accepted accounting principles
b. Reporting on management’s stewardship.
c. The need for conservatism.
d. The needs of the users of the information.
(CPA adapted)
Chapter
7-8
SO 2 Describe the basic objectives of financial reporting.
Conceptual Framework
Question:
How does a company choose an acceptable accounting
method, the amount and types of information to
disclose, and the format in which to present it?
Answer:
By determining which alternative provides the most
useful information for decision-making purposes
(decision usefulness).
Chapter
7-9
SO 3 Discuss the qualitative characteristics of accounting
information and elements of financial statements.
Conceptual Framework
Qualitative Characteristics
Relevance – making a difference in a decision.
Predictive value
Feedback value
Timeliness
Reliability
Verifiable
Representational faithfulness
Neutral - free of error and bias
Chapter
7-10
SO 3 Discuss the qualitative characteristics of accounting
information and elements of financial statements.
Conceptual Framework
Qualitative Characteristics
Comparability – Information that is measured and
reported in a similar manner for different
companies is considered comparable.
Consistency - When a company applies the same
accounting treatment to similar events from period
to period.
Chapter
7-11
SO 3 Discuss the qualitative characteristics of accounting
information and elements of financial statements.
Conceptual Framework
Elements of Financial Statements
“Moment in Time”
Assets
Liabilities
Equity
Chapter
7-12
“Period of Time”
Revenue
Expenses
Gains
Losses
SO 3 Discuss the qualitative characteristics of accounting
information and elements of financial statements.
Conceptual Framework
Illustration: Identify the element or elements associated with
items below.
(a) Obligation to transfer
resources arising from a
past transaction.
(b) Items characterized by
future economic benefit.
(c) Arises from income
statement activities that
constitute the entity’s
ongoing major or central
operations.
Chapter
7-13
Elements
(b) Assets
(a) Liabilities
Equity
(c)
Revenue
(c)
Expenses
SO 3 Discuss the qualitative characteristics of accounting
information and elements of financial statements.
Conceptual Framework
Illustration: Identify the element or elements associated with
items below.
Elements
(b) Assets
(a) Liabilities
(d) Residual interest in the net
assets of the enterprise.
(e) Increases assets through
sale of product.
Chapter
7-14
(d) Equity
(e)
(c)
Revenue
(c)
Expenses
SO 3 Discuss the qualitative characteristics of accounting
information and elements of financial statements.
Conceptual Framework
Operating Guidelines
Chapter
7-15
Assumptions
Assumptions provide a foundation for the
accounting process.
Monetary Unit
Economic Entity
Periodicity
Going Concern
Chapter
7-16
SO 4 Identify the basic assumptions used by accountants.
Assumptions
Monetary Unit
Only transaction data capable of being expressed in terms of
money should be included in the accounting records of the
economic entity.
Chapter
7-17
SO 4 Identify the basic assumptions used by accountants.
Assumptions
Economic Entity
Economic events can be
identified with
a particular unit of
accountability.
Chapter
7-18
SO 4 Identify the basic assumptions used by accountants.
Assumptions
Time Period
The economic life of a business can be divided into
artificial time periods.
Chapter
7-19
SO 4 Identify the basic assumptions used by accountants.
Assumptions
Going Concern
The enterprise will continue in operation long enough
to carry out its existing objectives.
Chapter
7-20
SO 4 Identify the basic assumptions used by accountants.
Principles
Accounting principles dictate how economic
events should be recorded and
reported.
Revenue Recognition
Matching (Expense Recognition)
Full Disclosure
Cost
Chapter
7-21
SO 5 Identify the basic principles of accounting.
Principles
Revenue Recognition
- companies should
recognize revenue in the accounting period in which it is
earned.
Chapter
7-22
SO 5 Identify the basic principles of accounting.
Principles
Matching - efforts (expenses) should be matched
with accomplishment (revenues) whenever it is
reasonable and practicable to do so. “Let the expense
follow the revenues.”
Illustration 7-4
Expense Recognition
Chapter
7-23
SO 5 Identify the basic principles of accounting.
Principles
Matching
Principle
Illustration 7-5
Basic Principles
Chapter
7-24
SO 5 Identify the basic principles of accounting.
Principles
Full Disclosure – Provided through financial
statements, notes to the financial statements, and
supplementary information.
Illustration 7-5
Basic Principles
Chapter
7-25
SO 5 Identify the basic principles of accounting.
Principles
Cost Principle – the price, established by the
exchange transaction, is the “cost”.
Chapter
7-26
Illustration 7-5
Basic Principles
SO 5 Identify the basic principles of accounting.
Principles
Illustration: Identify which basic principle of
accounting is best described in each item below.
(a) Norfolk Southern Corporation reports revenue
in its income statement when it is earned instead of
when the cash is collected.
Revenue
Recognition
(b) Yahoo, Inc. recognizes depreciation expense for
a machine over the 2-year period during which that
machine helps the company earn revenue.
Matching
(c) Oracle Corporation reports information about
pending lawsuits in the notes to its financial
statements.
Full
Disclosure
(d) Eastman Kodak Company reports land on its
balance sheet at the amount paid to acquire it, even
though the estimated fair market value is greater.
