SEDATIVE/HYPNOTICS (Antianxiety Drugs)
advertisement

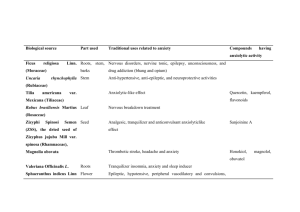
SEDATIVE/HYPNOTICS ANXIOLYTICS Martha I. Dávila-García, Ph.D. Howard University Department of Pharmacology Optimal Performance Nervous Breakdown Sedated Anxiety GOAL Manifestations of anxiety: • Verbal complaints. The patient says he/she is anxious, nervous, edgy. • Somatic and autonomic effects. The patient is restless and agitated, has tachycardia, increased sweating, weeping and often gastrointestinal disorders. • Social effects. Interference with normal productive activities. Pathological Anxiety Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): People suffering from GAD have general symptoms of motor tension, autonomic hyperactivity, etc. for at least one month. Phobic anxiety: Simple phobias. Agoraphobia, fear of animals, etc. Social phobias. Panic disorders: Characterized by acute attacks of fear as compared to the chronic presentation of GAD. Obsessive-compulsive behaviors: These patients show repetitive ideas (obsessions) and behaviors (compulsions). Causes of Anxiety 1). Medical: a) Respiratory b) Endocrine c) Cardiovascular d) Metabolic e) Neurologic. Causes of Anxiety 2). Drug-Induced: – Stimulants • Amphetamines, cocaine, TCAs, caffeine. – Sympathomimetics • Ephedrine, epinephrine, pseudoephedrine phenylpropanolamine. – Anticholinergics\Antihistaminergics • Trihexyphenidyl, benztropine, meperidine diphenhydramine, oxybutinin. – Dopaminergics • Amantadine, bromocriptine, L-Dopa, carbid/levodopa. Causes of Anxiety – Miscellaneous: • Baclofen, cycloserine, hallucinogens, indomethacin. 3). Drug Withdrawal: • BDZs, narcotics, BARBs, other sedatives, alcohol. Anxiolytics Strategy for treatment Reduce anxiety without causing sedation. Anxiolytics 1) Benzodiazepines (BZDs). 2) Barbiturates (BARBs). 3) 5-HT1A receptor agonists. 4) 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C & 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. If ANS symptoms are prominent: • ß-Adrenoreceptor antagonists. • 2-AR agonists (clonidine). Anxiolytics • Other Drugs with anxiolytic activity. – TCAs (Fluvoxamine). Used for Obsessive compulsive Disorder. – MAOIs. Used in panic attacks. – Antihistaminic agents. Present in over the counter medications. – Antipsychotics (Ziprasidone). • Novel drugs. (Most of these are still on clinical trials). – CCKB (e.g. CCK4). – EAA's/NMDA (e.g. HA966). Sedative/Hypnotics • A hypnotic should produce, as much as possible, a state of sleep that resembles normal sleep. Properties of Sedative/Hypnotics in Sleep 1) The latency of sleep onset is decreased (time to fall asleep). 2) The duration of stage 2 NREM sleep is increased. 3) The duration of REM sleep is decreased. 4) The duration of slow-wave sleep (when somnambulism and nightmares occur) is decreased. Tolerance occurs after 1-2 weeks. Sedative/Hypnotics 1) Benzodiazepines (BZDs): Alprazolam, diazepam, oxazepam, triazolam 2) Barbiturates: Pentobarbital, phenobarbital 3) Alcohols: Ethanol, chloral hydrate, paraldehyde, trichloroethanol, 4) Imidazopyridine Derivatives: Zolpidem 5) Pyrazolopyrimidine Zaleplon Sedative/Hypnotics 6) Propanediol carbamates: Meprobamate 7) Piperidinediones Glutethimide 8) Azaspirodecanedione Buspirone 9) -Blockers** Propranolol 10) 2-AR partial agonist** Clonidine Sedative/Hypnotics Others: 11) Antyipsychotics ** Ziprasidone 12) Antidepressants ** TCAs, SSRIs 13) Antihistaminic drugs ** Dephenhydramine Sedative/Hypnotics All of the anxiolytics/sedative/hypnotics should be used only for symptomatic relief. ************* All the drugs used alter the normal sleep cycle and should be administered only for days or weeks, never for months. ************ USE FOR SHORT-TERM TREATMENT ONLY!! Sedative/Hypnotics Relationship between Older vs Newer Drugs Barbiturates Glutethimide Meprobamate Benzodiazepines Zolpidem Zaleplon **All others differ in their effects and therapeutic uses. They do not produce general anesthesia and do not have abuse liability. SEDATIVE/HYPNOTICS ANXYOLITICS BENZODIAZEPINES BARBITURATES GABAergic SYSTEM Sedative/Hypnotics The benzodiazepines are the most important sedative hypnotics. Developed to avoid undesirable effects of barbiturates (abuse liability). Benzodiazepines • Diazepam • Chlordiazepoxide • Triazolam • Lorazepam • Alprazolam • Clorazepate => nordiazepam • Halazepam • Clonazepam • Oxazepam • Prazepam Barbiturates • • • • • • Phenobarbital Pentobarbital Amobarbital Mephobarbital Secobarbital Aprobarbital NORMAL ANXIETY _________ _________________ SEDATION HYPNOSIS Confusion, Delirium, Ataxia Surgical Anesthesia COMA DEATH Respiratory Depression BARBS BDZs Coma/ Anesthesia Ataxia ETOH Sedation Anticonvulsant Anxiolytic DOSE Respiratory Depression BARBS Coma/ Anesthesia BDZs Ataxia Sedation Anticonvulsant Anxiolytic DOSE GABAergic SYNAPSE glucose glutamate GAD GABA Cl - GABA-A Receptor BDZs BARBs GABA AGONISTS g d e • Oligomeric (dgepr) glycoprotein. • Major player in Inhibitory Synapses. • It is a Cl- Channel. • Binding of GABA causes the channel to open and Cl- to flow into the cell with the resultant membrane hyperpolarization. Mechanisms of Action 1) Enhance GABAergic Transmission frequency of openings of GABAergic channels. Benzodiazepines opening time of GABAergic channels. Barbiturates receptor affinity for GABA. BDZs and BARBS 2) Stimulation of 5-HT1A receptors. 