Cardiovascular system - INAYA Medical College
advertisement

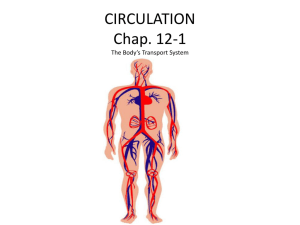
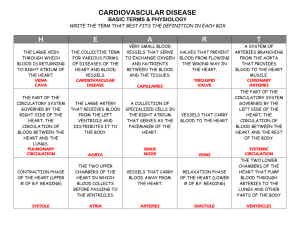
Foundation year Cardiovascular system T :sanaa abdel hamed After study this chapter you should be able to: 1. Label a diagram of the heart. 2. Trace the path of the blood flow through the heart. 3. Differentiate between arteries, veins and capillaries. 4. List and describe the main disorders that affect the heart and blood vessels. 5. Interpret medical abbreviations referring to the heart and blood circulation. 6. Identifying and use of the roots pertaining to the cardiovascular system. 7. Define the medical terms pertaining to the circulatory system. 8. Analyze case studies concerning the heart and circulation. Responsibilities of cardiovascular system: • 1. Pumping blood to the body tissues and cells. • 2. Supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and cells. • 3. Removing carbon dioxide and other waste products of metabolism from tissues and cells. • heart - pumper • vessels - container • blood - liquid Heart Center of the circulatory system The Three layers of the heart are: • Epicardium • Myocardium • Endocardium Chambers: Right atrium and left atrium Upper chambers Receiving chambers Right ventricle and left ventricle Lower chambers Pumping chambers Partitions: Interatrial septum • Separates right and left sides of atria Interventricular septum • Separates right and left sides of ventricles Arteries: Large, thick-walled vessels. Carry blood away from the heart. Arterioles: Thinner walls than arteries. Transport blood on to capillaries. Veins • Thinner walls than arteries. • Thicker walls than capillaries. • Transport blood from venules to heart. Venules • Smallest veins. • Collect deoxygenated blood from cells for transport back to heart. Capillaries: • Extremely thin walls (single layer). • Allow for exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid surrounding body cells. • One Cardiac Cycle = One Complete Heartbeat. • Diastole – Ventricles relax and fill with blood. – Relaxation phase of heartbeat. • Systole – Ventricles contract and force blood out of heart. – Contraction phase of heartbeat. • Blood Pressure – Pressure exerted by blood on walls of arteries. • Systolic Pressure – Maximum pressure reached within the ventricles. • Diastolic Pressure – Minimum pressure reached within the ventricles. MEDICAL TERMS RELATED TO CVS 1. Angi/o (an-ji-oh) related to blood vessels. Angioplasty (n): surgical repair of blood vessels. 2. Artery (n): large blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to all parts of the body. The combining form is arteri/o. 3. Vein (n): blood vessel which take deoxygenated blood containing waste carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the heart. The combining forms are ven/o and phleb/o. 4 4. Vessel (n): a tube in the body along which liquid flows. The combining forms are ves/o and angi/o. 5. Valve (n): means a flap, mainly in the heart or blood vessels or lymphatic vessel, which opens and closes to allow liquid to pass in one direction only. The combining form is valv/o. Valvular – adj. 6. Valvuloplasty (n): means surgical repair of the valve in the heart. 7. Vasodilator (n): means a drug which dilates or expands blood vessels. The opposites is vasoconstrictor. 8. Atrium (n): one of the two upper chambers of the heart. The combining form is atri/o. Atria – plural. 9. Ventricle (n): one of the two lower chambers of the heart. The combining form is ventricul/o. 10. Cardiac (adj) means pertaining to the heart. Heart – noun. 11. Cardiology (n) study of structure, functions and diseases of heart. Cardiological – adj. 12. Arteriosclerosis (n): means hardening of the arteries. -sclerosis means hardening. 13. Myocardium (n): middle layer of the wall of the heart. Formed of heart muscle. Myocardial – adj. 14. Myocarditis – noun (inflammation of the heart muscle). 15. Pericardium (n): membrane surrounding the heart. The prefix peri- means around, and the root word -cardium means heart. 16. Thrombosis (n): blood clotting. The prefix thrombo- means blood clot. The suffix –osis means abnormal condition. Thrombi – plural. 17. Attack (n) means a condition where the heart suffers from defective blood supply because one of the arteries become blocked by a blood clot. 18. Bradycardia (n): means slow heartbeat. Brady- means slow. The opposite is tachy- which means fast. 19. Arrhythmia (n): variation in the rhythm of heartbeat. a- means not or without, -ia means condition or state. 20. Bypass (n) means diversion of a flow from its normal channels, usually by means of surgery. 21. Catheter (n) means tube passed into the body along one of the passages in the body. 22. Pacemaker (n) ( payss-mayk-er): means a device used to produce and maintain a normal heart rate in a patient who have disorders of heart rhythm. 23. Ischaemia (n): means a deficient blood supply to part of the body. The prefix isch- means reduction or too little. The suffix – emia means blood condition. 24. Fibrillation (n) means rapid, random, chaotic and ineffective contraction of the heart. The combining form fibrill/o means muscular. Fibrillating – adj. fibrillate – verb. 25. Echocardiogram (n) means recording of heart movements using ultrasound. The prefix echo- means sound. The combining form cardi/o means heart. And the suffix –gram means record. 26. Electrocardiogram (n) means chart which records the electrical impulses in the heart muscle. The electrocardiogram is produced by electrocardiograph (instrument). 27. Phlebotomist (n) the person who draws blood samples from the patient. Phleb: vein, tom: cut or incision, and –ist: person. 28. coronary (n) arteries which supply blood to the heart muscles. The combining form coron/o means heart. 29. Sphygmomanometer (n) instrument which measures the blood pressure in the arteries. The prefix sphygmo- means pulse. The combining form man/o means pressure. And the suffix – meter means measure.