Pure Competition 177-178
advertisement

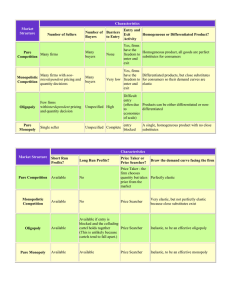
Pure Competition 177-178 Mr. Henry AP Economics Four Types of Markets • There are four types of market structures, each differing in several aspects: - Number of firms in the industry - Whether those firms produce a standardized product or try to differentiate their products from those of other firms - How easy or difficult it is for firms to enter the industry Characteristics of the Four Basic Market Models • After looking at the characteristics of a pure monopoly, what examples can you think of for a pure monopoly? • After looking at the characteristics of an oligopoly, what examples can you think of for this? Note: Collusion is when firms “work” together • After looking at the characteristics of monopolistic competition, what examples can you think of? • After looking at the characteristics of pure competition, what examples can you think of? Pure Competition Characteristics • Pure competition is relatively rare in the real world Characteristics include: - Must be very large numbers of buyers and sellers - Must deal in identical products - Must act independently (must compete) and is a “price taker,” meaning it is at the mercy of the market and cannot ask for more money - Firms are free to enter into, conduct, or get out of business, so there are no significant obstacles Demand as Seen by a Purely Competitive Seller AP Review Questions • A requirement of perfect competition is that i. Many firms sell an identical product to many buyers ii. There are no restrictions on entry into (or exit from) the market, and established firms have no advantage over new firms iii. Buyers are well informed about prices A. i only B. i and ii C. iii only D. i and iii E. i, ii, and iii E. i, ii, and iii • For a perfectly competitive corn grower in Nebraska, the marginal revenue curve is A. Downward sloping B. The same as the demand curve C. Upward sloping D. U-shaped E. Vertical at the profit maximizing quantity of production B. The same as the demand curve