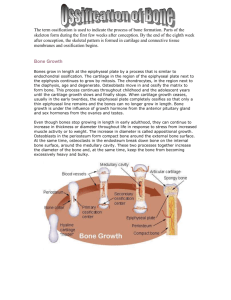
D170 W15 Cartilage and Bone Tissue Williams What three
advertisement

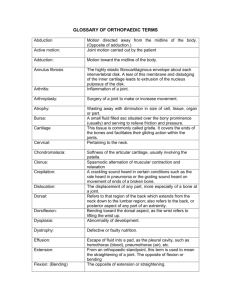
D170 W15 Cartilage and Bone Tissue Williams What three components make up the skeletal system? What are the nine locations of cartilage in the body, and where is each found? What are the differences between costal cartilages and articular cartilages? Describe the structure and function of the three types of cartilage in the body. (also see tables on pages 86 – 88). Be familiar with the visual histology of the tissue, cell names and structures. Hyaline cartilage – Elastic cartilage – Fibrocartilage – What are the six functions of bones in the body? What cells, fibers, and ground substance make up bone tissues? Take note of the following terms. (also see table on pages 88) Osteoblasts – Osteocytes – Osteoclasts – What are the four ways in which bones are classified? What is the major difference between spongy bone and compact bone? Describe the structure and function of a typical long bone, noting the following features: Diaphysis, Epiphysis, Blood vessels, Medullary cavity, Endosteum, Periosteum Review Table 6.1 and explain the general features of 1) projections that are sites of muscle and ligament attachment, 2) surfaces that form joints, and 3) depressions and openings. How would you describe the microscopy anatomy of compact bone? Define the terms osteon, lamella, central canal, perforating canal, and canaliculi. How does the microscopic anatomy of spongy bone differ? Describe the anatomy of the epiphyseal plate. How is the epiphyseal plate involved in postnatal bone growth? How do bone resorption and bone deposition contribute to bone remodeling? What four steps are involved in repairing bone fractures? Review Table 6.2 on page 142 and explain the differences between the six types of fractures. Vocabulary List Cartilage Hyaline cartilage Elastic cartilage Fibrocartilage Chondrocyte Chondroblast Lacuna (lacunae) Articular cartilage Costal cartilage Perichondrium Bone marrow Osteoblasts Osteoid Osteocytes Osteoclasts Long bone Short bone Flat bone Irregular bone Compact bone Spongy bone Trabeculae Diaphysis Epiphysis Epiphyseal line Medullary cavity Periosteum Endosteum Bone markings Osteon Lamella Central canal (Haversian canal) Perforating canals (Volkmann’s canals) Canaliculi Interstitial lamellae Bone remodeling Bone resorption Bone deposition Fracture Simple fracture Compound fracture Hematoma Soft callus Hard callus