3) Inhibit 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT3 receptors. Patch-Clamp Recording of Single Channel GABA Evoked Currents From Katzung et al., 1996 Benzodiazepines PHARMACOLOGY • BDZs potentiate GABAergic inhibition at all levels of the neuraxis. • BDZs cause more frequent openings of the GABA-Cl- channel via membrane hyperpolarization, and increased receptor affinity for GABA. • BDZs act on BZ1 (1 and 2 subunit-containing) and BZ2 (5 subunit-containing) receptors. • May cause euphoria, impaired judgement, loss of cell control and anterograde amnesic effects. Pharmacokinetics of Benzodiazepines Although BDZs are highly protein bound (60-95%), few clinically significant interactions.* High lipid solubility high rate of entry into CNS rapid onset. *The only exception is chloral hydrate and warfarin Lipid solubility Pharmacokinetics of Benzodiazepines Hepatic metabolism. Almost all BDZs undergo microsomal oxidation (Ndealkylation and aliphatic hydroxylation) and conjugation (to glucoronides). Rapid tissue redistribution long acting long half lives and elimination half lives (from 10 to > 100 hrs). All BDZs cross the placenta detectable in breast milk may exert depressant effects on the CNS of the lactating infant. Pharmacokinetics of Benzodiazepines Many have active metabolites with halflives greater than the parent drug. Prototype drug is diazepam (Valium), which has active metabolites (desmethyldiazepam and oxazepam) and is long acting (t½ = 20-80 hr). Differing times of onset and elimination half-lives (long half-life => daytime sedation). Biotransformation of Benzodiazepines From Katzung, 1998 Biotransformation of Benzodiazepines • Keep in mind that with formation of active metabolites, the kinetics of the parent drug may not reflect the time course of the pharmacological effect. • Estazolam, oxazepam, and lorazepam, which are directly metabolized to glucoronides have the least residual (drowsiness) effects. • All of these drugs and their metabolites are excreted in urine. Properties of Benzodiazepines • BDZs have a wide margin of safety if used for short periods. Prolonged use may cause dependence. • BDZs have little effect on respiratory or cardiovascular function compared to BARBS and other sedative-hypnotics. • BDZs depress the turnover rates of norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA) and serotonin (5-HT) in various brain nuclei. Side Effects of Benzodiazepines • Related primarily to the CNS depression and include: drowsiness, excess sedation, impaired coordination, nausea, vomiting, confusion and memory loss. Tolerance develops to most of these effects. • Dependence with these drugs may develop. • Serious withdrawal syndrome can include convulsions and death. Sedative/Hypnotics • They produce a pronounce, graded, dose-dependent depression of the central nervous system. Toxicity/Overdose with Benzodiazepines • Drug overdose is treated with flumazenil (a BDZ receptor antagonist, short half-life), but respiratory function should be adequately supported and carefully monitored. • Seizures and cardiac arrhythmias may occur following flumazenil administration when BDZ are taken with TCAs. • Flumazenil is not effective against BARBs overdose. Drug-Drug Interactions with BDZs • BDZ's have additive effects with other CNS depressants (narcotics), alcohol => have a greatly reduced margin of safety. • BDZs reduce the effect of antiepileptic drugs. • Combination of anxiolytic drugs should be avoided. • Concurrent use with ODC antihistaminic and anticholinergic drugs as well as the consumption of alcohol should be avoided. • SSRI’s and oral contraceptives decrease metabolism of BDZs. Pharmacokinetics of Barbiturates • Rapid absorption following oral administration. • Rapid onset of central effects. • Extensively metabolized in liver (except phenobarbital), however, there are no active metabolites. • Phenobarbital is excreted unchanged. Its excretion can be increased by alkalinization of the urine. Pharmacokinetics of Barbiturates • In the elderly and in those with limited hepatic function, dosages should be reduced. • Phenobarbital and meprobamate cause autometabolism by