Mitosis - Alvin ISD
advertisement

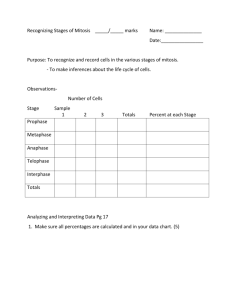
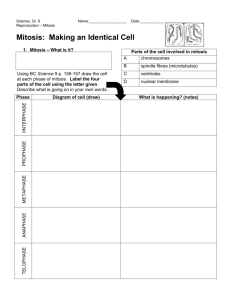
http://www.brainpop.com/health/bodysystems/cells/ Mitosis Cell division http://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/cellstructures/ Cell division All complex organisms originated from a single fertilized egg. Every cell in your body started here, through cell division the numbers are increased Cell then specialize and change into their various roles Mitosis Mitosis is the process by which new body cell are produced for: Growth Replacing damaged or old cells. Cell division occurs in a series of stages, or mitosis. Parent cell Chromosomes are copied and double in number Chromosomes now split 2 daughter cells identical to original Animated Mitosis Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm • Interphase • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase & Cytokinesis Interphase occurs before mitosis begins • Chromosomes are copied (# doubles) • Chromosomes appear as threadlike coils (chromatin) at the start, but each chromosome and its copy(sister chromosome) change to sister chromatids at end of this phase Nucleus CELL MEMBRANE Cytoplasm Interphase Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm Prophase 1st step in Mitosis • Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) • Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move to opposite end of the cell. • Spindle fibers form between the poles. Centrioles Sister chromatids Spindle fibers Prophase Animal Cell Plant Cell Spindle fibers Centrioles Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm Metaphase 2nd step in Mitosis • Chromatids (or pairs of chromosomes) attach to the spindle fibers. Centrioles Spindle fibers Metaphase Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm Anaphase 3rd step in Mitosis • Chromatids (or pairs of chromosomes) separate and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell. Centrioles Spindle fibers Anaphase Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm Telophase 4th step in Mitosis • Two new nuclei form. • Chromosomes appear as chromatin (threads rather than rods). • Mitosis ends. Nuclei Chromatin Nuclei Telophase Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis • Cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells – each with its own nucleus with identical chromosomes. Animal Mitosis -- Review Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Interphase Plant Mitosis -- Review Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Interphase Cell Cycle 20 - Cell Division The Cell Cycle 21 21 Mitosis Animation http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm Mitosis All daughter cells contain the same genetic information from the original parent cell from which it was copied. Every different type cell in your body contains the same genes, but only some act to make the cells specialize – e.g. into nerve or muscle tissue. Mitosis – bone cell slides 1 2 Chromosomes copied Parent cell 3 Copies separating Cells split 4 5 2 daughter cells Plants Rat – epithelial cells http://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/mitosis/