Chapter
7-27
Cost
SO 5 Identify the basic principles of accounting.
Constraints in Accounting
Constraints permit a company to modify
generally accepted accounting principles
without reducing the usefulness of the
reported information.
Materiality
Conservatism
Chapter
7-28
SO 6 Identify the two constraints in accounting.
Constraints in Accounting
Materiality
- an item is material if its inclusion or
omission would influence or change the judgment of a
reasonable person.
Illustration 7-6
Constraints
Chapter
7-29
SO 6 Identify the two constraints in accounting.
Constraints in Accounting
Conservatism
- When in doubt, choose the method
that will be least likely to overstate assets and income.
Illustration 7-6
Constraints
Chapter
7-30
SO 6 Identify the two constraints in accounting.
Constraints in Accounting
Illustration What accounting constraints are
illustrated by the items below?
(a) Crimson Tide Corporation does not accrue a
contingent lawsuit gain of $650,000.
Conservatism
(b) Sun Devil Corporation expenses the cost of
wastebaskets in the year they are acquired.
Materiality
Chapter
7-31
SO 6 Identify the two constraints in accounting.
Summary of Conceptual Framework
Chapter
7-32
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Classified Balance Sheet
Chapter
7-33
Illustration 7-8
Standard classification
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Classified Balance Sheet
Illustration 7-9
Proprietorship balance
sheet
A proprietorship, the balance sheet uses the term
“Owner’s equity” instead of “Stockholders’ equity”
Chapter
7-34
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Classified Balance Sheet
Illustration 7-10
Partnership balance
sheet
In a partnership, each partner has a separate capital
account.
Chapter
7-35
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Classified Income Statement
A multiple-step income statement generally includes
the following.
Sales revenue
Cost of goods
Operating
Other revenues and gains
Other expenses and losses
Two additional items are income tax expense and
earnings per share.
Chapter
7-36
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Classified Income Statement
Chapter
7-37
Illustration 7-11
Income taxes
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Classified Income Statement
Earnings
Per Share
=
Net Income
Number of Common Shares
Outstanding
Indicates the net income earned by each share of
outstanding common stock.
Chapter
7-38
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Analyzing Financial Statements
Three major characteristics are generally used:
Liquidity,
Profitability, and
Solvency.
Chapter
7-39
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Liquidity
This ratio means that current assets are more than two times
greater than current liabilities.
Chapter
7-40
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Liquidity
Working capital provides some indication of the company’s
ability to meet its existing current obligations.
Chapter
7-41
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Profitability
Chapter
7-42
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Profitability
Profitability ratios measure the income or operating success
of a company for a given period of time.
Profit Margin Percentage measures the percentage of each
dollar of sales that results in net income.
Chapter
7-43
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Profitability
Return on Assets is an overall measure of profitability.
Return on Common Equity shows the percentage of net income
earned for each dollar of owners’ investment.
Chapter
7-44
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
Solvency
Solvency measures the ability of an enterprise to survive over
a long period of time.
Debt to Total Assets measures the percentage of total assets
that creditors, as opposed to stockholders, provide.
Chapter
7-45
SO 7 Understand and analyze classified financial statements.
Statement Presentation and Analysis
An International Perspective
There are few recognized worldwide accounting
standards. The International Accounting Standards
Board (IASB), of which the United States is a member,
is working to obtain conformity in international
accounting practices.
Chapter
7-46
SO 8 Explain the accounting principles used in international operations.
All About You
Corporations Have Governance Structures—Do You?
Scandals and bankruptcies at Enron, WorldCom, and
other companies brought many changes to the way
America does business.
Many companies have developed a code of ethics to:
deter wrongdoing
promote honest and ethical conduct
indicate that management takes ethics seriously.
Chapter
7-47
All About You
Corporations Have Governance Structures—Do You?
Some Facts:
Under Sarbanes-Oxley, a company must disclose whether
it has a code of ethics.
Enron had a code of ethics. Enron’s board of directors
knowingly waived requirements of the code so that the
CFO could set up and run special purpose entities.
In a recent survey of 1,436 workers, 34% said that they
have seen unethical activities at their workplace, but
only 47% said they are likely to report these activities.
Chapter
7-48
All About You
Stockholders often lose money as a result of unethical
behavior by management and they often file lawsuits against
the company in an effort to recoup these losses.
Chapter
7-49
Source: Elaine Buckberg, Todd Foster, and Ronald I. Miller, “Recent Trends in Shareholder
Class Action Litigation: Are WorldCom and Enron the New Standard?” NERA Economic
Consulting, www.nera.com (accessed June 26, 2006).
All About You
What Do You Think?
Many universities have become concerned about student
cheating. Many schools now have student ethics codes. Do
you think that these ethics codes serve a useful purpose?
YES: Anything that will reduce unethical behavior is a
good thing.
NO: The existence of an ethics code won’t affect
student behavior.
Chapter
7-50
Copyright
“Copyright © 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted
in Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without
the express written permission of the copyright owner is
unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed
to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The
purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only
and not for distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no
responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the
use of these programs or from the use of the information
contained herein.”
Chapter
7-51