induction of liver enzymes. Properties of Barbiturates Mechanism of Action. • They increase the duration of GABA-gated channel openings. • At high concentrations may be GABAmimetic. Less selective than BDZs, they also: • Depress actions of excitatory neurotransmitters. • Exert nonsynaptic membrane effects. Toxicity/Overdose • Strong physiological dependence may develop upon long-term use. • Depression of the medullary respiratory centers is the usual cause of death of sedative/hypnotic overdose. Also loss of brainstem vasomotor control and myocardial depression. Toxicity/Overdose • Withdrawal is characterized by increase anxiety, insomnia, CNS excitability and convulsions. • Drugs with long-half lives have mildest withdrawal (. • Drugs with quick onset of action are most abused. • No medication against overdose with BARBs. • Contraindicated in patients with porphyria. Sedative/Hypnotics SLEEP PER NIGHT (%) Tolerance and excessive rebound occur in response to barbiturate hypnotics. CONTROL WITHDRAWAL REM NREM III and IV 1 2 3 NIGTHS OF DRUG DOSING Miscellaneous Drugs • • • • • • Buspirone Chloral hydrate Hydroxyzine Meprobamate (Similar to BARBS) Zolpidem (BZ1 selective) Zaleplon (BZ1 selective) BUSPIRONE • Most selective anxiolytic currently available. • The anxiolytic effect of this drug takes several weeks to develop => used for GAD. • Buspirone does not have sedative effects and does not potentiate CNS depressants. • Has a relatively high margin of safety, few side effects and does not appear to be associated with drug dependence. • No rebound anxiety or signs of withdrawal when discontinued. BUSPIRONE Side effects: • Tachycardia, palpitations, nervousness, GI distress and paresthesias may occur. • Causes a dose-dependent pupillary constriction. BUSPIRONE Mechanism of Action: • Acts as a partial agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor presynaptically inhibiting serotonin release. • The metabolite 1-PP has 2 -AR blocking action. Pharmacokinetics of BUSPIRONE • Not effective in panic disorders. • Rapidly absorbed orally. • Undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism (hydroxylation and dealkylation) to form several active metabolites (e.g. 1-(2pyrimidyl-piperazine, 1-PP) • Well tolerated by elderly, but may have slow clearance. • Analogs: Ipsapirone, gepirone, tandospirone. Zolpidem • Structurally unrelated but as effective as BDZs. • Minimal muscle relaxing and anticonvulsant effect. • Rapidly metabolized by liver enzymes into inactive metabolites. • Dosage should be reduced in patients with hepatic dysfunction, the elderly and patients taking cimetidine. Properties of Zolpidem Mechanism of Action: • Binds selectively to BZ1 receptors. • Facilitates GABA-mediated neuronal inhibition. • Actions are antagonized by flumazenil GABA (-) (-) (-) (-) (-) ? NE ANTICONVULSANT/ MUSCLE RELAXANT ? DA ACh 5-HT ANXIOLYTIC ? SEDATION ? Properties of Other drugs. • Chloral hydrate • Is used in institutionalized patients. It displaces warfarin (anti-coagulant) from plasma proteins. • Extensive biotransformation. Properties of Other Drugs 2-Adrenoreceptor Agonists (eg. Clonidine) • Antihypertensive. • Has been used for the treatment of panic attacks. • Has been useful in suppressing anxiety during the management of withdrawal from nicotine and opioid analgesics. • Withdrawal from clonidine, after protracted use, may lead to a life-threatening hypertensive crisis. Properties of Other Drugs -Adrenoreceptor Antagonists (eg. Propranolol) • Use to treat some forms of anxiety, particularly when physical (autonomic) symptoms (sweating, tremor, tachycardia) are severe. • Adverse effects of propranolol may include: lethargy, vivid dreams, hallucinations. OTHER USES 1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder Diazepam, lorazepam, alprazolam, buspirone 2. Phobic Anxiety a. Simple phobia. BDZs b. Social phobia. BDZs 3. Panic Disorders TCAs and MAOIs, alprazolam 4. Obsessive-Compulsive Behavior Clomipramine (TCA), SSRI’s 5. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (?) Antidepressants, buspirone ANXYOLITICS HYPNOTICS Alprazolam Chlordiazepoxide Buspirone Diazepam Lorazepam Oxazepam Triazolam Phenobarbital Halazepam Prazepam Chloral hydrate Estazolam Flurazepam Pentobarbital Lorazepam Quazepam Triazolam Secobarbital Temazepam Zolpidem References: • Katzung, B.G. (2001) Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. 7th ed. Appleton and Lange. Stamford, CT. • Brody, T.M., Larner,J., and Minneman, K.P. (1998) Human Pharmacology: Molecular to Clinical. 2nd ed. Mosby-Year Book Inc. St. Louis, Missouri. • Rang, H.P. et al. (1995) Pharmacology . Churchill Livingston. NY., N.Y. • Harman, J.G. et al. (1996) Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. McGraw Hill.