Plate 50
advertisement

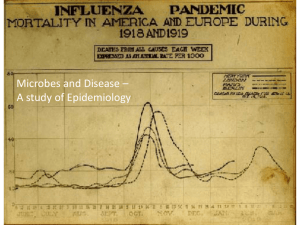
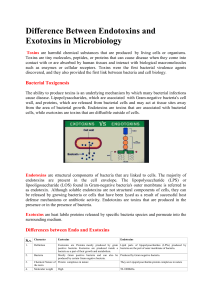
Plate 50 Toxins Toxins • Toxins: poisonous substances produced by organisms (microorganisms, in our case) Exotoxins • Exotoxins: produced within cytoplasm of bacteria and released into the surrounding environment – Exo = “out” – Produced by Gram-positive bacteria – Toxins are soluble in body fluids Exotoxins • Released after bacteria cell is inside the body or in food (and consumed by host) • Spread through body by blood and damage organs • Effects of exotoxins: – Damage cell membranes of tissue – Interrupt metabolic function – Interfere with cellular functions Exotoxins – Enterotoxin • Staphylococcus aureus produce enterotoxins that are absorbed by the cells that line the intestines • Entero = “intestine” • Symptoms: – – – – Nausea Vomiting Abdominal cramps Diarrhea • Ex: S. aureus can result in Toxic Shock Syndrome, commonly found in menstruating women who use tampons Staphylococcus aureus – “golden cluster seed” Staph Infection • Skin infections: – Pimples – Folliculitis – Impetigo Exotoxins – Neurotoxin • Clostridium botulinum produce neurotoxins that affect the nervous system • Neuro = “nerve” • Prevents the release of acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter) at neuromuscular junctions • Results in paralysis, since nerve impulses cannot pass to muscles Botulism Exotoxins – Neurotoxin • Clostridium tetani produce a neurotoxin that affects nerve cells responsible for skeletal muscle contractions • Muscles remain constantly contracted and rigid Tetanus • “Lock-jaw” – muscle contraction in the face and neck Tetanus Exotoxins – Cytotoxin • Corynebacterium diphtheriae kill respiratory cells by interfering with protein synthesis • Dead respiratory cells and debris collect in mucus, block small air passageways, and make breathing difficult • Cyto = “cell” Diptheria • Note the large whitish swelling in the throat Endotoxins • Endotoxins: made of components of bacterial cell wall – Endo = “in” – Produced by Gram-negative bacteria – Made of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) – Released when the bacteria cell wall is broken down (through phagocytosis or antibiotics) Endotoxins • Unlike some exotoxins, endotoxins are not tissue specific – they affect a wide range of tissues (systemic) • Symptoms: – – – – – – Dilate blood vessels (lower blood pressure) Tissue failure due to lack of nutrition and oxygen Fever Muscular weakness Low levels of white blood cells Hemorrhaging of blood vessels