Language
advertisement

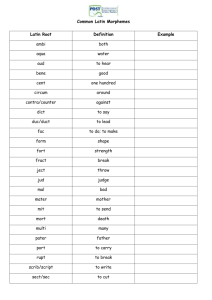
Language Structure of Language • Phonemes - Consonants, vowels, sh, ch,…. in the How th, many morphemes How many phonemes (sounds) following words? • Morphemes are People in these words? Swimming - Dog, van, ing, ed,… Thing Orange Psychology Literally Hopes Reddish Sun Radish Quickly Waited Wish George’s Weigh Misspell Laughed Antidisestablishmentarianism Structure of Language • Words = 1 or more morphemes • Syntax = set of rules to combine words “The girl the boy saw.” – violates syntax • Semantics govern meaning “The rapid freedom ran around the curious emptiness.” – obeys syntax, but makes no sense due to meaning of the words Language Development • Receptive Language - ability to comprehend speech • Productive Language – ability to produce words • Surface structure v. deep structure – “Joey was swinging too high, and the rope broke and he fell on his head.” – “Joey hurt his head when he fell off the swing.” Language Development • • • • Babbling stage (4 months) One-word stage (1 year) Two-word stage (2 years) Telegraphic speech Challenges in Language Development • Overextension – Same word applies to many things – “Juice” refers to milk, water, juice, etc. • Underextension – Only use word to apply to one specific example, rather than using it for others – Calls own dog “dog”, but not other dogs “dog” • Overregularization/overgeneralization – Apply grammar rules w/out making appropriate exceptions – EX: She “goed” to the store Thinking in Images • Implicit memory – mental picture of how you do a task • Watching an activity will activate brain’s internal stimulation of it – Pianist mentally rehearses song – Dancer mentally imagines choreography Explaining Language Development • Skinner & Behaviorism – Association for seeing & hearing words – Imitation – Reinforcement or punishment • Nature or nurture? Thinking & Language • Linguistic determinism (Whorff) – Language determines way we think – Culturally influenced • Nature or nurture? Thinking & Language • Bilingual advantage (Lambert) – Bilingual children who learn to inhibit one language while learning another, are also better able to inhibit their attention to irrelevant info Explaining Language Development • Chomsky (Nativist theory) & Inborn Universal Grammar – Language acquisition device: innate mechanism or process that allows language (unique to humans) – Universal grammar: common structure for language among all cultures • Nature or nurture? Explaining Language Development • Critical Periods – specific time period early in life for language development Do animals use language?